Ranking! Ranking! Ranking!
This is what matters most to anyone having an online business. After all this is a crucial step in getting that precious click that would lead to your website. What then is the magic recipe that leads to be listed on the first page of the Search Engine Result Page (SERP) of Google?
Well, first in the list of ingredients is “Keywords.” Lets dive in and explore the world of keywords.
List of Topics Covered:
Keyword
Importance
Organic Search
Types of keywords
Keyword Density
Keyword Stuffing
Keyword Weight
Keyword Difficulty
Do B2B keywords differ from B2C keywords?
Other Factors Influencing SEO
Keyword
A keyword is a word or a short phrase describing the topic of a webpage. It is the search query that you type into Google before hitting enter.
When someone searches Google for, say, “women’s bridal gowns” Google tries to discern what the user is looking for, and it returns a list of web pages that address that topic.
If your website uses the exact phrase the user searched for, part of the phrase (“bridal gowns”) or related phrases (“wedding dresses,” “wedding gowns” or “high quality wedding dresses”) Google is more likely to show the user your website.
Importance Of Keywords
Return Of Investment(ROI)!
Choosing the right keywords and using them correctly for Search engine optimization (SEO) is one of the easiest and most effective ways to get users to your site.
SEO basically means tweaking your website so that Google likes it and ranks it higher than your competition.
Users find their way onto your page in a variety of ways, including
 Referrals (links from other sites),
Referrals (links from other sites),
 Social media and
Social media and
 Direct traffic (typing in your URL).
Direct traffic (typing in your URL).
Organic Search
Organic search refers to the result set that Google’s algorithm selects because they meet the needs of the reader.
It represents 94.95% of all search traffic, or 35.21% of total traffic.
Only 1.97% of total traffic comes from users clicking paid advertisements, despite the fact that ads often comprise all the above-the-fold content. Keyword targeting is also more cost effective than paid ads.
First Page SERP
91.5% of search traffic goes to sites that rank on the first SERP. Of that, the top 3 results take 61.5% of the clicks, with 32.5% going to the first result. Unless you can rank in the top ten results, you’ll get very little search traffic.
Good SEO doesn’t just increase visitors and your ranking in the SERPs — it also means
- More conversions
- Better engagements
- Brand recognition
Types Of Keywords
Head Terms
These are usually single-word keywords with lots of search volume and competition. Examples are “insurance” or “vitamins”. Because searcher intent is all over the place – someone searching for “insurance” might be looking for a car insurance quote, a list of life insurance companies or a definition of the word.
Head Terms usually don’t convert very well.
Body
They are 2-3 word phrases that get decent search volume (at least 2,000 searches per month), but are more specific than Head Keywords. Keywords like “life insurance” or “order vitamins online” are examples of Body Keywords.
Body phrases always have less competition than Head Terms.
Long Tail
This contains at least three words and used to target niche demographics rather than mass audiences. They’re more specific and less competitive than generic keyword terms. Because of that, they provide both short-term and long-term benefits.
They allow you to rank highly in search results for popular topics relatively quickly while still gaining ground on head terms.
They tend to attract highly qualified traffic that’s more likely to convert to leads and customers.
Long Tail Keywords Help Your Content Strategy
As these keywords are far more descriptive, they tend to deliver more targeted traffic. A person searching for cheap flights to Barcelona Spain already knows exactly where they want to go and have decided to buy. Whereas, a person looking for cheap flights is not necessarily ready to get their wallet out – they’re still in the ‘browsing’ mind set.
The more specific your market is, the less competition you will have to compete with, allowing you to capitalize on highly targeted traffic.
The real beauty of long-tail keywords is that you can develop content that aligns your product or service with the needs and wants of people that don’t even know you exist. You can position yourself as the solution to all of their problems.
Keyword Density
How many times can we use Keywords on a page?
In essence:
(Number of keywords/ Total number of words) * 100
Today, density of keywords matters much less than site quality and site authority. If you think by using a keyword many times, it will rank higher in SERPs, its not so.
Placing your keyword in natural places in line with your content will work the best. 1-3% of keyword density along with “semantic keywords” works best.
Keyword Stuffing
This is a shady technique some marketers used to inflate their ranking by cramming in as many related terms as possible. For example, a company into ‘mobile app development’ might do an article titled “Gaming Mobile Apps,” and jam a bunch of loosely related keywords into it.
As Google got better at recognizing language, marketers couldn’t just publish massive lists of keywords. In fact, today Google punishes websites that use keyword stuffing.
You still should mention your keyword phrase a few times in the page but it’s much more important to write good, readable articles.
Keyword Weight
Search engines don’t just look at the text in your page — they also look at the code. When you do a search query, Google displays titles, URLs and descriptions of each page. In many cases, it also displays images, news results, videos and featured snippets. Tags tell Google what to show searchers, and many of these tags require their own types of keywords.
Title Tag
These are the bold lines of text that show up in a Google search. They’re also the titles displayed in the top of a visitor’s browser when they’re on a page. Title tags should be short because Google cuts off text that goes beyond 50-70 characters.
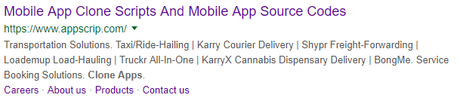
In most cases, a title tag should contain the primary keyword. E.g. in the picture above, “Mobile App Clone Scripts.”
Also put the keyword near the beginning of the title so the reader can still figure out what the article is about.
Header <H> Tags
The title at the top of a blog is an H1 header tag. Every page should have exactly one h1 tag, which should have the primary keyword included in it. Sometimes, sites use the same “title” for title tags and headers. As long as they both use the keyword, describe the content accurately and appeal to the audience, they’ll do well whether or not they’re the same.
Meta Description
Meta descriptions show up under the title tags in Google search results. They’re the slightly longer blurbs that describe what’s in the page. Think of this as your pitch. Viewers skim titles or descriptions pretty quickly, so having a keyword in here can help catch their eye. E.g “Top app development companies”
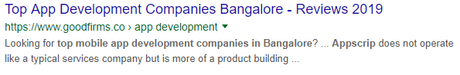
Optimize URLs With SEO keywords
These are those words located in the actual URL that leads to your website. E.g. “ios android clone scripts” in the address https://www.appscrip.com/ios-android-clone-scripts/

When I searched “how to select the right mobile app development company” one of the results showed
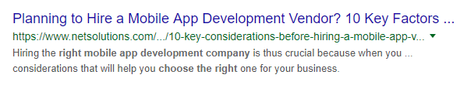
This above example shows why you don’t have to optimize for every keyword. Google knew “considerations before hiring a mobile app vendor” would give me valuable information, even though the article wasn’t optimized for my search term.
Also Read : Google Trends For Dummies
Keyword Difficulty
This helps you predict whether you are likely to outrank your competitors. The higher the number, the harder it will be for your content to appear on page one of the SERPs.
Difficulty Scores above 60 are typically hard to compete with, whereas scores in the 20s or 30s may offer more ranking opportunities for the average site.
KD is relative to Domain Authority. If your site has a DA of 80, a KD of 60 is actually very easy to compete with.
Different marketers and digital tools may define KD in their own way depending upon the proprietary algorithms.
Moz’s Difficulty Score evaluates and weighs the Domain Authority and Page Authority of organic listings that appear on the first page of SERPs.
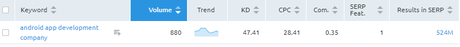
E.g. For keyword “Android App Development Company” using Semrush, KD is 47
Do B2B keywords differ from B2C keywords?
Yes, they do. Lets look at some keywords that specifically appeal to B2B audiences.
Reviews, Comparisons, and Testimonials
Feedback from past or current customers is an important part of buying decision. Prospects may be looking for more information before they close the deal.
Use modifiers like “reviews,” “testimonials,” and “feedback” in your copy.
Clients also look at comparisons of products or services e.g. “Microsoft Office vs. Google Docs” or “Oracle vs. MySQL”. So provide comparisons over why your offer better.
Other terms to consider are “proof of concept,” “business case,” and “return on investment.”
Jargon
It’s better to avoid jargon when targeting consumers. E.g. a first-time mobile app buyer isn’t going to use the same fancy terminology as an Augmented Reality App veteran.
With corporate customers, you can use jargon but don’t overdo it.
Services Terms
B2B clients are often looking for specific business services, such as consulting, web design, event catering, third-party health care management, job placement services and so on. These service names also work as keywords.
Choose keywords that distinguish between B2B and B2C services.
E.g. “corporate catering,” “office catering,” or “business catering” VS “wedding catering” or “private catering.”
Career Development Terms
Business clients are more likely to be looking for white papers, webinars, online certification courses, conferences and other learning opportunities to stay on top of their field. These types of educational content and events are great lead generation opportunities.
Keyword modifiers like “learn” and “guide” can help you attract people looking to grow their industry knowledge.
Other Factors Influencing SEO
Keywords are important, but they’re not magic. Good content is always key, and plenty of other things can influence the success of your website including:
- Backlinks
- Website design
- User experience
- Images and media
- Technical SEO
A company with a mature web presence and good rankings will need a different content strategy than an organization that is virtually unknown online. Keywords are just one of many tools to help find and engage customers and prospects.


