Osteoarthritis – Diagnosis and treatment
Osteo- means “bone,” and “Arth” refers to “Arthon,” which means joint, and -itis- means “inflammation,” so Osteoarthritis is a disease involving inflammation of the bone and joint cartilage. With Osteoarthritis, we are writing about one particular kind of joint: a synovial joint. The synovium’s composed of loose connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and on the surface, cells that clear cellular debris and cells that produce components of synovial fluid, which helps lubricate the two articular surfaces.
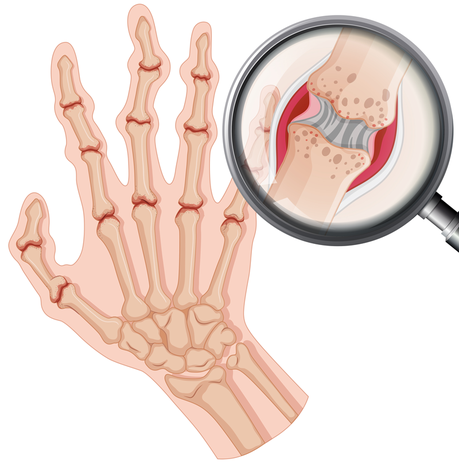
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis or OA is the most common type of arthritis. The disease usually targets the joints of the hands, thighs, knees, legs, and lumbar vertebrae. Sometimes the disease affects the wrists, elbows, and shoulders. Even if this disease does not cause joint deformities such as rheumatoid arthritis in you, it can greatly affect your daily activities. Osteoarthritis affects the cartilage. The disease causes abrasion, wear and tear and, in most cases, can destroy cartilage altogether, and the bone is placed on the bone. The result of this destruction will be a very annoying pain. By age 65, approximately 75% of people have radiographic evidence of Osteoarthritis in their hands, feet, knees, and thighs.
- Causes and risk factors
- Excessive joint activity and repetitive movements
- Obesity and overweight
- age increasing
- Congenital joint abnormalities
- Joint injuries in the past
- Some diseases such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, etc
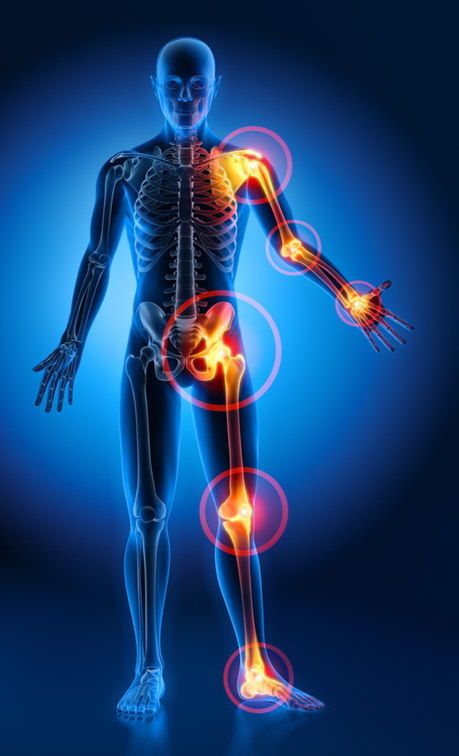
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
- Chronic joint pain
- Decreased range of motion of the joints
- Stiffness and stiffness of the joint involved
- Decreased joint flexibility
- Pain when moving joints
- Joint deformation
- Impairment of normal joint function
- Inflammation and swelling of the joint
- Mild fever
- Hearing a sound from the joint involved when moving
- Weakness and atrophy of the muscles around the affected joint
- Loosening of ligaments
- Limping
It is important to note that in Osteoarthritis, inflammation is not always the first sign, but the person may have some joint damage. It occurs in women around or after menopause. It occurs in men around or after middle age and in athletes and other people who have injuries to their joints. This type of joint involvement is a destructive joint disease (DJD). Early symptoms of Osteoarthritis include persistent or intermittent joint pain, dry joints after waking up, swelling and tenderness in one or more joints, and a tingling or tingling sensation in the joint (caused by rubbing bone on another bone)., Persistent pain during normal activities.
Posture Dysfunction and Flexion Dysfunction Exercises Learn More About Our Naturopathy ServicesTreatment of Osteoarthritis With Medication
Medications used in medicine are usually non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These include ibuprofen, naproxen, and other generic painkillers. Because these drugs are anti-inflammatory, they try to suppress inflammation in the joints, thus reducing pain. Although these drugs remove the cause of the pain from the tissue, they do not target the root cause of the problem. NSAIDs have been shown to act decisively as factors in slowing cartilage growth and repair. This is exactly why natural remedies (exercise and weight loss) and glucosamine supplements are effective in promoting joint health instead of destroying them. Unfortunately, 8 billion dollars is still spent annually on NSAIDs. For this reason, pharmaceutical companies have no desire to stop producing or recommending these drugs. Fortunately, as an informed consumer, you know these things better.
Surgical Treatment
In most cases of Osteoarthritis, surgery may be the only and first way to relieve pain and relieve the symptoms of damaged joints. These surgeries are often very expensive and also have complications and risks. In addition, the joint needs to be replaced again after a few years due to wear and tear. Osteoarthritis is much easier and less expensive to prevent and has no side effects.
Benefits of Glucosamine
Glucosamine has the ability to reduce pain in Osteoarthritis. Also, based on recent studies, experts believe that glucosamine has been useful for the first time in the reconstruction and repair of joint structures. Glucosamine is an over-the-counter (over-the-counter) dietary supplement in pharmacies. The best advantage of this joint supplement is that it is a completely safe, natural, and non-toxic combination. It is now known that glucosamine relieves joint discomfort such as pain and helps improve and repair the joint structure. Some studies have also shown that glucosamine is effective in regenerating a cartilage tissue.
What Is Glucose Amine?
Glucosamine is an amino sugar essential for connective tissue structure and cartilage tissue health. This substance is the main basis for making proteoglycans and other cartilage tissue preservatives. It is a vital building block for proteoglycans and other intra-articular compounds. Proteoglycans are large protein molecules that act as sponges in water retention and have elastic and cushion-like properties in connective tissue. These compounds also play a mediating role in protecting the joint against excessive wear and tear. Without glucosamine, tendons, ligaments, skin and nail tissues, bones, mucous membranes, and other body tissues cannot form properly.
Naturally, sufficient amounts of glucosamine are produced in our body to form the various compounds needed to build connective tissue and muscle health. But gradually, its production and destructive changes in our body increase with exercise, injuries, burns, arthritis and other inflammatory disorders, aging, and chronic destruction. In this condition, our body may not be able to meet the body’s needs for this essential substance, which reduces the amount of proteoglycan production in the body. This can also reduce the number of lubricants and joint protectors such as synovial fluid (intra-articular fluid) that act as a cushion and absorb pressure in our joints and protect them from damage. We generally need a lot of glucosamine. But we make a small amount of it.
Other Treatments For Osteoarthritis
Other practical methods for treating this disease are:
- Resting the affected joint and reducing the amount of activity with the joint is recommended in the first step to all patients with this complication, but the activity and mobility of the joint should not be reduced to zero, as this will intensify the dryness and stiffness of the joint.
- Warming the joint with hot compresses is also effective in reducing joint pain and inflammation.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, and others can be prescribed by a doctor.
- In severe pain, your doctor may suggest injecting steroids into the joint space.
- Physiotherapy is the most effective treatment for Osteoarthritis and its complications that you can use by visiting a physiotherapy clinic or doing physiotherapy at home under the supervision of a physiotherapist who graduated from the University of Rehabilitation Sciences.
If non-invasive methods cannot help reduce the patient’s symptoms and treat Osteoarthritis, surgery is the last resort. Joint replacement surgery is one of the most common types of surgery in the treatment of Osteoarthritis, which is performed by replacing a damaged joint with an artificial joint. After surgery, physiotherapy in a physiotherapy clinic or physiotherapy at home is also essential.) (Depending on their diagnosis, the physiotherapist may use other modalities such as electrotherapy, laser therapy, manual therapy, and so on.

