Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus has been taken from the Greek word Diabetes which means siphon (to pass through) and Latin word mellitus means sweet.It is a chronic disorder of carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism resulting from insulin deficiency or abnormality in the use of insulin.

What Are The Leading Causes Of Diabetes?
Major Causes of Diabetes Mellitus Can Be Categorized Into 3 Categories
1. Agent
The fundamental cause of diabetes mellitus is deficiency of insulin which affects partially in Type I Diabetes and completely in Type II diabetes. This may be due to the following reasons
2. Pancreatic Disorders
- Destruction of Beta cells by viral infections and chemical agents
3. Genetic mutations in genes
4. Host factors
- Age and sex- Though diabetes mellitus can hit at any age but youth get affected by malnutrition-related diabetes.
5 Genetic factors
- Studies show that in case of Type II diabetes there is 90% chances that it will pass on to the next generation while in case of Type I diabetes cannot be considered as a total genetic entity.
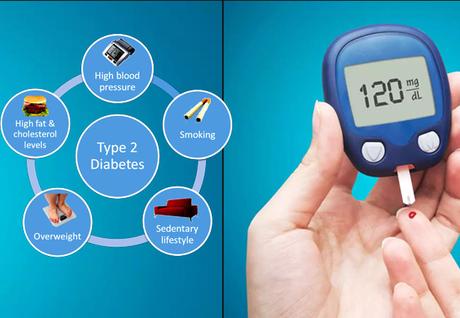
6. Obesity
- Intensity of risk depends on the degree of duration of obesity because obese people requires very large amount of insulin to maintain adequate blood glucose levels. Increasing BMI (Body Mass Index), waist to hip ratio (reflecting, abdominal or visceral adiposity) are major determinants of Type II Diabetes. Obesity tends to reduce the no. of insulin receptors on target cells. It doesn't play an important role in Type I diabetes.
7. Environmental factors
- Sedentary lifestyle - Lack of workout and exercise induces the symptoms of diabetes mellitus.
8. Diet
- Consuming a high saturated fat diet triggers insulin level and glucose tolerance in the body. Increased intake of dietary fiber on a daily basis helps in reduced blood glucose levels.
9. Malnutrition
- This results in reduced Beta-cell functioning in infants and children.
10. Alcohol
- This increases the risk of diabetes mellitus by damaging the pancreas, liver and symptoms of obesity.
11. Viral infections (rubella, mumps etc.)
- Triggers Immune-responses which causes destruction of beta-cells.
Chemical agents (alloxan, cyanide etc.), stress (trauma, surgery etc.) are one of the factors inducing diabetes mellitus.
Other Factors
Type I Diabetes is a chronic condition which occurs when the body's system against infection (immune system) initiates destroying the insulin producing beta cells of pancreas.
- Genetics play a crucial role in diabetes
- Increasing age
- Obesity, physical inactivity are significant causes of diabetes as being obese resist insulin production
- Stress affects normal functioning of pancreas
- Unhealthy dietary habits like consumption of high carbohydrate and sugar level in body
- Previous medication
- Viral infections like rubella, mumps and coxsackie
Types of Diabetes
- Type I-Formerly is known as Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM)
- Autoimmune disorder
- Destruction of beta cells of the pancreas which leads to reduced or no insulin production.
- May occur at any age but usually affects the age group below 15.
Type II Diabetes
- Type II-Formerly is known as Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
- Probably caused by disturbances in insulin reception in the cells.
- Reduced number of insulin receptors
- Loss of beta cells responsiveness to glucose leading to slow or decreased amount of insulin released from pancreas.
- Mostly occurs over age of 40 but can also occur in children.
- Common in overweight and obese people.
Gestational Diabetes
- This type affects females during pregnancy
- Undiagnosed or uncontrolled gestational diabetes can raise the complications during healthcare
- Pre-diabetes
- Impaired fasting glucose (IFG)
- FPG - 100-124mg/dL
- Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)
- OGTT- 140-100mg/dL
- Blood sugar levels
- BSL- Random= 100-140 mg/dL
- BSL-fasting = 70-110 mg/dL
- BSL-after meal=less than 200md/dL
- HBA1C- normal non diabetic HbA1c;
Who is at Risk?
Type I diabetes Risk factors
Type II diabetes risk factors-
Some of the Health Conditions Which Might Have Risk Factors Are
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes
-
Polyuria (increased urination)
-
Polydipsia (increased thirst)
-
Polyphagia (increased hunger)
-
Sudden and unexplained weight loss
-
Nausea/vomiting
-
Severe hyperglycemia
-
Recurrent infection
-
Prolonged wound healing
-
Altered inflammatory and immune response
-
Genital pruritus
-
Blurry vision
-
Itchy and dry skin
-
Yeast infections
-
Feeling of numbness in feet and hands
-
Erectile dysfunction (ED)
-
Deprived muscle strength in men
-
Increased appetite
Diagnosis of Diabetes
- Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test
- Random blood sugar test
- Fasting blood sugar test
- Oral glucose tolerance test
- HbA1c value
Pathogenesis of Diabetes
Our metabolism converts food into energy which is done with the help of insulin.
About insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced by pancreas, whenever we eat something sugar levels in our blood rise and simultaneously insulin is released in the bloodstream.
Role of insulin
-
Balances glucose levels in body
-
Inhibit the breakdown of glycogen
-
Stimulate the transfer of glucose into fat and muscle cells
-
Stimulate the storage of glucose in form of glycogen
It is believed that there is a direct link between nerve impulses and pancreas so when autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells leads to a deficiency of insulin secretion results in the metabolic derangement associated with Type I diabetic patients. This results in loss of insulin secretion, abnormal functioning of pancreatic alpha cells and excessive secretion of glucagon. The resultant elevated glucagon levels disturbs the metabolic defects and suppressed glucose metabolism.
Whereas in case of Type II diabetic patients there are two main pathological defects i.e. impaired insulin secretion by dysfunction of pancreatic beta cells and insulin action through insulin resistance.
Complications
- Acute and Subacute complications of diabetes mellitus
- Metabolic- Ketoacidosis, Coma, hyper osmolar nonketotic-coma and lactic acidosis
- Infections- UTI, lungs, bacterial and fungal infections
- Hypoglycaemia
Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetic neuropathy- renal disease mainly affecting renal system i.e. visceral-cardiovascular, somatic-poly and mononeuropathy
- Diabetic retinopathy- mainly affecting visual system
- Diabetic foot/ulcer
- Coronary artery disease/ cardiac diseases
What Are The Dosha Involved In Triggering The Symptoms Of Diabetes?
Diabetes which is also known as "Prameha " is believed to have 20 types depending upon the type of dosha i.e. Vata, Pitta and Kapha dosha (Tridosha). According to Ayurveda there are three main divisions of diabetes are-
- Kaphaja- Kaphaja imbalance causes nausea, vomiting, indigestion and lack of hunger.
- Pittaja- This causes insomnia, restlessness, urinary tract infections in women and diarrhea.
- Vataja - This causes sleeping and digestive disorders.
According to Ayurveda, diabetes is caused due to Nidana sevana which aggravates Kapha and vitiates Meda Dhatu. Kapha and Meda are Jala tattva, kidneys and greater omentum are considered as seat (moolsthana) of Meda dhatu. This in turn causes excessive urination and thirst.
Herbal Products for the Management of Diabetes
1. Neem powder
Neem patra powder contains wonderful herb i.e. Azadirachta indica possesses a bitter taste which makes it an amazing anti-diabetic herb. This helps in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, pacifies digestive fires and is effective in wound healing.
2. Diableen capsules
Diableen capsules contains some herbal ingredients like Methika (Trigonella foenum-graceum), Gurmar (Gymnema sylvestre), Haridra (Curcuma longa), Karvellak (Momordica charantia) and Jambul (Syzygium cumini). Methika in this herbal combination is highly effective in diabetes as it contains galactomannan, a natural fiber present in methi seeds which slows down the sugar absorption into blood. Other herbs in this Ayurvedic product works tremendously in maintaining healthy sugar levels.
3. Amalaki Rasayan
Amalaki Rasayan is an herbal remedy which contains Emblica officinalis, which helps in eliminating toxins from the body. Indian gooseberry is very beneficial in reducing obesity, regulates blood sugar levels and revitalizes the nervous system. Amalaki Rasayan improves the immunity naturally and rejuvenates the body.
4. Digestion support
These herbal capsules contains various traditional herbs like Amla (Emblica officinalis), Haritaki (Terminalia chebula), Bahera (Terminalia bellirica), Sounf (Foeniculum vulgare), Dhania (Coriander sativum), Pippali (Piper longum) and Jeerak (Cyminum cuminum). This supplement strengthens the digestive system and triggers the liver, intestines to secrete digestive juices. It also has beneficial properties which relieves constipation and other digestive ailments.
5. Immune Booster Capsules
Immune booster is a classical Ayurvedic remedy which have been formulated by Grape seed (Vitis vinifera), Cow colostrums (Bovine colostrums), Bhumi Amla (Phyllanthus niruri) and Amalaki (Phyllanthus emblica). This product is a great detoxifying agent and improves the immune system. Bhumi amla or Indian gooseberry possess antioxidant properties which is beneficial in treating cold, cough, asthma and various liver disorders. Cow colostrums are enriched with vitamins, micronutrients, proteins etc. which makes it significant in improving immunity.
6. Neem Capsules
Planet Ayurveda's neem capsules have been formulated from standardized extract of neem (Azadirachta indica) which possess anti-diabetic and anti-hemorrhoids properties. All the properties make it beneficial in treating various ailments like respiratory disorders, tooth decay, gum diseases and various skin related infections like Acne, Eczema, Psoriasis, etc. Neem tree is often considered as a Sarva Roga Nivarini which makes it beneficial in treating all ailments and disorders.
7. Karela Capsules
Karela (Momordica charantia) which is also considered as bitter melon and wild cucumber is an effective herbal supplement for diabetes. Some of the tremendous benefits of Karela capsules are-
Bitter melon contains lectin which helps in maintaining sugar levels by acting upon peripheral tissues and suppressing appetite.
Possess charanti and polypeptide-p (insulin-like compound) which provides karela anti-diabetic properties.
Contains vicine that helps in increasing insulin secretion, stimulates the liver, and glycogen synthesis.
8. Fenugreek capsules
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum) which is also known as Methika and Methi, are rich sources of minerals (copper, zinc, magnesium, calcium, potassium, etc.). Moreover, these capsules have been formulated by using the best quality of methi seeds. It's tremendous chemical and phytochemical constituents make it beneficial in maintaining healthy weight and stable blood glucose levels.
Panchakarma
Panchkarma for diabetes involves Snehapanam, Thalapothichil and Thakradhara which will help in eliminating vitiated dosha from the body. After Purvakarma, a person's body gets relaxed and loosened so for the proper management of diabetes Vamana, Virechana and Basti therapies of Panchakarma are commonly used by Ayurvedic experts.
Dietary Tips
What to Avoid?
- Avoid bakery products, sauces, fruit jellies, jams, sweets, artificial sweeteners, soups, ice-cream, chocolate, coconut bar, chutneys, pickles and fried foods
- You should not consume whole milk drinks and carbonated beverages.
- Frozen pulses and red chilies must be excluded from the diet.
- Whole refined flour, sugar and rice.
- Mango, litchi, grapes, dates, peanuts, cashew nuts and pistachio.
What to Eat?
- Veg upma, poha, porridge, idli, besan pancakes, Missi roti and plain chapati.
- Whole wheat, oatmeal, whole grains cereals, and oats.
- Okra, cauliflower, beans, cabbage, mushroom, spinach, eggplant, peas, capsicum, fenugreek and broccoli can be added to the diet.
- Spices like cumin, coriander, turmeric, ginger, pepper, fennel, and cinnamon can be taken in adequate quantities.
- Egg white, roasted, or grilled fish and chicken soup can be added to the diet.
Lifestyle tips
- Make a habit of walking at least 30-45 min daily
- Skipping meals should be avoided
- Stay hydrated and drink 8-10 glasses of water regularly
- Seasonal fruits and vegetables should be added to your daily
- Exercise daily and avoid a sedentary lifestyle in order to prevent obesity
- Regular follow-ups with a doctor should be conducted

