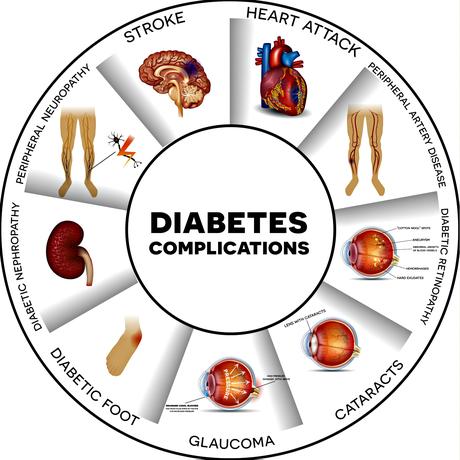
Diabetes complications
Complications occur because over time persistent high blood glucose levels can damage the body’s organs. This damage is referred to as diabetes-related complications. It may be frightening to think about complications when you’re still dealing with the news that you have diabetes, but taking action today can make a huge difference to tomorrow. With the support of your healthcare team you will be able to develop a daily self-management program that includes setting goals, taking responsibility and positive lifestyle choices.When diabetes is left undiagnosed or unchecked for too long, it can be responsible for a number of diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, limb amputation, erectile dysfunction and persistent infections.These complications are serious but keeping blood glucose, blood pressure and blood fat levels under control will greatly help to reduce the risk of developing complications.
Kidney disease
Your kidneys help to clean your blood. They remove waste from the blood and pass it out of the body as urine. Over time, diabetes can cause damage to the kidneys (diabetic nephropathy). You will not notice damage to your kidneys until it’s quite advanced, so it is important that you have the recommended tests to pick up any problems early. If the kidneys fail, toxic waste products stay in the body, fluids build up and the chemical balance is upset. If the kidneys are unable to function properly, dialysis treatments or a kidney transplant will be needed. The risk of developing kidney problems is reduced by managing your blood glucose levels, having regular kidney and blood pressure checks and leading a healthy lifestyle. Early signs of kidney problems can be detected through a urine test. Finding out about early kidney damage is simple and painless. Treatment at this time can prevent further damage.Hypoglycaemia
Hypoglycaemia (also called a hypo), is when your blood glucose level has dropped too low. While hypoglycaemia can be experienced by people taking certain tablets for their diabetes, it is more common in people who inject insulin. It is generally not a problem for people with type 2 diabetes who can manage their diabetes through a healthy eating plan and physical activity alone, however, it is possible.Oral health
People with diabetes, regardless of their age, are at greater risk of developing gum disease than people who do not have diabetes. People with diabetes who often have high blood glucose levels are two to three times more likely to develop gum disease than those with well managed diabetes.Nerve damage and lower limb complications
Diabetic neuropathy is the medical name given to progressive damage to the nervous system caused by diabetes. Diabetic neuropathy can lead to a loss of feeling in the hands and feet. Reduced circulation resulting from high blood glucose impairs normal wound healing in the extremities, so minor damage can linger and develop into permanent injury. Personal daily foot checks and thorough annual foot examinations conducted by your doctor or podiatrist will help to reduce your risk of lower limb complications.Sleep apnoea
Sleep apnoea is a type of sleep disorder characterised by pauses in breathing or instances of shallow or infrequent breathing during sleep. People with sleep apnoea commonly snore and although they may seem asleep, their quality of sleep suffers greatly. Constant gasping for air prevents sufferers achieving a deep sleep, leaving people sleep deprived.Sleep apnoea makes up around 80% of sleep-related breathing disorders, affecting up to four per cent of men and two per cent of women in Australia. Clinical studies have shown that diabetes and sleep apnoea are closely linked, with sleep apnoea sufferers nine times more likely to also have type 2 diabetes.

