
The Finance sector is currently undergoing a transformation that is making traditional banking processes obsolete. Advances in technology, such as application programming interfaces (APIs), cloud computing, smartphones, digital currencies, and blockchain technology, are disrupting the traditional banking systems of previous generations.
There is no shortage of factors that influence and disrupt the finance sector. New technologies like Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), API and cloud computing are revolutionizing the way financial institutions and intermediaries do business. New graduates and investors looking to stay at the forefront of the ongoing FinTech advancement should look to ramp up their skills. When it comes to understanding the intricacies surrounding the finance sector, Fintech Courses like Harvard’s VPAL FinTech online short course helps students and professionals alike. Find out how you can take your knowledge and skill set to the next level. Want to learn more? Click here.
According to the World Bank, as of 2021, 76% of adults now have an account at a bank, other financial institution, or with a mobile money provider, up from 68% in 2017 and 51% in 2011.
Digital disruptors in the finance sector are influenced by factors both on the supply side, through technological innovation, and on the demand side, reflected in the expectations of younger consumers. Traditional banks and financial institutions will continue to face greater competition in their core businesses, such as payment and advisory services, from other financial intermediaries as the consumer moves increasingly digital. A change in technology and in developing new services and business models has been unfolding, and we highlight a few areas with the largest impact below.
Contents
- 1 Online & Mobile Banking
- 2 AI & Machine Learning
- 3 APIs & Cloud Computing
- 4 Blockchain and Digital Currencies
Online & Mobile Banking
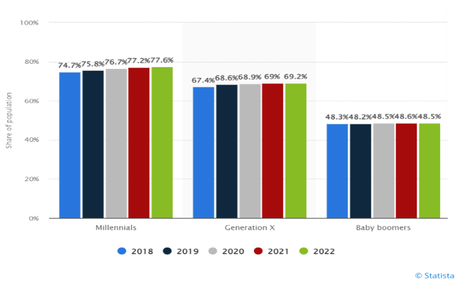
One of the most prominent examples of FinTech innovation is the adoption of online banking and payment services by younger generations. The chart above, published by the Statista Research Department in 2022, highlights growth and adoption between the Baby Boomer generation and Millennials from 2018 to present.
With greater access to smartphones and mobile devices, online banking has become indispensable in consumers’ daily lives. The expanded availability of financial services through mobile applications has provided consumers with multiple functions, including payments (i.e. digital wallets), money transfers, and online shopping. Venmo, WePay, Zelle, and PayPal are just a few well-known names globally, allowing easy access to money services without ever having to step into a traditional bank.
This push away from brick and mortar storefronts was exacerbated by COVID-19, as lockdowns forced individuals to use contactless technology to keep businesses running. According to S&P Global Market Intelligence data, banks closed a record 3,324 branches nationwide in 2020. With less foot traffic into branches, these traditional institutions are finding new creative ways to keep and bring in new consumers.
AI & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are continuing to advance the information processing of both hard information, verifiable and modifiable, and soft information, based on relationship banking, into tools and data that institutions use to tailor new solutions and services to their customers. With more transactions and payment services taking place through online and mobile platforms, these financial institutions and their tools can capture even greater data.
A great example of this is credit card monitoring for fraudulent activity. Institutions like AMEX, Visa, and MasterCard track your purchases, frequency, locations in real-time, and can take proactive steps to stop or block fraudulent activity as it occurs. While this type of monitoring is not new to the industry, AI and ML allow for reduced employee costs, as technology drives the monitoring of transactions. It also allows these firms to collect your spending data, and share (or sell) to other institutions to better tailor additional services and make more pointed advertisements.
Machine Learning has also opened the door for ‘Robo-advisors’, or computer programs, that allow for quicker financial recommendations and automated financial services servicing such as policy updates based on mathematical rules or algorithms like the Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT). The end goal of these FinTech solutions is always to reduce costs and improve customer experiences. Firms can then put that saved capital back to work on providing better services, promotions, and tailored offerings more specific to the consumer’s needs.
APIs & Cloud Computing
APIs are improving services, allowing payments to process faster, and making it easier for fiduciaries to unbundle services. Becoming the standard, APIs are allowing data sharing in open-sourced banking applications. Such applications allow third-party access to consumers’ bank data (with the consent of consumers) and are becoming a fundamental tool of digital disruption. They enable software applications to share data and functionality and represent a remedy for markets with high switching costs, as they help consumers compare product and service offers.
While cloud computing refers to the practice of using a network of remote servers, typically accessed over the internet, for IT services, storage and sharing of data. The cost-effectiveness and flexibility of using cloud infrastructure along with artificial intelligence is providing an advantage to financial intermediaries. Allowing them to provide improved customer relationships, accounting processes, tracking credit scores and offering promotions or advertisements that are more closely tailored to the client’s needs and spending habits.
Blockchain and Digital Currencies
Blockchain technology is another disrupter that enhances the effects of new companies in the traditional finance sector. Through a decentralized consensus, blockchain is helping to provide cost-saving innovations and give consumers more control over their data. By utilizing smart contracts, i.e. programs stored on a blockchain that run when predetermined conditions are met, this can help automate the execution of an agreement so that all participants can be immediately certain of the outcome. This allows the removal of intermediary involvement, reduces potential conflicts of interest, costs, and speeds up the agreement process. This fact exacerbates this disruptive impact that traditional banks have specialized in intermediation activities for decades.
The technology capabilities that come from blockchain also allow better auditing and control over users’ data. Through private and public keys, owners can control what third parties are allowed to access, and help remove the misuse of clients’ data. If personal data is stored on a blockchain, owners can control when and how a third party can access it.
