Loose skin versus fat is a prevalent concern for many people, particularly those on a weight loss journey. Confusion between the two can frequently lead to misunderstandings and undue anxiety. Your weight loss journey might be difficult, especially if you have previously gained weight and then lost it, resulting in excess skin. This fluctuation in body weight may prompt patients to consult with a plastic surgeon to better understand their treatment options. Your body type determines how you remove skin and eliminate fat deposits.
If you have already acquired weight and are considering fat loss, keep reading this site. Remember that patients have skin excision surgery, minimally invasive skin tightening techniques, and fat removal surgery. When having liposuction surgery, it is critical to avoid generating loose skin. The information supplied will help us differentiate them and develop effective management methods.
Loose skin vs fat- An Overview
The complexity of body composition frequently concentrates on two major components: loose skin and body fat. Loose skin is also known as extra skin. Understanding these components is critical for a thorough understanding of overall health.
what is loose skin
Loose skin refers to skin that has lost its elasticity and firmness, often resulting in a sagging or wrinkled appearance. This can occur due to various factors such as aging, significant weight loss, pregnancy, or prolonged sun exposure. When the skin loses its elasticity, it may not be able to snap back into place as it once did, leading to the appearance of loose or hanging skin in certain areas of the body.
First, we must identify l oose skin vs fat. The former, commonly called extra skin, is frequently caused by severe weight loss or aging. It appears in a limp form that drapes over specific bodily parts. The body has subcutaneous and visceral fat, with the former being beneath the skin and surrounding organs. Both contribute to obesity rates, which are currently affecting an estimated 93.3 million American adults.
Unique characteristics, including its texture distinguish loose skin. Pinched between fingers, it seems thin due to a lack of underlying tissue support, in contrast to areas with abundant subcutaneous fat, which have greater substance under the top layer.
In addition to touch-based identification methods, visual cues are important in recognizing the existence of loose skin on our bodies; unlike youthful firmness, which springs back promptly after stretching out, loose or aging skins hang freely.
- Paying attention to how your skin responds to stretching can help you determine if you have excess subcutaneous fat or genuine looseness within the dermal layers.
- Analyzing how your flesh feels under direct contact can help you distinguish between large fatty deposits and less dense patches that indicate a loosened epidermis.
- Familiarizing yourself with normal appearances rather than indicators such as drooping will help you recognize problems early on before they become severe.
Difference Between Loose Skin and Fat
Body contouring is a complex area that requires a thorough understanding of the human shape. One thing that frequently confuses individuals is distinguishing loose skin vs fat. Although they may appear similar, their underlying causes are drastically different, necessitating unique treatment techniques.
The Pinch Test to Determine Fat or Loose Skin
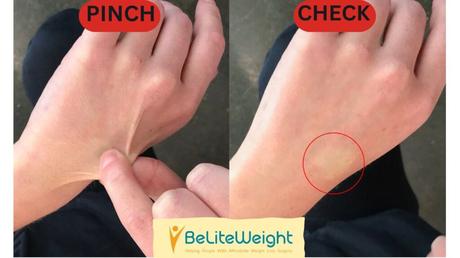
The pinch test provides an easy technique to distinguish between these two states. Pinching a spot on your body with two fingers reveals what is beneath the skin's surface. When you pinch the skin fold, there is usually very little substance within it, indicating loose skin. In contrast, a thicker layer that is soft to the touch may indicate extra subcutaneous fat.
This phenomenon, often known as ' skin remains vs. fat existing,' causes confusion due to its misleading nature. While drooping skin loses elasticity over time due to collagen degradation, 'fat hanging' refers to thicker tissue that does not return to place after major weight loss.
'fat hanging' refers to thicker tissue that does not return to place after major weight loss.
With this data, it is evident why discriminating loose skin vs fat is so important in cosmetic operations such as liposuction and stomach tucks.
During a tummy tuck, the plastic surgeon removes excess skin and unwanted fat that appears in the the abdominal area and tightens the underlying muscles. This procedure can also reposition the belly button, resulting in a smoother, more toned abdominal appearance.
Body shaping procedures can be an ideal cure for severe cases of skin that is loose and excess fat. These types of surgeries contour thecontour your body by removing extra tissues, leading to a more attractive shape.
A Range of Body Contouring Procedures

Abdominoplasty is only one piece of the jigsaw; other body sculpting procedures are available depending on the individual's needs. For example, liposuction is frequently used in conjunction with body lift operations to treat drooping skin around the hips, thighs, and buttocks following major weight loss.
Arm lifts (brachioplasty) and thigh lifts are also used to target areas with loose skin or resistant fatty deposits. Each technique has distinct advantages geared toward obtaining desired objectives while maintaining patient safety.
Risks of Plastic Surgery:
Being infected
Blood clots.
Anesthetic problems, among others.
All of these potential hazards should be discussed thoroughly with your surgeon before undergoing any surgery. This decision should not be taken lightly; cautious consideration must also extend to the healing time after surgery.
Lifestyle Changes and Non-Surgical Treatments: A Pathway to Prevention and Management

What are some successful ways to prevent and manage loose skin and fat? It turns out that lifestyle adjustments and non-surgical treatments have great potential. I think we should look at this more.
Physical activity can significantly improve weight management and skin health. Regular exercise reduces extra body fat and improves skin suppleness. This might vary from everyday walks to more strenuous workouts such as strength training exercises.
Rapid weight loss frequently results in sagging or loose skin since it is unable to keep up with your reduced body mass. As a result, taking a cautious and steady approach to weight loss gives your skin enough time to react.
The American Heart Association's guide, How To Lose Weight Without Dieting, provides helpful advice for achieving progressive weight loss without dieting.
Frequent variations in body mass contribute considerably to the production of stretch marks, which damage elastin fibers and cause loose skin. Sustainable eating practices that encourage long-term stability should be prioritized over yo-yo diets, which result in fast gains after losses.
Conclusion
Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, progressive weight loss, and avoiding yo-yo diets can all help prevent and manage loose skin and fat. These treatments improve skin elasticity, metabolic regulation, and long-term stability. You no longer have to worry about loose skin vs fat
FAQs
How do you say whether it is loose skin or fat in your body?The "pinch test" is one of the simplest ways to check. Pinch the area - if you can grasp a thin layer, it's likely loose skin. If you can pinch a thicker, softer layer, it's probably subcutaneous fat. Consult a professional for a proper assessment.
Does loose skin ever tighten?Yes, loose skin can tighten naturally over time, particularly in young people, as the body adjusts to weight loss. However, considerable loose skin may necessitate surgical procedures such as a stomach tuck to effectively tighten.
Will losing 50 pounds cause loose skin?Dropping a substantial amount of weight, like losing 50 pounds, may end in loose, sagging skin, mainly if the weight loss is quick.
What is the fat that looks like loose skin?Beneath the skin fat or the covering of fat directly below the skin, can give an impression of loose skin. Excess belly fat might appear loose and loosening, comparable to loose skin.

