 Pierre-Paul Prud'hon, L'enfant au chienLithograph, 1822
Pierre-Paul Prud'hon, L'enfant au chienLithograph, 1822Prud'hon hardly qualifies as a prolific printmaker. He made two etchings, and three authenticated and two attributed lithographs, and that seems to be it. Of the three undoubted original lithographs, I have one, a work of great style and authority. Entitled L'enfant au chien, it depicts the son of Maréchal Gouvion Saint-Cyr, and relates to a painting of the same subject exhibited at the Salon de Paris in 1822. The lithographic stones for this and another lithograph entitled La lecture were acquired in 1864 by M. Galichon for the Gazette des Beaux-Arts, which issued new editions (although possibly the works were never formally editioned prior to this). La lecture was included in the Gazette in 1870; although L'enfant au chien bears a credit to the Gazette as well as to the printer Bertauts, I can't find any record of it actually appearing in the revue. It is not listed in Pierre Sanchez and Xavier Seydoux's thorough and scrupulous catalogue, Les Estampes de la Gazette des Beaux-Arts. If anyone has access to the Gazette for 1869 and 1870, I would be grateful for any enlightenment as to whether L'enfant au chien is in there or not.
 Alfred Taiée, Tombeau de Mlle C. Mayer et de Prud'honEtching, 1879
Alfred Taiée, Tombeau de Mlle C. Mayer et de Prud'honEtching, 1879The date of 1822 is a notable one, because it means this tender study of a boy and his dog was executed while Prud'hon himself was suffering intolerable agony. Prud'hon had married at the age of 19. The marriage was unhappy, although the couple had six children, and his wife was eventually admitted to an insane asylum. From 1803, Prud'hon's intimate partner in both life and art was his ex-pupil Constance Mayer. There's a good post on their relationship here, at The Jade Sphinx. Supposedly, on her deathbed, Mme Prud'hon begged him never to re-marry, and he vowed that he would not. When Constance Mayer heard the news, she went to Prud'hon's studio, picked up his cutthroat razor, and slit her throat. Prud'hon was devastated by Mayer's death, sank into depression, and died himself in 1823. The lovers were buried in the same tomb in Père Lachaise; I have an etching of this by Alfred Taiée.
 Engraving by an unknown hand after a drawing byPierre-Paul Prud'hon of Constance Mayer, c.1805
Engraving by an unknown hand after a drawing byPierre-Paul Prud'hon of Constance Mayer, c.1805The remaining images in this post are etchings after Prud'hon, Mayer, or Prud'hon and Mayer combined. One of the puzzles with Prud'hon is exactly where his work stops and Constance Mayer's starts. He seems to have enjoyed drawing more than painting, and left a good deal of the execution of his large allegorical paintings to her; so much so that some authorities now credit the works to both artists. Constance Mayer was also an artist in her own right, with her own studio and her own pupils, and her work under her own name is certainly very similar to that of Prud'hon.
 Léopold Flameng (1831-1911), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Vénus au bain, ou L'innocence1863
Léopold Flameng (1831-1911), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Vénus au bain, ou L'innocence1863 Adolphe Lalauze (1838-1906), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon and Constance Mayer, L'innocence préfère l'amour à la richesse1876
Adolphe Lalauze (1838-1906), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon and Constance Mayer, L'innocence préfère l'amour à la richesse1876 William Barbotin (1861-1931), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, L'amour et l'innocence1903
William Barbotin (1861-1931), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, L'amour et l'innocence1903 Arthur Mayeur (1871-1919), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Nymphe et amours1903
Arthur Mayeur (1871-1919), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Nymphe et amours1903Prud'hon began to study drawing at the age of 16, at the Académie des Beaux-Arts de Dijon under François Devosge. In 1780 he entered the Royal Academy, then based in the Louvre. Two years after that, he won the a Burgundian three year scholarship to live and study in Rome. The years he then spent in Italy were crucial to his artistic development. According to the J. Paul Getty Museum biography, "his experience in Italy from 1784 to 1787, when he absorbed the softness and sensuality of Correggio's works and Leonardo da Vinci's sfumato, gave his art its distinctive style." His mastery of tonal effects in academic figure drawing has never been equalled.
 Achille Gilbert (1828-1899), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Portrait de Millevoye1880
Achille Gilbert (1828-1899), etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Portrait de Millevoye1880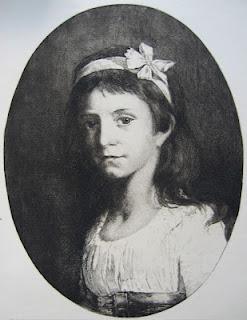 Jules G. Romain, etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Portrait de Mlle Pierre de Vellefrey1907
Jules G. Romain, etching afterPierre-Paul Prud'hon, Portrait de Mlle Pierre de Vellefrey1907There's a good essay on Prud'hon by Fred Stern here, relating to the Prud'hon exhibition at the Metropolitan Museum, New York, in 1998.
 Eugène Gaujean (1850-1900), etching afterConstance Mayer, Le rêve de bonheur1879
Eugène Gaujean (1850-1900), etching afterConstance Mayer, Le rêve de bonheur1879Constance Mayer (full name, Marie-Françoise-Constance Mayer La Martinière) was born in Paris in 1775, seventeen years Prud'hon's junior. Like him, she had a meteoric rise in the art world, first exhibiting at the Paris Salon in 1796. She studied under Joseph-Benoît Suvée and Jean-Baptiste Greuze, and admired Prud'hon's artistic adversary Jacques-Louis David. Why in 1803 she would need to enrol as a pupil with Prud'hon is not immediately apparent, and it seems likely that the status of élève was a convenient mask for their affair, rather than a full master-pupil relationship. It was Constance who suffered from this subterfuge, because it meant that she was always viewed in the shadow of the master. No one knows how many drawings and paintings now attributed to Prud'hon are actually the work of Constance Mayer. Her 1805 painting Vénus et l’Amour endormis caressés et réveillés par les Zéphirs, ou Le sommeil de Vénus, for instance, initially bought by the Empress Josephine, when it passed into the collection of Sir William Wallace, had Mayer's signature removed and replaced by that of Prud'hon. Apart from anything else, a nude by a female artist was not to be thought of. The painting remains in the Wallace Collection, now reattributed to Mayer, though their description still maintains that Prud'hon provided the "initial ideas": i.e. he did the preparatory drawings and Mayer merely painted his design.
 Augustin Mongin (1843-1911), etching afterConstance Mayer, Portrait de Mlle Sophie Lordon1879
Augustin Mongin (1843-1911), etching afterConstance Mayer, Portrait de Mlle Sophie Lordon1879Constance Mayer killed herself in Prud'hon's Paris studio on 26 May 1821. He withered without her, and died of consumption on 16 February 1823.



COMMENTS ( 1 )
posted on 26 September at 03:21
Le efant by Prud'hon original litho can be found in the gazette des beaux arts. December 1869 Vol. 162, Happy Hunting Rafael