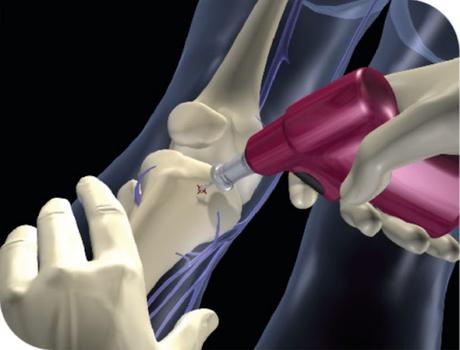
When it is not feasible to acquire intravenous access, intraosseous infusion devices are medical devices that are utilised to enter the vascular system in emergencies. These tools make it possible to inject fluids and drugs directly into the bone marrow, which contains a large number of blood arteries that may swiftly transport the therapy to the rest of the body.
In recent years, intraosseous infusion devices have grown in popularity, especially in urgent cases where time is of the importance. It can be the difference between life and death to be able to provide life-saving fluids and drugs promptly in situations involving cardiac arrest, severe trauma, or other critical circumstances. When conventional intravenous access methods are not feasible, intraosseous infusion devices provide a quick and efficient approach to administer these therapies.
The equipment used for intraosseous infusion come in both manual and automated varieties. While automated devices employ a motorised mechanism to inject the needle, manual systems require a healthcare expert to physically enter the needle into the bone. Both kinds of gadgets are made to be simple to use and quick to employ in emergency scenarios.
The fact that intraosseous infusion devices may be used to a range of patient groups, including adults, kids, and even newborns, is one of its advantages. This is crucial in emergency settings when typical intravenous access sites might not be readily available. Depending on the patient's age and health, intraosseous infusion devices can be placed in a number of different places, such as the sternum, tibia, and femur.
Intraosseous infusion devices can be utilised for long-term treatment of individuals with chronic medical disorders that need regular medicine or fluid delivery in addition to their usage in emergency circumstances. This is especially true for patients who struggle with conventional intravenous access, such those with cancer or chronic renal illness.
The high success rate of intraosseous infusion devices is one of its key benefits. When intravenous access is not feasible, intraosseous infusion, which has a success rate of over 90%, is a dependable access option. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that intraosseous infusion devices are both safe and efficient, with minimal reported side effects or problems.
When standard intravenous access is not accessible, intraosseous infusion devices provide a quick, dependable, and efficient way to provide fluids and drugs. They can be easily deployed in several areas and utilised with a range of patient groups, such as adults, kids, and newborns. Intraosseous infusion devices are a useful tool for medical practitioners in emergency and critical care situations because to their high success rate and shown safety and efficacy.
