Power transmission is an engineering method that engages the machine and the working part of the machine in terms of energy configuration, movement, speed, and motion form.
Well, there are different products, including small and large mechanical components, that make the transmission of power possible. And, when it comes to power transmission, everyone requires optimal reliable and functional mechanical products. Various organizations carry a vast portfolio of power transmission products that aren’t only strong but also efficient.
There are four types of power transmission that are currently used:
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Hydraulic
- Pneumatic
In this guide, we provide a detailed guide over these types and cover each one with its pros and cons. So, let’s have a look!
What is Mechanical Power Transmission?

Power transmission is the flow of energy from its point of source to a location where it’s employed to accomplish useful work using simple machines, mechanical power transmission elements, and linkages. Usually, every machine works after power and motion transmission from an input source.
Well, there are various methods to generate power but sometimes it’s impossible to generate power in the right form, direction, and magnitude where it’s required. This is where electrical & mechanical power transmissions play a vital role in any engineering product design.
4 Types of Power Transmission
1. Mechanical Transmission
#1 Gear Transmission

Gear transmission is one of the most and extensively used forms of transmission in mechanical transmission. The ratio of transmission generated from it is more accurate, stable, and highly efficient. Even it produces a compact structure, reliable operation, and long service life. Gear drives provide comprehensive coverage of gears and gear drives.
Spur, helical, bevel, worm gearbox are all covered with proper accuracy control, load capacity, and manufacturing. It can obtain the transmission between the parallel axis, the intersecting axis of any angle, and the staggering axis of any angle.
Advantages
- Long service life and high reliability;
- Has a compact structure and produce stable, accurate, and efficient transmission;
- Applicable in a wide range of peripherals.
Disadvantages
- High accuracy during installation, and has a high cost;
- Not a reliable choice for transmission between two axes at a long distance;
- No overload protection.
#2 Turbo Vortex Drive
It is suitable for motion and power between two axes with vertical and non-intersecting areas.
Advantages
- Large transmission ration;
- The structure is compact.
Disadvantages
- Substantial axial force
- Low efficiency
- Only one-way transmission
- Easy to heat
#3 Belt Drive

A belt drive is a mechanical transmission that uses an adjustable belt, which is tensioned on a pulley for motion or power transmission. It usually consists of a drive wheel, a compulsive wheel, and an unending belt that is tensioned on the two wheels. The type of belt is available in three categories: flat belt, V belt, and a special belt. The overall purpose of the belt drive is to evaluate transmission ratio, stress analysis calculation of the belt, and allowable power of the single V-belt.
Advantages
- The belt has amazing flexibility and can absorb vibration.
- Prevent damage while slipping
- Simple structure and low cost
Disadvantages
- The outer dimension of the transmission is large
- a fixed gear ratio can’t be guaranteed due to slippage
- Has a short life span
- Low transmission efficiency
2. Electric Drive
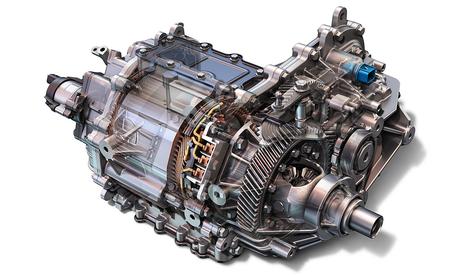
Generally, an electric drive is used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is further used to drive various types of production machinery, transportation vehicles, and other items that are necessary to be moved in life.
- High Precision: As a power source, a servo motor is used. Whereas, the ball screw and timing belt are used for a simple and efficient transmission mechanism. A press brake machine is using this transmission.
- Energy-Saving: The energy liberated in the deceleration phase of the work cycle can be transformed into electrical energy for reuse. This further will help in reducing operating costs. The attached electrical equipment only requires 25% of the power equipment for hydraulic driving.
- Precise Control: With the support of high-precision sensors, measuring devices, computer technology, you can set accurate control according to set parameters. This will considerably surpass the accuracy achieved by other control methods.
- Environmental Protection: The pollution and noise are decreased due to the reduction of energy use and its optimized performance. This further gives a better guarantee of environmental protection.
- Cost-Saving: The cost of hydraulic oil and the trouble caused are removed. There is no hard pipe or soft pipe, and also no need to cool the hydraulic oil.
3. Hydraulic Transmission

Hydraulic transmission is a transmission system that employs fluid as a working mechanism for transferring engine power to drive wheels. It is a set of hydraulic mechanisms that allows the transfer of energy from the driving element to the driven one, in which the movement is transmitted using a compressed fluid.
Advantages
- If you evaluate from a structural point of view, you’ll see that the output power per unit weight and size is constricted in the four types of transmission modes. When the same power is transferred, the capacity of the hydraulic transmission is small. Hence, it provides a low weight, low inertia, compact structure, and flexible layout.
- You can get a fast response if you evaluate it from the performance point of view, you need to adjust the speed, torque, and power. In addition, you’ll receive a wide range of speed (up to 100:1 to 2000:1), fast action, simple control and adjustment, convenient operation, and labour-saving. It’s adapted to assist with the electrical control, and the connection with the CPU (computer) to facilitate industrialization.
- The components of the hydraulic transmission device are featured with good-lubricating properties. Even, with these components, it’s easy to achieve generalization, standardization, and serialization.
- All equipment with hydraulic technology is safe and reliable.
- The resilience and variability of hydraulic technology are very strong. It can improve the flexibility of plastic and adjust the production process. All these components are comparatively inexpensive to manufacture and have moderately high versatility.
- A reliable combination of hydraulic technology with technologies like microcomputer control establishes the “machine-electric-hydraulic-light” integration. It becomes the trend of world development and is easy to realize digitalization.
4. Pneumatic Transmission
Pneumatic transmission is a transmission in which movement is transmitted using compressed air. The source of energy is produced using compressed gas as the working medium, and the fluid transmission of the power. However, due to a significant change in the volume of air from an increase in pressure, the mechanisms of the working medium can have sharp fluctuations during movement.
Therefore, pneumatic transmissions can be used only in cases where a great smoothness of movement is not required. Pneumatic transmissions are used for control mechanisms on machines equipped with compressors for remote control of dozer drive winches.
Advantages
- With air, a compressed gas as a working medium is easy to obtain. Whereas the used air is discharged into the atmosphere, which is convenient to handle.
- As the viscosity of air is very small, its loss is also small. And due to this, it becomes convenient to provide gas supply and long-distance transportation. The availability of external leaks will not pollute the environment.
- As compared to hydraulic transmission, the pneumatic transmission has a quick action, fast response, simple maintenance, clean working medium, and zero deterioration.
- It is cost-effective and overload can be automatically protected.
- In a harsh environment, it grasps good adaptability.
Conclusion
Well, every application requires a different approach. In order to accurately handle a process of power transmission, it’s recommended that you take help from professionals. Professionals are well equipped with a thorough understanding of mechanical products and can guide you over them.
About Author: Maye Pang is a leading contributing editor in the field of mechanical engineering, specializing in automation products. She is the business development manager of Shafttech, a mechanical components powerhouse based in Asia. Connect with her on Linkedin.

