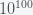Estimates from the Kepler satellite suggest that there could be at least 40 billion exoplanets capable of supporting life in our galaxy alone. Given that there are perhaps 2 trillion observable galaxies, that amounts to a lot of places where life could exist. And this is only counting biochemical life as we know it. There could also be non-biochemical lifeforms that we can't even imagine. I chatted with mathematician Morris Hirsch a long ago in Berkeley and he whimsically suggested that there could be creatures living in astrophysical plasmas, which are highly nonlinear. So let's be generous and say that there are 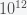 planets for biochemical life to exist in the milky way and
planets for biochemical life to exist in the milky way and 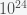 total in the observable universe.
total in the observable universe.
Now, does this mean that extraterrestrial life is very likely? If you listen to most astronomers and astrobiologists these days, it would seem that life is guaranteed to be out there and we just need to build a big enough telescope to find it. There are several missions in the works to detect signatures of life like methane or oxygen in the atmosphere of an exoplanet. However, the likelihood of life outside of the earth is predicated on the probability of forming life anywhere and we have no idea what that number is. Although it only took about a billion years for life to form on earth that does not really gives us any information for how likely it will form elsewhere.
Here is a simple example to illustrate how life could grow exponentially fast after it forms but take an arbitrarily long time to form. Suppose the biomass of life on a planet,

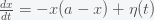
where
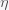
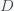






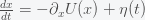
where
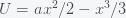
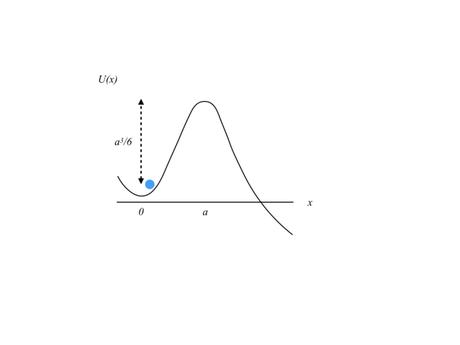
The probability of life is then given by the probability of escape from the well
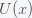
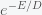
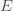
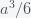


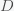
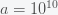
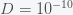

Now, how could it be that there is any life in the universe at all if it had such a low probability to form at all. Well, there is no reason that there could have been lots of universes, which is what string theory and cosmology now predict. Maybe it took