I pass this on because it seems like a very striking result. Douaud et al. find that high-dose B-vitamin treatment (folic acid 0.8 mg, vitamin B6 20 mg, vitamin B12 0.5 mg) causes a 7-fold decrease in cerebral atrophy of nerve cell areas most vulnerable to the Alzheimer's process over a 2-year period in a group of elderly subjects with increased dementia risk. (For comparison, Centrum Silver 50+ has Folic Acid 0.4 mg, Vitamin B6 3 mg, and Vitamin B12 0.025 mg.) The supplements decrease plasma levels of one of the bad players in the Alzheimer's story, homocysteine. (Homocysteine is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine,and can be recycled into methionine or converted into cysteine with the aid of B-vitamins.) Here's the abstract:
Is it possible to prevent atrophy of key brain regions related to cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease (AD)? One approach is to modify nongenetic risk factors, for instance by lowering elevated plasma homocysteine using B vitamins. In an initial, randomized controlled study on elderly subjects with increased dementia risk (mild cognitive impairment according to 2004 Petersen criteria), we showed that high-dose B-vitamin treatment (folic acid 0.8 mg, vitamin B6 20 mg, vitamin B12 0.5 mg) slowed shrinkage of the whole brain volume over 2 y. Here, we go further by demonstrating that B-vitamin treatment reduces, by as much as seven fold, the cerebral atrophy in those gray matter (GM) regions specifically vulnerable to the AD process, including the medial temporal lobe. In the placebo group, higher homocysteine levels at baseline are associated with faster GM atrophy, but this deleterious effect is largely prevented by B-vitamin treatment. We additionally show that the beneficial effect of B vitamins is confined to participants with high homocysteine (above the median, 11 µmol/L) and that, in these participants, a causal Bayesian network analysis indicates the following chain of events: B vitamins lower homocysteine, which directly leads to a decrease in GM atrophy, thereby slowing cognitive decline. Our results show that B-vitamin supplementation can slow the atrophy of specific brain regions that are a key component of the AD process and that are associated with cognitive decline. Further B-vitamin supplementation trials focusing on elderly subjets with high homocysteine levels are warranted to see if progression to dementia can be prevented.Here is one figure from the paper:
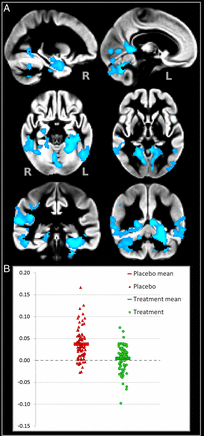
B-vitamin treatment significantly reduces regional loss of gray matter. (A) Brain regions in blue demonstrate where B-vitamin treatment significantly reduces GM loss over the 2-y period. All blue areas correspond to regions of significant loss in placebo and known to be vulnerable in AD. (B) Percentage of GM loss for the 156 participants over the 2-y period, averaged across those brain regions that showed significant effect of B vitamins: placebo group (red triangles) had an average loss of 3.7% (±3.7), whereas the B-vitamin group (green circles) showed a loss of 0.5% (±2.9).

