Imagine a virus so deadly that it can cause fatal bleeding, organ failure, and shock within days. This virus exists, and it's called Ebola. Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) was first discovered in 1976 near the Ebola River in Central Africa. With no known cure and a history of high fatality rates, it's essential to understand this dangerous disease. So, let's see everything about the virus, from how it spreads to how it can be treated.
What is Ebola Virus?
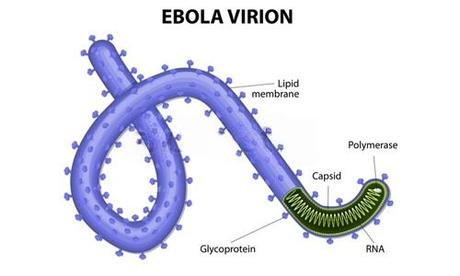
Ebola Virus Disease is a rare but severe illness caused by the Ebola virus, which belongs to a family of viruses known as Filoviridae. It leads to severe illness, often characterized by bleeding, organ failure, and, in many cases, death. The virus targets the immune system and internal organs, causing extensive damage with high mortality rates. The virus affects humans and primates (monkeys, gorillas, and chimpanzees) and leads to severe viral hemorrhagic fever.
Types of Ebola Virus
It isn't just one virus but has multiple strains. There are five known species of the virus, and four of them can infect humans:
1. Zaire ebolavirus
The most dangerous and deadliest strain, responsible for most major outbreaks.
2. Sudan ebolavirus
Also highly fatal but with a slightly lower mortality rate than in Zaire.
3. Taï Forest ebolavirus
Found primarily in Africa, is a rare strain with only one confirmed human case.
4. Bundibugyo ebolavirus
Discovered in Uganda and associated with sporadic outbreaks. It also causes smaller outbreaks but with a moderate fatality rate.
5. Reston ebolavirus
Interestingly, this strain primarily affects animals and has not caused illness in humans so far.
Each of these species has its own characteristics and lethality, but the Zaire strain is the one responsible for the largest outbreaks.
How is Ebola Transmitted?
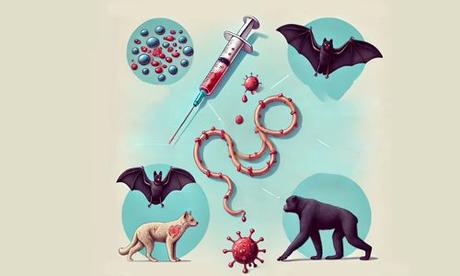
The transmission occurs through direct contact with:
- Blood or bodily fluids (saliva, sweat, urine, vomit) of someone who is infected or has died from this disease.
- Contaminated objects like needles or surfaces.
- The virus can jump from animals to humans, primarily through contact with bats or primates.
Healthcare workers and family members of infected individuals are particularly vulnerable.
Symptoms of Ebola
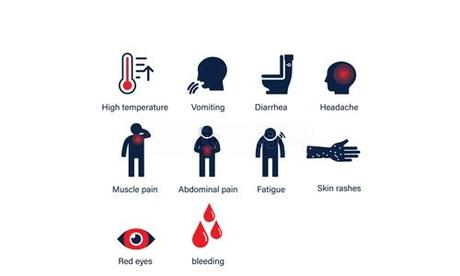
Once the virus enters the body, it begins to replicate rapidly and incubates for 2 to 21 days. But how do you know if someone has this disease? Here are some telltale symptoms:
Early symptoms include:
As the disease progresses, it leads to more severe symptoms like:
The severity of these symptoms underscores the importance of early detection and treatment.
Diagnosis & Tests for Ebola Virus Disease
Diagnosing is challenging in the early stages due to its similarity to other diseases like and typhoid. Diagnosis is typically done through:
- Blood tests to look for the presence of the virus RNA or antibodies.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test amplifies the viral genetic material for easy detection.
- ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detects antibodies to confirm if a person has had this disease.
Timely diagnosis is crucial for isolating the patient and preventing the virus from spreading.
Treatments for Ebola
Currently, there's no guaranteed cure, but early medical care can improve survival chances. Treatments mainly focus on supportive care, such as:
- Hydration (to replace lost electrolytes), oxygen therapy (to maintain oxygen levels in the blood), and blood pressure management are essential.
- Drugs like Remdesivir and Inmazeb (a combination of three monoclonal antibodies) have shown promise in recent outbreaks.
- The Ervebo (rVSV-ZEBOV) vaccine has been approved and can prevent the Zaire strain.
Prevention & Control of Ebola Virus Disease
Preventing requires a combination of personal hygiene, community awareness, and healthcare intervention. Key prevention methods include:
- Avoid contact with the blood and bodily fluids of infected people or animals.
- Using protective gear (like gloves and face masks) when caring for an infected person.
- Isolating patients who are infected to prevent the virus from spreading.
- It can be transmitted through the body of a deceased person, so strict burial practices must be followed.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for healthcare workers.
- Frequent handwashing with soap or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers .
Survival Rate of Ebola Virus Disease
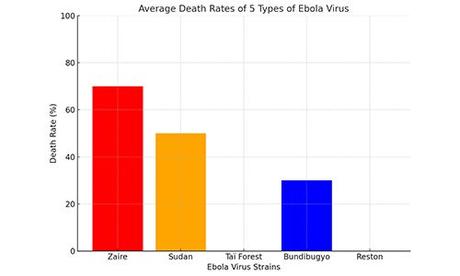
It can vary significantly, depending on the strain and access to medical care. For example, the Zaire strain has a mortality rate as high as 90%, while other strains, like Sudan, have lower fatality rates (around 50-60%). The Ervebo vaccine and experimental drugs have also helped to increase survival rates in recent outbreaks.
Additional Common Questions

While there's no specific cure, vaccines and experimental treatments have helped reduce mortality rates.
Survivors typically develop immunity to the strain they were infected with, but they can still contract a different strain.
No, it is not airborne. It spreads through direct contact with infected bodily fluids.
- How is Ebola different from other viruses?
Its high fatality rate and hemorrhagic symptoms (bleeding) make it far more dangerous than common viruses like the flu or COVID-19.
Ebola Virus Disease may be one of the deadliest viral diseases, but with increased awareness, prevention strategies, and vaccines, there's hope for controlling future outbreaks. While the survival rate can be daunting, early intervention, proper medical care, and following preventive measures make a huge difference.


Ashley completed her degree with nutrition as her major. She loves sharing her knowledge with others and playing with words. After struggling for almost a year to find a job that could make her feel lively, she ended up as a freelance writer. Ashley writes health-related blogs and articles. She makes sure that her works always stand unique and are useful for everyone. Ashley is also a YouTuber who shares health-related videos. She knows the value of the right information and how it can be beneficial to others. Therefore, her only motto is to provide accurate information. If Ashley sounds like that neighbor who you can ask for health tips, take a look at her works.

