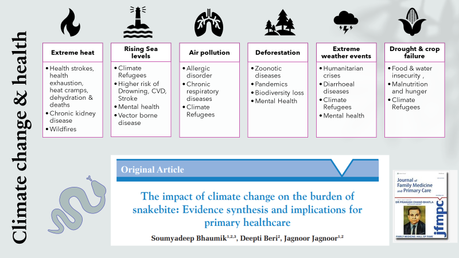
Snakebite is a public health problem in rural areas of South Asia, Africa and South America presenting mostly in primary care. Climate change and associated extreme weather events are expected to modify the snake-human-environment interface leading to a change in the burden of snakebite. Understanding this change is essential to ensure the preparedness of primary care and public health systems.
An evidence synthesis to better understand this aspect was published in Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care and is available (open acess) here.