Operations performed on the blockchain, such as smart contracts, are automatically verified by the participants of the decentralized network within this blockchain. The benefit comes from trusting only the network and not individual third parties because that’s what blockchains were designed to do. Nevertheless, there are times when data from outside is needed to be provided by third parties. But blockchains themselves cannot access data outside their network. So how can real-world data get into the blockchain?
To solve this problem so-called blockchain oracles were created. Smart contracts basically can only refer to manually generated events in a blockchain. And as usual, they describe nothing than sequences of events: “If condition A has occurred, operation B is carried out”.
But to check condition A, sometimes we need the data, which often comes from the real world. However, in order to provide information from the real world, sensors must be connected to the blockchain. These sensors are sources of real-world information called oracles.
As a simplified example of a blockchain oracle use case, imagine an insurance company that implements insurance policies through a smart contract that pays out compensation when certain wind speeds occur. In such a scenario, the customer would not have to inform the insurance company about the damage. Everything would be fully automated and verified in the background, and the customer would be paid without any further interaction. But then, a blockchain oracle is needed to provide reliable information about wind speed.
How Does A Blockchain Oracle Work?
To be able to use external data in blockchains, the data needs to be validated first. Because even if an oracle can provide the data for the blockchain, it cannot verify it. It just wasn’t designed for that. This, of course, leads to a fundamental security problem with oracles as it cannot be guaranteed that the data is not manipulated. This is due to the fact that oracles involve accessing data from external parties. Therefore, this data is not trustworthy per se, which in turn contradicts the basic principle of blockchain. So what to do in this case?
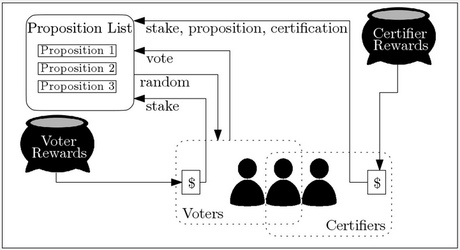
In order to address this problem, the so-called Astraea protocol was developed which is considered the pioneer of blockchain oracles. Astraea is a general-purpose decentralized oracle (a blockchain application) to determine the authenticity or falsity of data.
This happens in a voting-based interaction between participating blockchain users. These can either “play” the role of the voter or the verifier to determine the authenticity or falsity of the data. The main purpose of this procedure is to ensure the protection against manipulation of the external data and thus, the protection against manipulation of the entire blockchain. In return, the participants get rewards for checking the data. That’s how oracles basically work. However, they still have to be integrated into smart contracts.
Integration Of Oracles Into Smart Contracts
Oracles are added to the blockchain by so-called multi-signature contracts. That’s why these types of smart contracts are also just called “multisigs”. These smart contracts are signed by multiple parties. And they must be defined accordingly, for example, by declaring that person A wants to process data exchange with person B, and this should only be possible if certain conditions are met.
These conditions are then supplied by data from the oracle. Even if persons A and B want to execute the smart contract “manually” it wouldn’t work. Instead, it could only be executed when the condition is fulfilled that can be checked against the oracle data.
5 Types Of Blockchain Oracles
- Software Oracles: These relate to data that are available online, such as temperatures, flight delay data, etc.
- Hardware Oracles: These refer to data processed directly from the real, physical world. An example of this is data coming from supply chains.
- Inbound Oracles: These oracles provide a smart contract with information from the outside world. An example could be an automated buy order as soon as a certain currency rate is reached.
- Outbound oracles: This enables smart contracts to send data from the blockchain to the outside instead of just receiving it. This is necessary, for example, if a payment has to be made on the blockchain.
- Consensus-Based Oracles: It is a combination of several oracles. The various oracles build a consensus to make decisions are written down in the blockchain protocol. For example, a rule can be defined that at least three of five oracles must agree for an operation to be carried out.
Blockchain Oracle Projects
As mentioned, the Astraea Oracle is considered a pioneer of such applications. Since then, there have been various developments, like the three following projects:
Chainlink: Probably The Most Well-Known Blockchain Oracle
Chainlink was developed in 2017. Therefore, this project is, together with Astraea, one of the pioneers of blockchain oracles. Chainlink’s purpose is to retrieve aggregated information from different oracles through a marketplace.
Chainlink works with the rule that only registered oracles can provide data into a blockchain. Therefore, it is a participant-restricted (“permissioned”) protocol.
Because of that, Chainlink is a kind of multiple “chain” oracle network that provides tamper-proof inputs and outputs for smart contracts. The smart contracts of this oracle network are connected to a range of real data such as asset prices, price feeds, weather data, etc.
API3-Protocol
API3 is a DAO-driven oracle project. DAO stands for Decentralized Autonomous Organization, meaning an organization encoded by a transparent computer program. Records and program rules of a DAO are based on distributed ledger technology.
What API3 does is create APIs for decentralized applications (dAPI). The applications are widely available and can be built by combining multiple operators and running oracle nodes without an intermediary. For this purpose, decentralized APIs provide data for blockchain projects and dApps with quantifiable and trusted security guarantees.
What is the difference from other blockchain oracles? Oracle projects usually aim to provide an interface between any two systems. The API3 project does not focus on the interface itself but tries to solve the problem of the so-called API connectivity, also known as the “oracle problem”.
What is the API connectivity problem? As mentioned, a blockchain cannot access external data, and oracles supply and verify the data. But in the end, this data still has to be injected into the blockchain. Hence, there has to be something, that takes the verified data and puts it into the blockchain using a smart contract. And that is exactly what AP3 is trying to solve. But what may sound easy is actually one of the biggest obstacles and challenges when it comes to the injection of external data into the blockchain.
DIA: Decentralized Information Platform
DIA, short for Decentralized Information Asset, is an open-source oracle platform that enables participants to source, deploy, and share trusted data.
DIA is a non-profit project that provides access to financial data verified by blockchain users. The aim of the project is to build a fair, symmetrical financial ecosystem by providing transparent, secure and verified market data. The project also aims to solve the problem of data reliability, which is what Astraea and Chainlink projects are trying to do, too.
However, the DIA project takes a different approach. The goal of building a financial ecosystem is supposed to work like a kind of Wikipedia. DIA itself does not generate any data, nor does it manage it. Instead, anyone can participate in the ecosystem through DIA, and provide data or check its quality. In return, participants receive rewards in the form of DIA tokens.
Conclusion
One of the characteristics of a blockchain is that it cannot interact with the real world. This problem can also be compared to a computer that is not connected to the Internet.
Blockchain oracles are becoming increasingly important and well-known for providing data from the external world for the blockchain, validating it, and injecting it into the blockchain. More and more crypto companies are investing in this infrastructure to feed decentralized applications with real-world data.
The goal of the blockchain oracle is to link the digital, decentralized blockchain world with the data and information of the real world.
It can be assumed that blockchain oracles will continue to gain importance, and the market for oracle-based tokens should continue to grow. But as always, this technology and the concept are still in their infancy, and it remains to be seen which one will be successful in the market.
Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work. The subscription will be proceeded via substack.com. There, you can subscribe for free content but also for premium content. Just check it out by clicking the button below! If you would like to publish content on substack, please click here.
SUBSCRIBE TO A NEWSLETTER