Basically, Google works using robots (known as Googlebot, crawler or spider), which go from link to link identifying the pages on the internet, classifying and indexing on their servers. Whenever the search is performed on Google, its algorithm organizes the results to prioritize the best (and most relevant) content.
Instead of reading, how about listening to the article? Try it on the player below:
One of the first steps to succeed with Digital Marketing is to understand basically how Google works, in relation to indexing and displaying websites.
Before even working with SEO (that is, optimizing a website for the search engine), it is necessary to find out how Google works and how it presents its search results.
Currently, Google users perform more than 3.5 billion searches every day. The number of sites indexed by the search engine since its foundation, in 1998, has already exceeded 60 trillion.
With so many exorbitant numbers, how can your company stand out? How to be on the first page of the search engine among so many competitors?
eBook The Complete SEO Guide
Everything you need to know to stay on the first page of Google and attract more qualified visitors

Searches are divided into 2 types of results on the SERP (Search Engine Results Page):
1 – Paid results
They are those that appear in the search through ads produced via Google Ads and are located above and below the organic results.
They are classified, differently from organic, through CPC (Cost Per Click) bidding, ad quality score, and other factors.
To learn how to create effective ads, you can read our eBook on the topic .
2 – Organic results (free)
These are those that Google ranks according to its search algorithm and lists which sites are most relevant and suitable for your search. There is no cost here for the website owner.
They are located in the center, among the paid results.
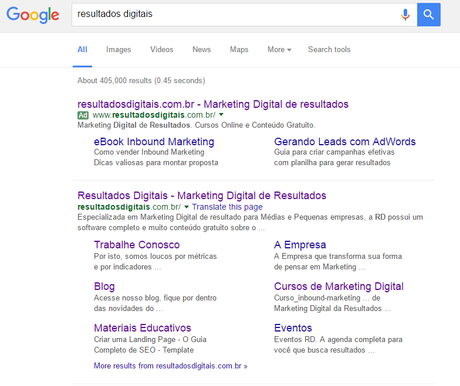
Example of search with paid (above) and organic (below) results.
How Google's algorithm works
Let's imagine that you entered a large library looking for a book on "Digital Marketing". In this place there are thousands of subjects, themes and the most diverse authors at your disposal. At this point you follow the following steps:
- Limits the theme related to the subject
- Observe the title, subtitle, cover, index, table of contents and a little bit of content
- Identifies the best works and most recognized authors
- Remember the nominations we've already received
- Sorts the best according to relevance
- Choose one or more books after this selection
In the case of Google, the objective is really: choose the pages that define the theme well and rank according to relevance. What changes is the qualification process for choosing the results.
Understanding how Google search works
Google has a system of "crawlers" to discover the available public pages. Basically it goes from link to link and just doesn't crawl pages that contain the code “nofollow” or “noindex”, an indication that those pages should not be found.
The most well-known crawler is called "Googlebot". These robots scour the pages and read all the content available there, going to the most diverse addresses and bringing data about these pages to Google's servers.
Another way for Google to discover content is with the company that owns the site creating a sitemap – a list of all the pages on your site that is sent to search engines, making indexing easier.
Information, searches and indexing
The crawl process begins with a list of sites that have gone through previous crawls and sitemaps provided by the sites. When visiting these addresses, crawlers look for links to other pages and visit them. Google pays special attention to indexing new sites, changes to existing sites and inactive links. Thus, it keeps the database updated.
Robots determine which sites to crawl, how often and how many pages to search on each site. It is not possible to pay Google for your site to be crawled more often or to gain organic benefits in search results. The main objective of the search engine is to identify the best possible results to offer the best user experience.
When Google finds a page, it makes a kind of copy on your server. This means that the page has been indexed, that is, it is on the Google list and can appear as a result of searches if Google so wishes.
How indexing and organizing information works
After Google inserts all of these pages in its library, the most sophisticated part of the tool enters, which is to evaluate, among more than 200 different signals, which is the one that will best serve the user.
When you do a search on Google, the algorithm is able to process in milliseconds an analysis of several criteria trying to understand which pages of the index are ideal to meet the search terms (keywords).
The first most evident point, therefore, is whether there is in fact a correlation between the page and what the user searched for. With that we fall on the first pillar: content
1st Pillar – Content
Within a page, there are some “noble spaces”. Just as the cover of a book says a lot about the subject of the book, there are elements like the title of a page, for example, that are very strong indicators of the correlation with the subject.
It is these specific parts of a page that have greater weight in the search and deserve special attention.
Working with them means having a greater chance of Google considering it a good result for a desired search.
- Title (Page Title) – It is the most important element of the page in the eyes of Google. It is the text that appears on the browser tab.
- Headings – These are markings in the code that indicate the page's subtitles and their hierarchies. The markings range from H1 (most important) to H6.
- Texts – It is the content of the website. The appearance of the keyword and synonyms throughout the content is quite relevant.
- URL – It is the web address of the link – Always optimize Ex: www.site.com/keywords
- Alt attribute – It is the text that appears if the image is not displayed and what Google uses to “understand” what is in the image.
All of the above topics are compared with the words searched, thus seeking to recognize some relationship.
Google also tries to look at other items, such as the context in which the page is displayed. For example, an ecommerce site that has a page that sells balls benefits and gains correlation when a sports website that talks about different ball models links the page in the article.
2nd Pillar – Website authority and user experience
It is common for Google to find several pages with good signs that answer the user's question. Then comes the second challenge: which one is the best?
Google needs to understand how relevant each page is in order to be able to order them and the main parameter for this is the number of times the page and the website as a whole are referred by third parties.
On the internet this takes the form of incoming links, which act almost like votes. The more links and more authoritative sites a page has, the more likely it is to reach Google's top positions.
Within the website itself you can also understand whether your company considers the page important or not. If it is many clicks away from the home, for example, Google may take it as an indication that it may not be that relevant.
There are also other items that denote that the user had a good experience: page loading speed, the fact that the visitor returns or not to Google after entering the page (if he returns it is because he did not find what he was looking for – bad experience).
Currently, there are also Google tools that help to analyze the performance of your site. An example is PageSpeed Tools , which optimizes the site according to best practices for the web.
Conclusion
What we've talked about so far is just the beginning of the road in relation to Google and SEO. It is important to be aware of all these ranking factors in order to position yourself well on Google, but the main factor that surrounds all these strategies is still quality content.
Produce unique and relevant information for your audience, even if you are not among the first, this content can create great engagement, generate visits and make you get excellent results.
Now that you know how Google works, it's time to learn how to turn Google into a traffic machine for your company's website. Download the free eBook “The Complete SEO Guide” and find out!
Post originally published in June 2016 and updated in April 2020
Labels:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
