Most runners that you see, specially here in the Philippines have slim body and from the almost zero (0) body fat, their body is also obviously has lesser muscle mass compared to other type of athletes.
Our genes plays an important role in this outcome of our muscle and built but it doesn't mean that our body also requires lesser protein, or that we don't need it at all.
Running is a great way to stay in shape and maintain a healthy lifestyle. However, in order to truly optimize your performance and recovery, it's important to pay attention to your protein intake.

Protein is one of the three (3) macronutrients that our body needs in large quantities, along with carbohydrates and fats. It is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of our muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other tissues.
When we run, we put a lot of stress on our muscles. This causes microscopic tears in the muscle fibers, which need to be repaired in order to get stronger. Protein is essential for this repair process, as it provides the necessary amino acids for the body to rebuild and strengthen the damaged tissue.
But it's not just about recovery and muscle repair, protein also helps in maintaining a healthy weight and preventing muscle loss, which can occur as we age.
Additionally, protein helps to regulate blood sugar levels and keeps you feeling full and satisfied, which can help to prevent overeating and weight gain.
Adequate protein intake can also help to reduce muscle soreness and fatigue, as well as improve overall recovery time. This is especially important for runners, who may be doing high-intensity training on a regular basis.
When adequate protein is not consumed, muscle repair and growth may be impaired, leading to reduced athletic performance and increased risk of injury.
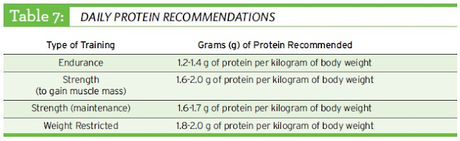
The recommended daily protein intake for athletes is generally higher than for sedentary individuals. This is because athletes have an increased need for protein to support muscle repair and growth.
For runners, the recommended daily intake of protein is between 0.5 and 0.75 grams per pound of body weight. This can be easily achieved by eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein-rich foods such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and plant-based sources like beans, lentils, and quinoa.

Protein can be obtained from a variety of natural sources, including meats, dairy products, fish, eggs, and legumes. For vegetarian and vegan athletes, plant-based sources of protein such as beans, lentils, and nuts are good options.
In addition, protein supplements are available in the form of powders, bars, and drinks, and can be a convenient way for athletes to meet their protein needs.
It is important for athletes to choose high-quality protein sources that provide all of the essential amino acids.

Strategies for Meeting Protein Needs
To meet protein needs, athletes should focus on consuming a balanced and varied diet that includes a variety of protein sources.
Meal planning and nutrient timing can also be important strategies. Athletes should aim to consume protein throughout the day, rather than all at once, as this can help to optimize muscle repair and growth.
Additionally, combining different proteins in one meal can improve the quality of the protein that is consumed.
Lastly, proper hydration is important for athletes, since proper hydration can ensure that the protein is effectively utilized for muscle repair and growth.
In conclusion, adequate protein intake is crucial for runners to optimize their performance and recovery, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent muscle loss. Make sure you're getting enough protein in your diet and you'll be on your way to reaching your running goals.
Proper hydration is also important to ensure that the protein is effectively utilized for muscle repair and growth.
By following these guidelines, athletes can optimize their athletic performance, reduce their risk of injury, and support their overall health and well-being.
