At a cybersecurity conference in San Diego, academics from University of Michigan and University of California were able to hack into Gmail accounts with 92% success rate by exploiting a weakness in smartphone shared-memory. The hack was possible because of a vulnerability in the shared-memory which gives them access to number of apps by installing malicious software which can be done by just downloading another app.
The hack involves accessing the shared-memory which is used by the apps to run. The malicious software which exploits this vulnerability could be any harmless app which you could have downloaded from the Play Store.
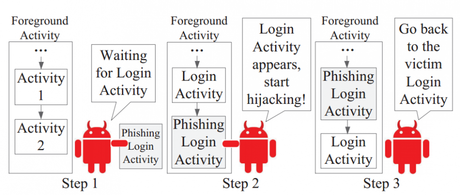
Every app you run used a shared-memory and by analysing its use researchers were able to figure out when a user was logging into apps. Once logged in, they were able to steal account usernames and passwords.
Similarly, they were even able to get access to user’s signature and bank details by exploiting the same shared-memory vulnerability in the Chase Bank App. The Chase Bank apps allows their customers to pay in cheques by taking pictures of their cheques with their device’s camera. When a picture is taken by the Camera App, it is stored in the shared-memory before it is shared and sent to the Chase Bank servers through the app.
“The assumption has always been that these apps can’t interfere with each other easily. We show that assumption is not correct, and one app can in fact significantly impact another and result in harmful consequences for the user.“ said an assistant professor at the University of California and one of the researchers involved in the study.
All the shared-memory vulnerability test were carried out on Android devices but researchers are certain that this might work on other major operating systems which use the same shared-memory mechanism for their window managers. These include the popular Mac OS X, iOS and Windows Operating Systems.
The researchers found out that 6 out of the top 7 popular Android Apps are vulnerable to this attack out of which Amazon was the least affected and Gmail being the most affected App. For all apps except Amazon, the average accuracies for the top 1 candidates are 82.6–92.0%, while the top 2 and top 3 candidates’ ac-curacies exceed 91.4% and 93.6%.
This research paper was presented and submitted by the researchers at the ’23rd USENIX Security Symposium, San Diego, CA, August 2014.
