 The world powers – U.S., France, Germany, Britain, China and Russia – reached an agreement with Iranian leaders early Sunday (24th Nov. 2013) in Geneva to curb Iran’s nuclear program in exchange for a gradual easing of economic sanctions. President Obama said the tentative pact will “cut off Iran’s most likely paths to a bomb…While today’s announcement is just a first step, it achieves a great deal,” Mr. Obama said. “For the first time in nearly a decade, we have halted the progress of the Iranian nuclear program, and key parts of the program will be rolled back.
The world powers – U.S., France, Germany, Britain, China and Russia – reached an agreement with Iranian leaders early Sunday (24th Nov. 2013) in Geneva to curb Iran’s nuclear program in exchange for a gradual easing of economic sanctions. President Obama said the tentative pact will “cut off Iran’s most likely paths to a bomb…While today’s announcement is just a first step, it achieves a great deal,” Mr. Obama said. “For the first time in nearly a decade, we have halted the progress of the Iranian nuclear program, and key parts of the program will be rolled back.
Iran has committed to halting certain levels of enrichment, and neutralizing part of its stockpile. Iran cannot use its next-generation centrifuges—which are used for enriching uranium.” Mr. Obama said the U.S. and its partners will not proceed with new sanctions that would scuttle the deal. (Source e.g. The Washington Times ) In return for Iran agreeing to increased international inspections of its facilities, the U.S. and its partners will suspend sanctions on gold and precious metals, Iran’s auto sector, and Iran’s petrochemical exports, potentially providing Iran about $1.5 billion in revenue.
The subsequent economic crisis in Iran discredited the policies of former President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, changed the thinking of the supreme leader and ultimately led to the electoral victory of President Hassan Rouhani. Previous international negotiators entered talks with Iran at a disadvantage because Iran had no need for negotiations. This has changed because Iran needs a negotiated deal as well, and it cannot get sanctions relief without international cooperation. This transformation in the negotiations dynamic made the deal now possible.
From other side Washington was hoping during the Arab Spring that at some point in Iran there would be an uprising that would overthrow the regime. The 2009 uprising, never really a threat to the regime, was seen as a rehearsal (see e.g IRAN – revolution postponed and Iran – no Revolution but potential for Change anyway). U.S was expecting Arab Spring to yield more liberal regimes. That didn’t happen. Egypt has not evolved, Syria has devolved into civil war, Bahrain has seen Saudi Arabia repress its uprising, and Libya has found itself on the brink of chaos. Not a single liberal democratic regime emerged. It became clear that there would be no uprising in Iran, and even if there were, the results would not likely benefit the United States.
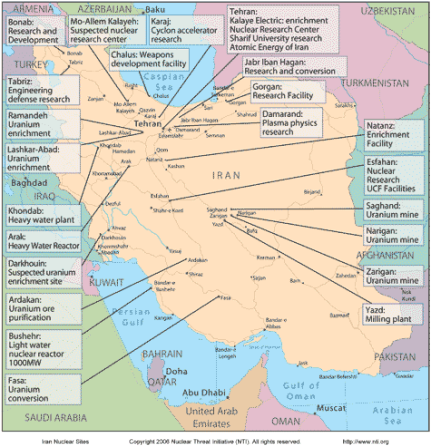
Iran nuclear sites
Key Elements of Iran Nuke Deal
According US State Department fact sheet on Iran nuclear deal the key elements of Iran nuke deal are following:
Iran has committed to halt enrichment above 5%:
- Halt all enrichment above 5% and dismantle the technical connections required to enrich above 5%.
Iran has committed to neutralize its stockpile of near-20% uranium:
- Dilute below 5% or convert to a form not suitable for further enrichment its entire stockpile of near-20% enriched uranium before the end of the initial phase.
Iran has committed to halt progress on its enrichment capacity:
- Not install additional centrifuges of any type.
- Not install or use any next-generation centrifuges to enrich uranium.
- Leave inoperable roughly half of installed centrifuges at Natanz and three-quarters of installed centrifuges at Fordow, so they cannot be used to enrich uranium.
- Limit its centrifuge production to those needed to replace damaged machines, so Iran cannot use the six months to stockpile centrifuges.
- Not construct additional enrichment facilities.
Iran has committed to halt progress on the growth of its 3.5% stockpile:
- Not increase its stockpile of 3.5% low enriched uranium, so that the amount is not greater at the end of the six months than it is at the beginning, and any newly enriched 3.5% enriched uranium is converted into oxide.
Iran has committed to no further advances of its activities at Arak and to halt progress on its plutonium track. Iran has committed to:
- Not commission the Arak reactor.
- Not fuel the Arak reactor.
- Halt the production of fuel for the Arak reactor.
- No additional testing of fuel for the Arak reactor.
- Not install any additional reactor components at Arak.
- Not transfer fuel and heavy water to the reactor site.
- Not construct a facility capable of reprocessing. Without reprocessing, Iran cannot separate plutonium from spent fuel.
Unprecedented transparency and intrusive monitoring of Iran’s nuclear program
Iran has committed to:
- Provide daily access by IAEA inspectors at Natanz and Fordow. This daily access will permit inspectors to review surveillance camera footage to ensure comprehensive monitoring. This access will provide even greater transparency into enrichment at these sites and shorten detection time for any non-compliance.
- Provide IAEA access to centrifuge assembly facilities.
- Provide IAEA access to centrifuge rotor component production and storage facilities.
- Provide IAEA access to uranium mines and mills.
- Provide long-sought design information for the Arak reactor. This will provide critical insight into the reactor that has not previously been available.
- Provide more frequent inspector access to the Arak reactor.
- Provide certain key data and information called for in the Additional Protocol to Iran’s IAEA Safeguards Agreement and Modified Code 3.1.
Limited, Temporary, Reversible Relief
In return for these steps, the P5+1 is to provide limited, temporary, targeted, and reversible relief while maintaining the vast bulk of our sanctions, including the oil, finance, and banking sanctions architecture. If Iran fails to meet its commitments, we will revoke the relief. Specifically the P5+1 has committed to:
- Not impose new nuclear-related sanctions for six months, if Iran abides by its commitments under this deal, to the extent permissible within their political systems.
- Suspend certain sanctions on gold and precious metals, Iran’s auto sector, and Iran’s petrochemical exports, potentially providing Iran approximately $1.5 billion in revenue.
- License safety-related repairs and inspections inside Iran for certain Iranian airlines.
- Allow purchases of Iranian oil to remain at their currently significantly reduced levels — levels that are 60% less than two years ago. $4.2 billion from these sales will be allowed to be transferred in installments if, and as, Iran fulfills its commitments.
- Allow $400 million in governmental tuition assistance to be transferred from restricted Iranian funds directly to recognized educational institutions in third countries to defray the tuition costs of Iranian students.
Putting Limited Relief in Perspective
In total, the approximately $7 billion in relief is a fraction of the costs that Iran will continue to incur during this first phase under the sanctions that will remain in place. The vast majority of Iran’s approximately $100 billion in foreign exchange holdings are inaccessible or restricted by sanctions.
In the next six months, Iran’s crude oil sales cannot increase. Oil sanctions alone will result in approximately $30 billion in lost revenues to Iran
The western powers have cut Iran’s oil sales from 2.5 million barrels per day (bpd) in early 2012 to 1 million bpd today, denying Iran the ability to sell almost 1.5 million bpd.
Secret talks paved the way
The negotiations started in Geneva on Nov. 2013 but as usual secret talks paved the way for the historic deal since March 2013. Some of the points comprising the interim agreement reached between Iran and the six powers were based on these secret talks between the U.S. and Tehran, integrated by the Americans into the official document. The existence of the secret channel between Iran and the United States was revealed publicly for the first time only on Sunday by the Associated Press and by blogger Laura Rozen on the Al-Monitor news website. The two reports appeared simultaneously, right after Iran and world powers signed an agreement in Geneva. The discussions were kept hidden even from America’s closest friends, including its negotiating partners and Israel, until two months ago, and that may explain how the nuclear accord appeared to come together so quickly after years of stalemate and fierce hostility between Iran and the West. However the Israeli government learned of the secret negotiations sometime near the beginning of the summer through intelligence it managed to obtain.
The talks were held in the Middle Eastern nation of Oman and elsewhere with only a tight circle of people in the know, the AP learned. Since March, Deputy Secretary of State William Burns and Jake Sullivan, Vice President Joe Biden’s top foreign policy adviser, have met at least five times with Iranian officials. The last four clandestine meetings, held since Iran’s reform-minded President Hasan Rouhani was inaugurated in August, produced much of the agreement later formally hammered out in negotiations in Geneva.
Meanwhile Le Figaro reported that the U.S. is already conducting secret bilateral talks with Iran on a number of topics.Among other things, the sides are discussing Syria, Afghanistan, Iraq, and accelerating trade relations between Tehran and Washington immediately after the signing of the interim agreement in Geneva, according to the French newspaper. A reliable source in the Gulf revealed these details to a senior correspondent for the newspaper, Georges Malbrunot who specializes in the Middle East. The source said that the contacts between U.S. and Iranians began on the day following the U.N. General Assembly in late September following a telephone conversation between President Obama and his Iranian counterpart Rouhani. Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif stayed in the U.S. for an additional ten days following the U.N. General Assembly, along with 75 colleagues from President Rouhani’s entourage — businessmen, industrialists and representatives of the Iranian gas and oil sector, who met with representatives of American oil companies Chevron and Exxon. (Source e.g: Report: Secret US-Iran talks laid the groundwork for deal )
IAEA reports Iran nuclear activity slowed not reduced

Iran now self-sufficient in uranium ore
The latest quarterly report on Iran’s nuclear activities was issued on 14th Nov. 2013 by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). It noted a slowdown, but no reduction in Tehran’s nuclear activity.
The report was the IAEA’s first meaningful assessment since Iran’s President Rouhani took office. It comes as representatives from the P5+1 powers (US, UK, China, Russia, France and Germany) and Iranian officials prepare to meet again next week to further consider an interim agreement over Iran’s nuclear programme.
The IAEA report found that during the past three months, four advanced centrifuges had been added at the central Natanz plant, in comparison to 1,861 during the previous three-month period. The report concludes activity has been “more or less frozen” at the Arak heavy water plant, where it is feared plutonium is being developed which could speed up nuclear activity. However, Iran’s stockpile of 20 per-cent enriched uranium, considered just a short step away from weapons-grade material, has increased by five per cent to 196kg since August. Despite the slight increase, this is still below the 240kg mark specified last year by Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu as his “red line” which may precipitate action against Iran’s nuclear facilities. ( Source Bicom )
Israeli reactions
From Israel’s perspective, the accord is a strategic defeat for the West, since it legitimizes Iran’s status as a nuclear threshold state. The Iranians, says Jerusalem, are giving up nothing, while getting sanctions relief. The Iranian commitment not to enrich uranium to 20 percent for the next six months is no Iranian concession since the Iranians have already been careful not to cross Netanyahu’s red line of 220 kilos of such uranium. The Iranian commitment not to operate the heavy water reactor in Arak for the next six months is similarly “a joke,” Israel says, since Iran anyway can’t do so. The reactor is still under construction, and will be so for at least another 12 months. Israel’s security cabinet took earlier the unusual step of releasing a public statement, which affirmed Israel’s support for a diplomatic solution to Iran’s nuclear development, should Tehran comply with four measures: cease all nuclear enrichment, remove all stockpiles of enriched uranium, dismantle the Qom and Natanz facilities and stop work at the Arak heavy water reactor.

Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu expressed deep skepticism that Iran would abandon its nuclear ambitions. “What was achieved last night in Geneva is not a historic agreement; it is a historic mistake …Today the world has become a much more dangerous place because the most dangerous regime in the world has taken a significant step toward attaining the most dangerous weapon in the world.” (Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu)
Despite this irate response from the Prime Minister’s Office to the agreement signed in Geneva between Iran and six world powers, the deal might not be really a bad one even from an Israeli perspective. Geneva deal places serious restrictions on Iran and provides the West with valuable information on its nuclear program. Israeli President Shimon Peres gave a more measured response, saying time would tell whether the agreement was effective. Leftist Meretz Chairwoman Zahava Gal-On delivered the only positive Israeli response so far to the nuclear deal, saying her colleagues’ attack on the deal missed the fact that the agreement was intended to slow down Iran’s fast track to a nuclear bomb. After Iran nuke deal in Israel the Likud leadership anticipates a diplomatic and political crisis next spring. If Netanyahu wants to run again he will have to become even more extreme and speed toward Obama on a collision course. It might be that Geneva ended Netanyahu’s era. In a new reality, Israel might need new leadership.
Follow-ups
Saudi Arabia, Iran’s regional rival, at times opposed Islamist radicals (in Saudi Arabia) and supported them elsewhere (in Syria or Iraq). The American relationship with Saudi Arabia, resting heavily on oil, had changed. The United States had plenty of oil now and the Saudis’ complex strategies simply no longer matched American interests.
The Iran nuke deal is only – sure core one – part of story. The deal but especially the secret U.S.-Iran talks before the deal may have also big geopolitical affect. When the nuclear issue is out from agenda and the sanctions removed, then matters such as controlling Sunni extremists, investment in Iran and maintaining the regional balance of power would all be on the table.
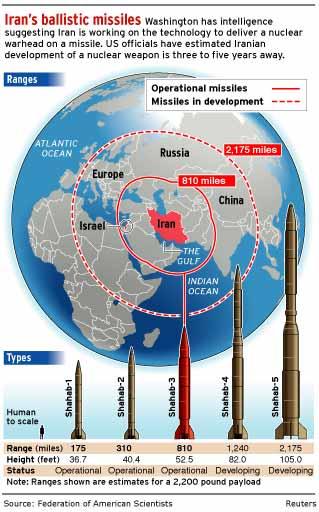
Challenges
- Arak plutonium reactor: Arak need to be followed closely. Before the French intervention during the last round of talks, the Arak clause was problematic, proposing that Iran could not commission the facility but could continue construction in the next six months. One idea is that it will be converted into a light water reactor from a heavy water plant, this is something else.
- The Iranian narrative, that they have the ‘right’ to enrichment, has become an issue of their national pride. As a result, any deal will probably allow a degree of enrichment, but round the clock inspections by the IAEA will be essential to manage this.
- One key challenge is that the P5+1 powers should agree among themselves on a clearly defined endgame to the talks after an interim accord of six months.
The bottom line
”(the P5+1 agreement) puts time on the clock.” (John Kerry)
Israel, the US and the major EU powers share the assessment that Iran’s programme is intended to give it the capacity to build nuclear weapons at its time of choosing. Now the Iran nuke deal concludes an interim accord as a prelude to a more comprehensive agreement. It would require Iran to freeze aspects of its nuclear programme for six months, in return for limited concessions on sanctions. Despite hard words one should remember that Iranian foreign policy has been extremely measured. Its one major war, which it fought against Iraq in the 1980s, was not initiated by Iran. Already some months ago Russia and U.S. managed to deal with Syria’s WMDs restoring trust to the great Middle East. Based on this history and the new deal with Iran I think that the détente has took a remarkable step forwards.
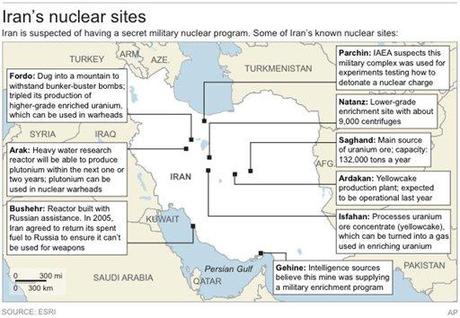
Iran nuclear sites
Some of my previous articles related to nuclear Iran:
- Instead Iran The Saudis Can Be The Next Nuclear Power
- US Giving a “Yellow Light” to an Israeli Strike
- Saudi-Israeli cooperation for attacking Iran
- Cyber war has become a tool between political and military options
- End Game Approaches on Nuclear Iran
- Iran’s nuclear program at the crossroads
- Iranians And Israeli Instead Of Israel Vs. Iran

