There are some minor devils in the detail; but overall this paper is a nice concrete tutorial on how to develop information spaces, how to test them empirically and how to evaluate the results that come out. The overall process will benefit from committing more fully to a mechanistic, real-parts criterion but otherwise shows real promise.
Figure 1. The not-at-all-dodgy-looking set up
for dynamic touch
Dynamic Touch
The experimental task is to wield or swing rods that vary in their length. You hold the objects out of view by a common handle and try to judge the length just by moving the object. The judgements were made by having the participant move a marker on a ruler in front of them out to where they thought the end of the rod was (see Figure 1).Information Space for Dynamic Touch
Previous research has shown that two variables can account for over 90% of the variance in judgements; the 1st and 3rd moments of inertia. Michaels et al combined these into a single higher order relation with the equation E(b,c) = b ln(I1) + c ln(I3) Using logarithms allowed them to use multiple regression to estimate b and c, but otherwise there's no specific justification for proposing this particular higher order information space.This function has a single peak at a specifying combination and you can generate a gradient towards that peak to drive learning. Note that again, at this point, there is no independent evidence that this entire information space and information for learning (now referred to as convergence information) can be embodied in the dynamic touch energy array.
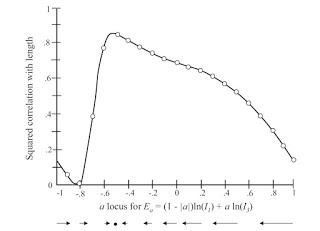
Figure 2. The information space (a) and information for learning vector
field for the hypothesised information variable E(b,c) = b ln(I1) + c ln(I3)Pilot testing revealed people were already too good at the task, leaving little room for learning. Michaels et al then did a nice trick, in which they first gave false feedback based solely on a=0 to move them away from the peak, and then gave correct feedback. There were 7 blocks; baseline (no feedback), 2 training blocks with a=0, a post-training/new baseline block, 2 blocks of correct feedback, and a final post training assessment.Results
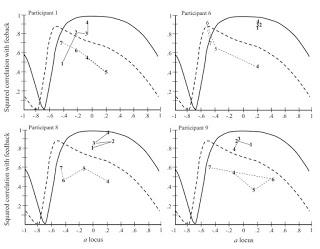
Figure 3. Individual data from 4/9 participants. The solid lines are data from the a=0 blocks; the dotted lines from the correct feedback blocks. Note performance in Block 4 is evaluated twice; once with respect to the a=0 variable as post-training and once with respect to the correct answer as a new baseline.
On average the information space analysis did a good job accounting for how people's performance changed over blocks. People first began tuning into a=0 as information then switched towards the better variable with the correct feedback. This double step training is a nice trick for this kind of work.The authors note a few conclusions
- The chosen information space was appropriate because performance never went above the maximum level of performance that variable could support at various places in the space. That's an important diagnostic check on your space.
- Different participants at different points in time seemed to be living in quite a wide range of places in the space, supporting treating this space as continuous. Recall, though, from my last post, that I suspect this might be an artefact of the analysis and that behavior that looks continuous might reflect various levels of ability to discriminate and use discrete variables.
- There was a high correlation between the trajectory of learning and the form of the information-for-learning, convergence information vector field. The authors argue this supports the hypothesis that information for learning exists and is used as they propose.
Assessment
The Information Space
First, the authors combine the two most useful discrete variables identified in past work (the 1st and 3rd moments of inertia) into a single dimensional higher order combination expressed by the equation above. This works out ok (the data behave themselves as described above) but to my mind (and to Michaels et al) this still begs the question of whether this higher order relation exists in the dynamic touch array. That remains an important question that requires independent evidence.Convergence Information
Second, the individual learning trajectories were not all always following the convergence information vector field, although overall and on average the correlations between learning and the field were high. The individual level is important here, though; people don't perceive and act on average. In the General Discussion, the authors do work through an analysis on a candidate convergence information variable, although they do not commit themselves to this being the actual information. Convergence information must be detectable, and it should specify how to change variable use. The latter means the information is defined over time (here over multiple trials); you need at least two points to get a direction in the information space. The authors propose that the relation between the error feedback and the mass of the rods being wielded and show it produces the right kind of vector field. But the correlation of this variable to performance is merely 0.396; significant, but hardly specification. They conclude their candidate is not the right variable.While the tutorial on proposing and evaluating a candidate convergence variable is good, the fact their sensible swing doesn't work is interesting. First, it shows that even though the error-mass relation produces an appropriate vector field, there's no reason to think this relation is specified, i.e. it's not obviously a real part. Because this analysis is not moored to a mechanistic mindset, it can easily produce false starts. That said, they show how to check it, and that is excellent.Other Learning Processes
They then discuss alternative learning processes; trial and error, and gradient descent. I still suspect that something like this is going on, and they haven't ruled it out yet. This would be the idea that instead of learning being driven by a continuously specified convergence information vector field, errors would drive people to bounce around the region of the information space at random and try to figure out which direction reduces the error best. This didn't best explain performance in the current study, although that analysis compared the gradient error to their candidate convergence information variable which didn't seem to be working anyway.They also note that their account might easily get recast into a cue-combination story, which reinforces my concern that their information spaces are just this. Cue combination lets you combine the variables any way you like because the combination happens in the head; for ecological types, the higher order relation between variables must be specified in an array in order to be used.