What is a CDN? How Does a CDN Work?
You may be familiar with the term Content Delivery Network (CDN) as a way that webmasters speed up their sites. While the digital workings of getting a CDN developed and deployed are on the technical side, the principle behind it is fairly easy to grasp. In fact, without CDNs, the internet would be a much more frustrating place for visitors, and quite possibly a less profitable one for businesses using their website for ecommerce or lead generation.
A content delivery network (CDN) is a geographically distributed group of servers that work together to provide fast delivery of cached internet content. A CDN allows for the quick transfer of assets needed for loading HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images and videos. The popularity of CDN services continues to grow, and most web traffic is now served through them. Also, when a CDN is correctly configured, it can protect your website from some malicious attacks, such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS).
Though a CDN cannot substitute the need for web hosting and doesn’t host content, it aids with static cached content at the network end to improve website performance. Many times, traditional hosting services are unable to meet the performance needs of websites, and it is at this stage that they need the help of a CDN. CDNs use static cached content to reduce bandwidth hosting, prevent website downtime and improve website security.
For example, assume that your main server is hosted in Orlando, Florida, and someone in Reims, France, tries to access it. In that case, they will be redirected to the nearest server, which could be in Paris. This would limit the number of internet hops required to send the static files to the end-user.
Your proximity to the web server has a direct impact on the load time. If you deploy your content across different geographical distributed servers, you can increase the load time of your content, which improves the user experience (UX). The closer you are to the CDN server, the faster you get the content.
For those interested in conducting more extensive research, Cloudflare – a provider of CDN solutions – offers a free series of lessons on the workings of a CDN on its website
How does a CDN work?
To increase the proximity of the end user and the website server, a CDN stores a static cached version of its content in different geographical locations, which is also known as PoPs or points of presence. Every PoP consists of a number of cache 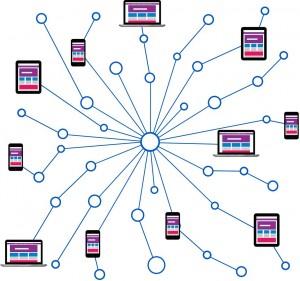 servers, which are responsible for content delivery to people within its vicinity.
servers, which are responsible for content delivery to people within its vicinity.
This means that a CDN puts your content at several locations at any given time, providing an improved user experience (UX) to all of your customers. Returning to our first example, when someone in Paris accesses a website hosted in the United States, it is made possible by a local French Point of Presence (PoP). The travel time drastically reduces here, and the load time increases substantially, which ultimately improves the UX.
Who uses a CDN?
WordPress users, a popular content management system for websites – and the one we use on eServe – and most of the predominant platforms for blogs, websites using any of those will achieve the full benefits of a CDN. WP Beginner offers this infographic on content delivery networks that tells the full story. However, most websites that make use of a CDN is common practice for sectors that include e-commerce, advertising, mobile, media, entertainment, healthcare, government and higher education.
Chris Love – The PWA Guy give his top 3 reason to use a CDN
” data-lang=”en”>
3 Reasons Why You Should Use a CDN #webperf #onlinemarketing https://t.co/XmsBHOwWDM pic.twitter.com/M6os6Kc1y9
— Chris Love – The PWA Guy
(@ChrisLove) April 10, 2018
Why should you use a CDN to host jQuery?
Though not a language, jQuery is a fast and concise free JavaScript library that simplifies HTML document traversing, event handling, animating and Ajax interactions for rapid web development. For faster access and improved performance, web developers use a CDN to host their jQuery library. Using a CDN reduces the jQuery library download time. Visitors in the United States use the U.S. CDN, and those in Europe use a European CDN, which significantly reduces the overall page load time.
The benefits of using a CDN
Having a CDN can positively impact the performance of your website. Here are some of the main benefits.
- It improves the load speed of your website – Visitors tend to leave the websites that take too long to load, and many never return. By making the content available closer to the visitors, the nearby CDN server significantly increases the load speed of your website. As the load speed increases, a CDN helps lower the bounce rates and increases the amount of time people spend on your site.
- It improves SEO – Fast-loading pages allow your website to rank higher in searches, as Google has indicated that site speed is one of the signals its algorithm uses to rank pages
- Increases availability of content and redundancy – Too much traffic and hardware glitches can disrupt normal website functioning. As a distributed system, a CDN can handle large amounts of traffic and can also weather hardware glitches.
- It reduces bandwidth costs – When it comes to website hosting, bandwidth consumption is the primary component that increases your overall cost. CDNs substantially reduces the hosting costs for websites through optimizations and caching, which lowers the amount of data an origin server needs to provide.
- It improves your website security – A CDN can help organizations keep their website safe, as it prevents or mitigates DDoS attacks. A CDN can protect your website by automatically absorbing the load.
Interested in using a CDN? Here are the Best CDN Companies!
As CDNs becomes even more indispensable, an ever-increasing number of companies are entering the market as CDN providers – such as Akamai, Amazon AWS, Cloudflare, Incapsula, StackPath (formerly MaxCDN) and Rackspace
Of course, safe and secure content delivery is also important. eServe is a secure content delivery platform that enables both e-learning leaders and high-tech manufacturers to reduce their risk of revenue loss with the loss of their intellectual property.
With the flexibility to use eServe as either a stand-alone learning platform or an arsenal for all of your intellectual property, businesses of all sizes and types can benefit from the security we provide. Whether you want to share corporate training content with remote teams, travel on mobile devices and stay secure, or send secure product plans or contracts to your partners overseas, eServe can meets your needs. Contact us to learn more.


