Arrays hold values.
An array is an ordered list of values.
Arrays are 0-based, in that the first value is 0, not 1 in terms of its position.
A JavaScript array has the following characteristics:
- First, an array can hold values of mixed types. For example, you can have an array that stores elements with the types number, string, boolean, and null.
- Second, the size of an array is dynamic and auto-growing. In other words, you don’t need to specify the array size up front.
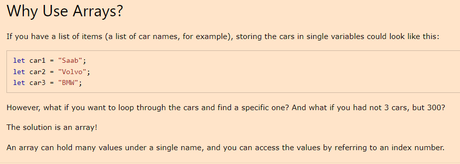
W3schools describes an array as a “special variable, which can hold more than one value”.
An array can hold many values under a single name, and you can access the values by referring to an index number.
Creating & Fetching JavaScript arrays
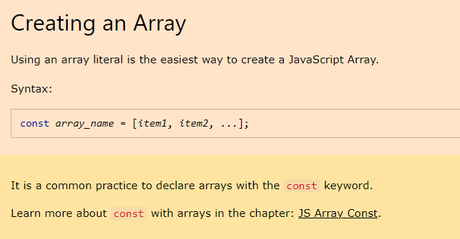
JavaScript provides you with two ways to create an array.
It is a common practice to declare arrays with the const keyword.
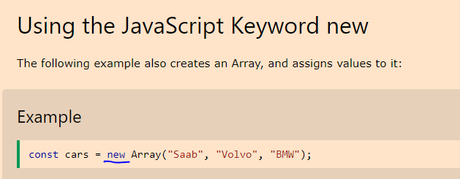
You can also use the following code to create a new array:
let values = new Array();
or
let values = [item1,item2,...]
Once you’ve created your array, you can print the values to the console.log with the code:
console.log(values);
With “values” being the name of the array.
You can call “values.length” to get the length of the array
console.log(values.length);
Again, in the above code “values” is the name of the array.
You can define and name an array, and then “push” values into it later:
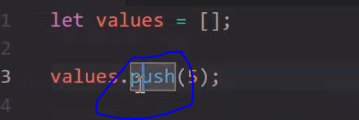
The above code will add a single value of 5 to the array named “values”.
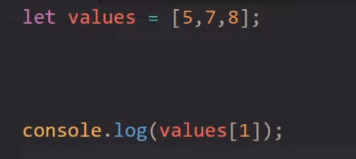
console.log(values[1]); will print the second value – 7
console.log(values[0]); will print the first value – 5
In summary – to create an array, it’s generally best to use the “const” keyword, or the “new” keyword.
Adding & Changing Stuff Within Arrays
Below, the array name is used,and the variable number to update, the first variable.
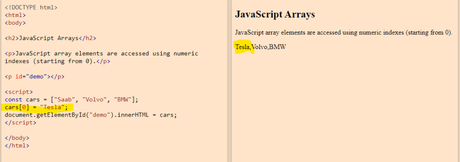
You can try it yourself on the w3 schools website.
Accessing Arrays
You access an array element by referring to the index number:


