As the world's population steadily becomes larger, it is clear that the urban areas are the ones that are going through and will have to go through many more transformations. Not only does half of the Earth's population live in urban areas today, but it is estimated that this percentage will rise to 60% by the year 2050. The amount of people living in these megalopolises puts an enormous strain on the environment and resources. Governance and technology are also subjected to this growing strain.
Let us paint the picture for you with this example:If the entire population of our planet, for instance, gets moved to the Republic of South Africa, the population density would still be significantly lower than it is in Tokyo today.
This is why scientists and politicians started to devise plans about transforming urban areas into smart cities. We are talking about the most crucial areas related to everyday lives of people living in the cities. These are traffic, parking, railway system, infrastructure, water, food and other supplies. Managing all of these became increasingly difficult due to the increasing number of people living in the cities.
ButWhat is Internet of Things and how can it help with city management?
Can it improve the quality of life while protecting the environment and help in efficiently handling the city's resources?
Briefly about what is IoT
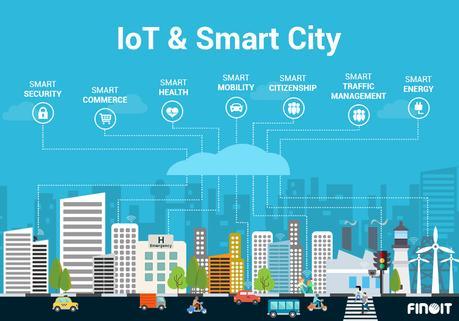
What comprises a smart city
What's the role of Internet of Things in smart cities
Smart city's segments such as Smart Traffic, Smart Rail, Smart Infrastructure, Smart Water and other
How these work and their impact as a whole
Lastly, the challenges associated with Internet of Things for Smart Cities.
Internet of Things stands for this massive ecosystem of sensors and devices connected over one network. The value Internet of Things provides is hidden in all of the data that gets collected on this network. Interpreting this data gives important insights on all of the crucial aspects of life in the city. This data has to be used to bring improvements in all of the aspects we have discussed above.
And this is exactly where the problem lies. Cities need to have an infrastructure that supports Internet of Things, along with custom made software that will store and analyze the copious amounts of data collected through sensors and various devices. We will come back to the challenges of implementing Internet of Things for smart cities a little bit later.
The Best Example and Role Model?
In the world as we know it, there is one city that is a bit smarter than the other smart cities. It is one of the top world finance centers - Singapore. This, city-state is truly state of art when it comes to Internet of Things. Since there are dozens of IoT implementations throughout the city, many consider the people living in Singapore to be the world's first Smart Nation.
There are millions of sensors and devices communicating in the IoT network of Singapore. These sensors are provided by the non-governmental companies, and the amount of data collected via these sensors is huge. It is so big that Singapore authorities had to get custom built software that would collect and interpret it. This program is called Virtual Singapore, and through the interface of this program the authorities of Singapore successfully manage the city.
Currently, IoT is implemented in parking systems and monitoring, efficient lighting, and the garbage collection and disposal system. They have even implemented IoT in the elder care facilities. This segment of IoT is on a voluntary basis. People who use it will get notified if their significant other stops moving for too long. The new IoT system named "Telehealth" allows patients to have a face-to-face conversation with their doctor without the need to leave their homes.
In one the many interviews, Chan Cheow Hoe, Singapore's chief information officer, stressed how important IoT is for the Singapore authorities. They have recognized the benefits of IoT and how building a smart city not only helps the environment and saves resources, but also significantly increases the quality of life. This is why Singapore authorities have adopted a strategy called Smart National Platform.
He also stated that implementing Internet of Things in transportation brought many benefits. Especially because Singapore is an island nation and building new infrastructures is out of the question. Optimizing the use of the current infrastructure is a far better and cheaper solution than building a new one. And, according to him, Internet of Things is what makes this possible.
Since Singapore has high temperatures over longer periods of time during the year, IoT helps by increasing power savings. Many buildings in this city are now armed with sensors that track temperature and occupancy, and turn the air conditioning systems on or off according to these values.
What comprises a smart city and what's the role of Internet of Things
In order to get the full insight of how IoT can transform urban areas and life as we know it, we have divided the IoT implementation into following areas that comprise a smart city.
Smart TrafficOver the last few decades, we have developed a strong car culture, which means that no matter how good public transportation is, in most of the world's largest cities, people will always prefer driving their own cars to work. For instance, in the US only, commuters have lost $124 billion in 2013 due to the value of time wasted in traffic and the cost of fuel.
This inevitably results in high traffic during the peak hours of the day. With high traffic, there is also a high chance for a traffic jam to occur. This can be resolved by IoT implementation. Making the city's traffic smart by installing tracking sensors and cameras on major intersections throughout the city can benefit the traffic system in many different ways.
For instance, communication equipment, such as ANPR cameras, detectors with Bluetooth technology and CCTV feeds that transmit vehicle related data to city traffic management centers can be used to prevent traffic bottlenecks from occurring. This is done by prioritising traffic and smoothing it out with traffic lights that respond in real time. This response gets custom-tailored depending on traffic load.
One of the main sources of air pollution in cities are cars. The majority of polluting gas gets emitted during the stop-start driving that happens in spots where traffic is regulated by lights. By making traffic smart, you can also reduce the pollution throughout the entire city.
Smart traffic can also be used to smooth out the public transportation traffic during rush hours. This has to be done because buses take up much of the space and are significantly slower than cars. Smart traffic can ensure that every bus gets through the "green wave" thus significantly improving the traffic flow.
With IoT powered traffic management systems, the response time to traffic incidents becomes much shorter. With this system in place, all of the data is being gathered and analysed in real time, which allows the system to make real time adjustments to traffic regulation via traffic lights.
Smart RailSmart rails are also one of the many possibilities offered to us by the Internet of Things movement. The idea behind the smart rails is to take the load of the road traffic, ensure that commuters get to work on time, prevent pollution from greenhouse gasses, and increase the safety of the passengers. Smart rail also affects the traffic in the metropolitan area of the megalopolises by making the transition from rail transportation to buses and other transportation means more synchronized.
This is done by analysing all of the data collected via numerous sensors and cameras installed on the railway stations along the way. This data is predominantly used to identify and analyse the commuting patterns.
This data is then used for real time adjustments to the train schedule. The system can, for instance, increase the frequency of railway transportation during identified rush hours, while decreasing them during the hours when there are significantly less passengers on the train.
Furthermore, by comparing the data received by the system handling the traffic lights and bus schedule, smart rail management system can adjust the schedule so that passengers arrive in time to make a smooth transition to a bus.
Smart rail management system also takes care of safety measures. By installing the latest safety measures, such as warning signs and gates at rail crossings, fencing and other signs and integrating all the sensors attached to them into one system, the safety is brought to an entirely new level. Synchronizing data from rail and car traffic also empowers the system to calculate for how long the gates at the rail crossings should be kept closed. This significantly improves the traffic flow during rush hours.
Also, a computerized system keeps track of all the trains' locations at all times, preventing any collisions from occurring. Smart rails in cities and those that connect cities have the potential to prevent traffic jams, increase the flow of traffic, and to significantly reduce the pollution in urban areas.
Smart InfrastructureA city's infrastructure is another area where IoT can be implemented. This is all possible due to the development of technologies and digital abundance. Thanks to these technologies, such as AI, 3D printing, robotics, and small reliable sensors, infrastructure can be delivered, managed and automatically controlled in a completely different way.
This unique way of applying digital infrastructure composed of Machine Learning, Big Data, Sensors, IoT, Networks etc. to physical infrastructure allows the systems in place to provide an accurate real time information feed. Faster, cheaper and better decision making can then be used in areas of physical infrastructure.
When we talk about physical city infrastructure, we are referring to transport, energy, water, telecommunications, and waste. And we already have examples of Internet of Things implementations in the real world, making each of these aspects smart. At the beginning of the article, we have mentioned Singapore as a world leader when it comes to smart technology implementation.
In this city, for instance, there are sensors installed into waste containers which inform the garbage collection and disposal center on the capacity status of each waste disposal unit across the town. This eliminates the need for regular and on schedule waste collection trips across the town, thus lowering the expenses, air pollution and removing strain from the traffic.
IoT can cut down electricity expenses for the city too. In one Dutch city, Eindhoven, authorities have installed LED bulbs and connected the lighting system with software which uses data gathered by sensors on the streets of this town. The system now turns off lighting on the streets that are not busy, thus significantly reducing the energy costs for the city.
Other smart city initiatives include implementation of smart cooling systems, smart windows and other smart infrastructure perks that increase the efficiency of using current technologies. Let's not forget the benefits of having a free-flowing Wi-Fi ecosystem throughout the entire urban area. All these IoT implementations help citizens, industries and the environment to thrive.
Smart Water and OtherBy now, you can probably guess that IoT can also be used for water management, as well as for the gas and electric utilities. The devices that allows this implementation are called smart meters. When cities attach these devices to their smart system, every company that supplies energy to buildings can do this in a more efficient manner.
Big cities put enormous strain on water supplies. This is why it has become very important to conserve water. IoT helps in water conservation by allowing water utility companies to use sensors that track water consumption, pressure, temperature and quality. Companies and citizens have a direct insight into the values such as average water consumption per household and the ability to compare it to their current one.
On top of that, water leak detectors are also gaining in popularity, since they both prevent serious water damage to households, but also allow water utility companies to prevent water leaks that might cause water shortage during hot months.
Smart meters are also used in homes to help users determine their energy consumption. This monitoring proved to have a significant financial effect.
Challenges in IoT Implementations /strong>Implementation of IoT is a highly complex process. It requires a lot of planning and sometimes a significant amount of finances. This is because an Internet of Things system consists of many different components. Implementation of each of the IoT component bears different challenges along with it, and in order to get the full picture of this complexity, we have divided Internet of Things implementation into Standards, Networks, Sensors, Analysis and Actions.
StandardsStandards apply to the data collected by the sensors in the IoT ecosystem. The standards should encompass data storing, processing and handling. Standardizing this process increases the value of the collected data.
If the system has access to big data that is frequently updated and sufficiently scaled, it will be much easier to analyse it and to get accurate results. The data compiling process has to be done by using numerous standards, and things get more complicated since standards depend on the IoP application in use.
The two main standards are technology standards and regulatory standards. The first one includes a data gathering and compiling process, and communication and network protocols, while the second one includes security and data privacy.
The main challenge lies in structuring big chunks of unstructured data and handling privacy and security issues for each data market with regard to regulatory standards of the country where IoT is going to be implemented. IoT companies are also faced with a shortage of talent able to plan, execute and maintain IoT systems on the market.
NetworksSince the IoT ecosystem is composed of dozens of sensors, these sensors have to communicate with the main server, and in some cases with one another. This data gets transmitted and carried over the network, and the entire communication is powered by different technologies ranging from Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to WiMAX and Long Term Evolution.
This enormous amount of devices connected to networks puts a significant strain on it, and the main challenge in this area is network implementation. This refers to network coverage, power consumption and, of course, network security.
SensorsIoT ecosystems collect data by utilizing active and passive sensors. Due to the rapid advancement of technology, IoT companies have access to a variety of small, smart and cheap sensors, but as you might have guessed, there are some challenges that come along with the sensors used in IoT systems. Those are interoperability, security, reliability, accuracy and power consumption.
AnalysisAnalysis is a process of extracting meaningful and actionable insight from a big chunk of data. Internet of Things companies use cognitive technologies to process the information gathered from numerous sensors. Without cognitive technologies, it would be impossible to analyse real-time streams of field-data, but this technology still needs improvements to be able to handle terabytes of unstructured data.
Some of the challenges in the field of data analysis are the inability to manage a real-time data stream, restricted ability to analyse unstructured data, and inability to analyse data that doesn't fit in with the predicted data model. We will have to wait for more advanced cognitive technology that will be able to process varied forms of data streamed in real time.
ActionsActions within the IoT can be done through UI and UX technologies when we are talking about machine-to-human and human-to-machine interaction and automatic actions that happen as a result of two machines communicating with one another. Two factors have the main influence on the actions within the IoT ecosystem: effective machine learning and low machine-hardware prices.
The main challenges of this aspect are slow adoption rate of the newest technologies, the human factor, machine actions in unpredictable situations, machine interoperability and numerous security issues. On top of that, custom tailored software that collects, compiles, and analyses the data from sensors is very expensive.
The Road AheadFrom what we have seen now, the Internet of Things ecosystem is quite robust and complex. The main paradigms in all of the practical sciences dictate that the implementations be simplified, but it seems that IoT implementation in smart cities is definitely not going to be less complex in the near future.
The main thing that can catalyse this process is standardization, and we have seen that it is happening, but at a very slow pace. One thing is certain, though, IoT brings a lot of benefits for both city authorities and citizens. This is why we can safely assume that this industry will grow exponentially into a multi-billion dollars one.
The smartest cities on the globe are the models to be looked upon. If we want to transgress from smart cities into a smart civilization and to reap all the benefits this technology has to offer, we have to overcome the challenges IoT implementation brings. This is not something that can be achieved overnight and we are placing our hopes in the innovators and experts in this field to lead us to the smart future.
Conclusion
From the examples we have talked about in this article and the current situation in the world of IoT, it's safe to assume that we are going to see more and more smart cities in the future. As we could see, IoT not only makes city management much easier and more efficient, but it also increases the quality of life of it's inhabitants.
It is also important to mention that as every other big change, IoT implementation in large urban areas will take time, effort, strategy and significant funds. This is why governments across the globe are trying to make markets more friendly for startups that are working on developing IoT solutions for the city needs.
In the mid November another Smart City Expo will take place in Barcelona, which is ranked as number 2 on the list of the world's smartest cities. We are looking forward to see new projects regarding IoT implementation in urban areas.
This year's congress topics are all about implementing IoT in governance, mobility, safe cities, economy, sustainability, circular economy, society, and data and technology. There will be more than 400 influencers and innovators in this field who will share their knowledge and experience regarding this exciting topic.
The world needs smarter and more sustainable cities, and IoT has already proven that this can be achieved. Currently, the only thing left is to see what the future holds for us. We are already excited, are you?
You may also be interested in The impact of IoT on on Brick and Mortar stores?
Finoit has been helping enterprises in planning and implementation of their IoT initiatives. For any query related to Internet of Things (IoT) Solutions & Service , Enterprise IOT please drop an email to [email protected]
Tags Internet of Things for Smart Cities, Internet of Things for smart city, Internet of Things in smart city, IOT challenge for smart city, IoT Challenges for Smart Cities, IOT challenges for smart city, IOT for smart cities, IOT for smart city, IOT in smart cities, IoT Solutions for Smart Cities, Role of IOT for smart city, role of IOT in smart city, smart city iot projects
