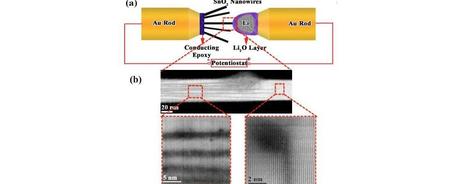
 Above (a), the nanobattery setup inside AC-STEM. Below (b), atomic resolution imaging of the front line of lithium ions entering a SnO2 nanowire. The images show the parallel Li-ion channels and the formation of dislocations at the tip of the channels. (Credit: See citation at the end of this article)
Above (a), the nanobattery setup inside AC-STEM. Below (b), atomic resolution imaging of the front line of lithium ions entering a SnO2 nanowire. The images show the parallel Li-ion channels and the formation of dislocations at the tip of the channels. (Credit: See citation at the end of this article)To get more power out of lithium ion batteries, scientists are studying various battery materials and designs. However, the essential processes in a battery occur at the atomic level, and it’s been nearly impossible to find out exactly what’s happening at this scale. Now, scientists at the Michigan Technological University have created a device that makes it possible for researchers to look at individual lithium ions—and potentially develop the next generation of batteries.
“You might get seven or eight hours out of your iPhone on one charge, maybe a day,” says Reza Shahbazian-Yassar, an associate professor of mechanical engineering at Michigan Technological University. “This is not enough for many of us. A fully electric car, like the Nissan Leaf, can go up to 100 miles on a single charge. To appeal to a mass market, it should be about 300 miles. We want to increase the power of these systems.”
Batteries are pretty simple. They have three major components: an anode, a cathode and electrolyte between the two. In lithium batteries, lithium ions travel back and forth between the anode and cathode as the battery discharges and is charged up again. The most commercially popular negative electrode material used in lithium-ion batteries is graphite, but scientists are testing other materials (e.g., silicon) to see if they can last longer.
“As soon as lithium moves into an electrode, it stresses the material, eventually resulting in failure,” said Yassar. “That’s why many of these materials may be able to hold lots of lithium, but they end up breaking down quickly.
“If we were able to observe these changes in the host electrode, particularly at the very early stage of charging, we could come up with strategies to fix that problem.”
Ten years ago, observing light elements such as lithium or hydrogen at the atomic level would have been out of the question. Now, however, it’s possible to see light atoms with an aberration corrected scanning transmission electron microscope (AC-STEM). Yassar’s team was able to use one at the University of Illinois at Chicago, where he is a visiting associate professor.
To determine how the host electrode changes as lithium ions enter it, the team built a nano-battery within the AC-STEM microscope using a promising new electrode material, tin oxide, or SnO2. Then, they watched it charge.
“We wanted to monitor the changes in the tin oxide at the very frontier of lithium-ion movement within the SnO2 electrode, and we did,” Yassar said. “We were able to observe how the individual lithium ions enter the electrode.”
The lithium ions moved along specific channels as they flowed into the tin oxide crystals instead of randomly walking into the host atoms. Based on that data, the researchers were able to calculate the strain the ions were placing on the electrodes.
The discovery has prompted inquiries from industries and national labs interested in using his atomic-resolution capability in their own battery-development work.
“It’s very exciting,” Yassar said. “There are so many options for electrodes, and now we have this new tool that can tell us exactly what’s happening with them. Before, we couldn’t see what was going on; we were just guessing.”
Reza S. Yassar, Hasti A. Ardakani, Anmin Nie, Li-Yong Gan, Yingchun Cheng, Qianqian Li, Cezhou Dong, Runzhe Tao, Farzad Mashayek, Hong-Tao Wang, Udo Schwingenschlögl, Robert F. Klie (2013). Atomic-Scale Observation of Lithiation Reaction Front in Nanoscale SnO2 Materials ACS Nano DOI: 10.1021/nn402125e
