Starting the domain name name of your web site with www. or www2. or www3. is a common convention and nothing more. There is nothing in the HTTP specification that says a web site must start with www. or any other prefix. It is simply a convention that began in the early days of the web and was used to distinguish a company's web server from its FTP server, gopher server, mail server, etc... But no such distinction is necessary, because this part of the URL, 'www.' help it decide how to perform this internal routing.
Usually this type of configuration is stored in your .htaccess file, located in public_html.
Another example is role-based routing. For example, store.company.com and developer.company.com are both hosted at company.com, but serve different roles on the web; one is an online store, the other is a site with resources for programmers. (And each is probably also load-balanced in ways that don't rewrite your URL.)
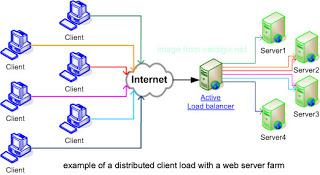
Some companies use 'www2.', 'www3.', etc, to perform 'load balancing'. An initial request to the 'www.' server may get redirected to a less-busy server, such as 'www2.'
In some cases, the specific hostname may be obscured, creating the appearance that the user is viewing the "www" subdomain, even if they are actually viewing a mirror site.
In short, anything after the protocol (http://) and before the domain ('company.com') is managed by the host organization, for a variety of different reasons such as load balancing, roles, marketing, etc.. Although, these domains might be treated as different domain names by search engines.
