
How many times did your parents tell you, "Drink your orange juice; you need to get more vitamin C?."
Chances are good you then went to school and heard more about the benefits of vitamin C in health class.
You also may have some hazy recollection from history class that a lot of sailors and explorers used to suffer from scurvy owing to a lack of vitamin C.
You may remember the tale of Jacque Cartier saving his men by boiling needles from a tree to make a tea rich in vitamin C back in 1536.
Thankfully, scurvy is a rare issue in First World countries nowadays. Not a lot of people have a vitamin C deficiency.
So what does vitamin C do for you on a daily basis?
In this article, I will share with you the scientifically backed benefits of this essential nutrient, as well as a few possible benefits which researchers still are not sure about.
But first, let’s talk a little bit more about vitamin C itself.
What Is Vitamin C?
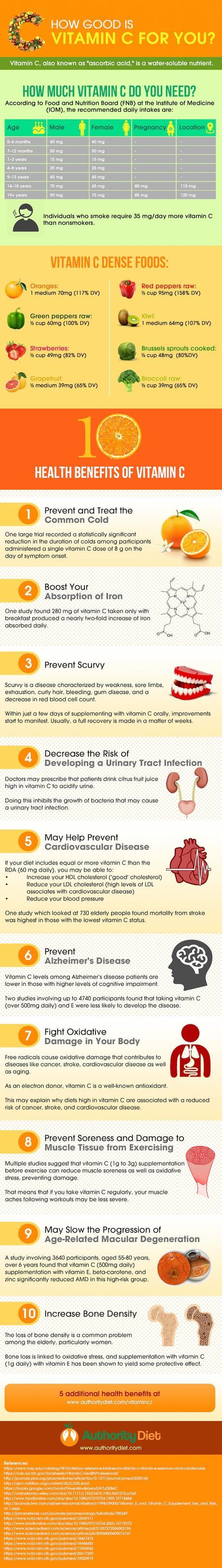
Vitamin C, also known as “ascorbic acid,” is a water-soluble nutrient which is found in many different foods.
It is a powerful antioxidant, protecting your body from the damage of free radicals.
Free radicals play a key role in the aging process, so getting plenty of vitamin C can protect your health both now and over the years to come.
Share This Infographic On Your Site
<p><a href='https://www.authoritydiet.com/health-benefits-vitamin-c-why-good-you/'><img src='https://www.authoritydiet.com/images/i/vitamin-c-benefits-infographic-hd.jpg' border='0' /></a><br /><strong>Please include attribution to AuthorityDiet.com with this graphic.</strong></p>
How Much Vitamin C Do You Need?
The amount of vitamin C that you require depends on how old you are.
According to Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) at the Institute of Medicine (IOM), growing infants require 50 mg (20), but then the amount drops down to 15 mg for children up to three years old.
It climbs slowly back up from that point, maxing out at 90 mg for adult men and 75 mg for adult women.
Here is a comprehensive table (36):
Age
Male
Female
Pregnancy
Lactation
0–6 months
40 mg*
40 mg*
7–12 months
50 mg*
50 mg*
1–3 years
15 mg
15 mg
4–8 years
25 mg
25 mg
9–13 years
45 mg
45 mg
14–18 years
75 mg
65 mg
80 mg
115 mg
19+ years
90 mg
75 mg
85 mg
120 mg
Individuals who smoke require 35 mg/day more vitamin C than nonsmokers.
* Adequate Intake
How to Get More Vitamin C in Your Diet

While you can supplement with vitamin C, or take vitamin C as part of a multivitamin, you can also get ample amounts of vitamin C through diet.
Here are some foods which contain high amounts of vitamin C (35):
- Citrus fruits such as oranges (1 medium 70mg, 117% DV) and grapefruit (½ medium 39mg, 65% DV)
- Red peppers raw: ½ cup 95mg (158% DV)
- Green peppers raw: ½ cup 60mg (100% DV)
- Kiwi: 1 medium 64mg (107% DV)
- Strawberries: ½ cup 49mg (82% DV)
- Tomatoes raw: 1 medium 17mg (28% DV)
- Broccoli raw: ½ cup 39mg (65% DV)
- Baked potatoes: 1 medium 17mg (28% DV)
- Cantaloupe: ½ cup 29mg (48% DV)
- Foods fortified with vitamin C
- Beverages fortified with vitamin C (many teas have vitamin C added)
- Fruit or vegetable juices
There are probably multiple foods and beverages on this list which you enjoy on a regular basis.
If you want to increase your vitamin C intake, increasing these foods in your diet is an easy, enjoyable way to do it.
Diabetics and those on low-carb should be aware that some fruits are natures candy and particularly fruit juices are high in sugar.
Vitamin C can help increase iron absorption, so if you are in need of more iron, try taking the two supplements at the same time, or eating a food which contains ample amounts of both, like broccoli.
KEY POINT: There is a reason not a lot of people suffer from scurvy anymore. Many foods rich in vitamin C are a part of most everyday diets in the first world. Eating more fruits and vegetables can increase your intake.
15 Health Benefits of Vitamin C Backed by Science
Here are 15 evidence-based health benefits of vitamin C:
1. Prevent and Treat the Common Cold
It is a common practice to increase vitamin C intake during the winter months to prevent the common cold and flu.
The common cold is more formally referred to as an "upper respiratory tract (URT) infection."
Despite the common practice of treating URT infections with vitamin C, research has demonstrated mixed results. So somewhat surprisingly, this is a subject of controversy.
Still, one large trial "recorded a statistically significant reduction in the duration of colds among participants administered a single vitamin C dose of 8 g on the day of symptom onset" (1).
The link above takes you to a research review of multiple studies. While the large trial mentioned previously demonstrated vitamin C’s effectiveness combating the common cold, the reviewers found that "no benefits have been observed from therapeutic use of doses totalling 10 g that was divided for the first three days of illness."
In other words, a single larger dose of vitamin C on the day of symptom onset yielded improvements, but several smaller doses spread out across three days did not.
This indicates that the effectiveness of vitamin C in combating the common cold depends both on the dosage level and how you time your intake.
Another study (2) looked at the effect of vitamin C on several groups of people under extreme climate conditions or physical fatigue.
The groups included children at a skiing camp in the Swiss Alps, participants in a 90 km race, and troops training in Northern Canada.
The researchers reported, "In each of the three studies, a considerable reduction in common cold incidence in the group supplemented with vitamin C was found."

This indicates that vitamin C may be particularly helpful bolstering the immune system against respiratory illnesses when the body is already under some degree of physical stress.
Common colds are of course pervasive among the general population, but athletes may be at a heightened risk during periods of intense training, as well as during the one- or two-week period which follows a marathon (5).
One study (4) looked at ultramarathon runners to try and determine what the effects of 600 mg of vitamin C would be regarding preventing URT infections after races.
The researchers found that vitamin C supplementation was effective in enhancing resistance to post-race upper respiratory tract infections.
They also found that supplementing with vitamin C could reduce the severity of common cold infections in sedentary people.
That means that whether you are an athlete or not, taking vitamin C can help you to fight URT infections.
KEY POINT: Vitamin C can help you to fight the common cold, but how effective it is depends on the dosage you take and the day you take it (more research is warranted).
Additionally, vitamin C may be especially useful boosting your immune system if you are involved in athletics or are in an harsh climate.
2. Boost Your Absorption of Iron
As previously mentioned, vitamin C can help you to increase your absorption of iron.
In fact, according to one study (3), "280 mg [of vitamin C] … taken only with breakfast … would produce a nearly two-fold increase in the amount of iron absorbed daily."
Iron plays a key role in forming hemoglobin, and also supports muscle and brain function. Adequate iron absorption is necessary to avoid anemia and fatigue.
So while these are not direct benefits of vitamin C, they are all indirect benefits.
KEY POINT: Iron is a necessary mineral which your body requires to form new hemoglobin and regulate brain and muscle function. If you have a hard time absorbing adequate iron, try supplementing with vitamin C. The vitamin C can increase your iron uptake.
3. Prevent Scurvy

Scurvy is a disease characterized by weakness, sore limbs, exhaustion, and curly hair.
It may also lead to bleeding, gum disease, and a decrease in red blood cell count. These symptoms can become quite severe.
Ultimately, scurvy is lethal if it goes untreated. Usually, death is the result of complications from infection or bleeding.
Scurvy is the direct result of a lack of vitamin C, a relationship which is well-documented throughout history (6).
Thankfully you are unlikely to develop scurvy, as it takes a month or more of minimal or no vitamin C in your diet before symptoms manifest.
It has however been known to occur with alcoholics (this is rare), and may also sometimes present in seniors who are unable to adequately live without assistance.
Sometimes scurvy is also seen in patients with mental disorders. In short, anyone who cannot feed themselves a proper diet may still develop scurvy.
Treating scurvy is simple. Within just a few days of supplementing with vitamin C orally, improvements start to manifest. Usually, a full recovery is made in a matter of weeks.
KEY POINT: If you are severely deprived of vitamin C, it is possible you will develop scurvy. Thankfully these situations are rare in the modern world. Scurvy can be quickly cured through vitamin C supplementation.
4. Decrease the Risk of Developing a Urinary Tract Infection
If you have ever suffered from a urinary tract infection, you know it is an experience you never want to repeat.
Unfortunately, UTIs are quite common, and many people experience multiple UTIs over the course of their lives.
Vitamin C may make it less likely that you will develop a UTI.
Doctors may prescribe that patients drink citrus fruit juice high in vitamin C to acidify urine (7).
Doing this inhibits the growth of bacteria which may cause a urinary tract infection.
KEY POINT: Vitamin C may be useful in managing and reducing the prevalence of urinary tract infections.
5. May Help Prevent Cardiovascular Disease

Diets which are high in vitamin C are associated with improvements in cardiovascular health.
If your diet includes more vitamin C than the RDA, you may be able to increase your HDL cholesterol ('good' cholesterol) while reducing your LDL cholesterol (high levels of LDL associates with cardiovascular disease). You also may be able to reduce your blood pressure (8).
Nonetheless, the exact role of vitamin C in cardiovascular health is still ambiguous to researchers.
One study which looked at 730 elderly men and women found no link between vitamin C intake and coronary heart disease (9).
The same study did, however, find a link between vitamin C intake and stroke, noting that "mortality from stroke was highest in those with the lowest vitamin C status."
Another study (10) found that vitamin C "did not seem to substantially reduce risk for stroke." The researchers did say however that it may have had "modest effects."
All this conflicting data seems to suggest that vitamin C can help prevent cardiovascular disease, but if so, it may only be significantly within certain contexts.
It is likely that other dietary factors are involved. Further research is warranted.
KEY POINT: Research suggests that vitamin C may play a role in protecting cardiovascular health. Diets high in vitamin C seem to be associated with reduced risk factors for stroke and heart disease.
As results are mixed and scientists still do not fully understand vitamin C’s role, more research is needed before anything conclusive can be stated.
6. Prevent Alzheimer's Disease (Possibly, When Taken with Vitamin E)
Another area of research where vitamin C shows promise is in the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers have found that plasma vitamin C levels among Alzheimer’s disease patients are lower in proportion to higher levels of cognitive impairment (11).
This is despite patients taking in the same amount of vitamin C, which seems to indicate that damage from free radicals is responsible for the damage.
Nonetheless, supplementation may be able to help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s in the first place.
One study (12), which looked at 633 participants over the age of 65, tracked dietary habits and symptoms over a period of 4.3 years.
Multivitamins alone were not found to reduce the likelihood of developing Alzheimer's, but it found that those who took high doses of vitamin E and C were less likely to develop the disease.
Further insight is provided by this (13) study of 4,740 participants. Researchers found no reduction in risk for Alzheimer’s disease among patients who took multivitamins alone, or who took vitamin E alone, vitamin C alone, or either in conjunction with vitamin B complex.
But they did find that taking vitamin E and vitamin C (over 500mg daily) supplements together reduced "prevalence and incidence" of Alzheimer’s disease.
KEY POINT: Preliminary research indicates that supplementing with vitamin C with vitamin E may help to reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. More research is needed to establish a firm link.
7. Fight Oxidative Damage in Your Body

As an electron donor, vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant (14).
This may explain why diets which are high in vitamin C are associated with a reduced risk of cancer, stroke, and cardiovascular disease.
Patients who eat diets high in vitamin C also tend to live longer (15).
While scientists are still not positive that the protective effects of these diets can be attributed to vitamin C or some more complex interplay of nutrients, it is likely that vitamin C plays a potent role because of its status as an antioxidant.
Free radicals are known to play a role in the development of disease (16) and aging (17).
That means that antioxidants like vitamin C can help to prevent disease and slow the aging process.
KEY POINT: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant. Free radicals which cause oxidative damage contribute to diseases like cancer, stroke, and cardiovascular disease.
Vitamin C can help to fight these free radicals, potentially reducing your risk of developing these diseases later in life.
8. May Reduce the Chances of Developing Cataracts
Multiple studies have shown that vitamin C may reduce the chance of developing cataracts. This includes animal studies (18) and human studies (19).
In fact, the human study linked above examined hundreds of participants aged 56-71 years (all women). Over a 10-12 year period, it found that "long-term consumption of vitamin C supplements may substantially reduce the development of age-related lens opacities."
On the other hand, there is some conflicting data. One much larger study from Sweden looked at 24,593 women and concluded just the opposite (38). The results from this study indicated that taking vitamin C supplements might actually increase the risk of age-related cataracts.
KEY POINT: It is possible that vitamin C might reduce your risk of cataracts - then again, supplementing with too much vitamin C might also do the opposite.
More research is needed to establish whether vitamin C supplementation if beneficial to eye health or detrimental.
9. Possibly Slow the Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Not only might vitamin C be able to reduce the chances of developing cataracts, but it is possible that it may also help to prevent age-related macular degeneration.

One study (21) looked at whether the use of antioxidant and/or zinc supplements might delay the progression of age-related macular degeneration and the development of blindness.
The antioxidants used in the study included vitamin C (500mg daily), vitamin E, and beta-carotene.
The researchers reported, "Both zinc and antioxidants plus zinc significantly reduced the odds of developing advanced AMD in this higher-risk group."
Based on their findings, they concluded that people who are age 55 or above should consider taking a combination of antioxidants (including vitamin C) and zinc if they are at risk for AMD or are already developing the condition.
KEY POINT: If you suffer from age-related macular degeneration and are looking for a way to postpone the loss of your vision, a combination of zinc, vitamin C, vitamin E and beta-carotene may help to slow the progression of the disease.
10. Increase Bone Density
The loss of bone density is a common problem among the elderly, particularly women. Decreased bone density can lead to osteoporosis and fractures.
Bone loss has been linked to oxidative stress (22), but supplementation with vitamin C has been shown to yield some protective effect (23).
Researchers suggest 1,000 mg of ascorbic acid along with 400 IU of alpha-tocopherol as a preventative for age-related osteoporosis.
This same dosage may help to treat osteoporosis in those who have already developed the disease.
KEY POINT: If you are at risk for osteoporosis, taking 1,000 mg of vitamin C each day may help you to retain your bone density, preventing the development of the disease.
If you already have osteoporosis, taking the same dosage may help you to maintain the density you have and prevent the disease from progressing.
11. Prevent Soreness and Damage to Muscle Tissue from Exercising

If you are looking for a supplement which can speed recovery after strength training and other forms of exercise, vitamin C may be able to help.
Multiple studies (24, 25) suggest that vitamin C (1g to 3g) supplementation before exercise can reduce muscle soreness as well as oxidative stress, preventing damage.
That means that if you take vitamin C regularly, your muscle aches following workouts may be less severe.
Your muscles may also recover more quickly, allowing you to reduce your rest time and get back to exercising sooner.
KEY POINT: Vitamin C can reduce oxidative stress, muscle soreness, and damage from exercise.
12. Improve Mood and Libido
If you suffer from depression or other mood disorders, you may find that vitamin C helps to restore some emotional balance.
In one study (26), hospitalized patients took either vitamin C (500mg twice daily) or vitamin D, and researchers measured the effect upon their mood.
No significant improvements in mood were recorded among those who tried the vitamin D therapy.
With the vitamin C therapy however, a 34% reduction in mood disturbance was reported.
Another study (27) found that taking vitamin C (3g daily) led to improvements in mood and libido in participants, resulting in more sexual activity.
KEY POINT: Supplementing with vitamin C may help to reduce mood disturbances while also stimulating libido.
13. Improve Blood Circulation
Another benefit of vitamin C is in boosting blood circulation.
Because vitamin C can reduce oxidative stress, it can prevent vascular dysfunction induced by oral glucose load (28).
Vitamin C may also improve circulation in patients with postural tachycardia syndrome (29).
Further, it can help to regulate blood pressure and vasodilator response in obese children who are suffering from mental stress (30).
Taking vitamin C can likewise combat endothelial dysfunction following short-term cigarette smoking (31).
KEY POINT: Vitamin C can regulate blood pressure and improve circulation for patients with a range of different conditions.
14. Reduce Wrinkles and Age Lines While Treating Sun Damage

Both oral and topical application of vitamin C can help to combat the free radicals which cause skin damage associated with aging.
That includes sagging, wrinkles, fine lines, age spots and sun damage.
The best results can be achieved by applying vitamin C directly to the skin rather than by ingesting it.
These results have been demonstrated in clinical trials (32, 33).
In fact, the second study linked above had astonishing results. Photographic assessment demonstrated an improvement of 57.9% in patients who treated their skin with vitamin C regarding wrinkles, tactile roughness, coarse rhytids, skin laxity/tone, sallowness/yellowing and overall features versus those that did not.
KEY POINT: Vitamin C’s powerful antioxidant properties can help to combat the effects of age and sun damage on skin. Applying it topically through a serum is the best way to clear up wrinkles and discoloration.
15. Increase the Absorption of Calcium
Iron is not the only nutrient which can be absorbed more effectively with the aid of vitamin C.
Research also shows (34) that vitamin C as ascorbic acid can enhance intestinal absorption of calcium.
Incidentally, calcium is included in many buffered vitamin C supplements to help maintain pH balance and aid in digestion.
So taking vitamin C and calcium together confers multiple benefits.
KEY POINT: Vitamin C can boost calcium absorption. Taken together, calcium can also make it easier for your body to digest vitamin C.
Is It Possible to Get Too Much Vitamin C?
If you are planning on supplementing with vitamin C beyond the dosage included in your regular multivitamin, you are probably wondering whether it is possible to get too much.
As a reminder, 75-90 mg is the recommended daily amount of vitamin C for adults.
There is an upper limit, but it is incredibly high: 2,000 mg per day (36).
Generally speaking, vitamin C is considered a very safe supplement. You are unlikely to experience any harmful effects from high amounts, but at very high dosages, you might experience any of the following side effects:
- Gastrointestinal effects like nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, heartburn, bloating or cramps
- Kidney stones
- Headache
- Insomnia
If you experience any of these side effects, reduce your dosage to a level which is more suitable for your body.
Vitamin C Supplements
While a diet rich in citrus and other foods and beverages containing vitamin C should be adequate for most needs, there may be times when you want to take vitamin C supplements, such as to prevent the cold.
Vitamin C supplements may take several different forms. While ascorbic acid is the most common, you may also sometimes encounter calcium ascorbate, sodium ascorbate, ascorbic acid with bioflavonoids, or mineral ascorbates.
No particular form is superior to any other (37), so go with a product which provides you with the dosage you need at an affordable price.
If you are looking for recommendations, please see our Guide to the Best Vitamin C Supplements.
Conclusion: More Research Is Needed to Fully Understand Vitamin C, But It is a Vital Part of a Healthy Diet
Despite the fact that you likely grew up with parents and teachers telling you time and again, "Drink your orange juice," our scientific understanding of the role of vitamin C in health is surprisingly ambiguous at this point.
We know that vitamin C can help us to absorb iron more effectively and prevent scurvy.
It appears it may also have benefits for cardiovascular and brain health as well as (potentially) eye health. This is likely because it is a potent antioxidant. It also may be able to help prevent and treat the common cold.
More research is needed in all of these areas. Until then, a diet high in vitamin C will nourish your body with a wide array of essential nutrients.

