
One of the crucial steps in creating a better environment for future generations is to reduce the burning of fossil fuels and slow down the rise in global temperatures to carve a path for more sustainable, cleaner, and reliable energy sources.
In a digitally and technologically advanced era, the rest of the world depends mostly on machines that use electricity to operate. The overuse of energy has mostly contributed to the increase of carbon footprint through the burning of fossil fuels. Hence, the release of carbon dioxide emissions into our atmosphere, which is one of the main reasons for global warming.
Fortunately, there's an alternative that can sustain electricity production and consumption that is stable, reliable, and, most importantly, environmentally-friendly.
The microgrid.Quick links -
What is a microgrid?
A microgrid is a local energy grid with control capability, which means it can disconnect from the traditional grid and operate autonomously.
The US Department of Energy
One of the simplest definition of microgrid.
First, pick up the keywords in this definition -
- "local energy grid"
- "control capability"
- "disconnected from the traditional grid"
- "operate autonomously"
Let's dig a little deeper into understanding microgrid.
- It's more of a local energy grid system, meaning it's a compressed version of the national electrical grid that powers our country. In practice, a microgrid works just for a smaller geographic area, like a couple of buildings or a local community.
- It has control capability, meaning to meet the electricity demands of its users, a microgrid must have power generation source and its own controls. Traditionally, often the source was fossil fuel generators. However, with the reduction of the solar cost and the environmental benefits of switching from fossil fuel to solar energy, many of the microgrids are being designed to supply electricity with a combination of solar plus battery storage.
- Microgrid can work independently from being disconnected with the national power grid and are capable of becoming isolated from the grid in the event of an outage. When the national grid (or the main grid) goes down due to any issue, microgrid continues to produce electricity on its own.
- In practice, microgrid is a small-scale power grid that can operate independently or collaboratively with other small power grids. The practice of using microgrid is known as distributed, dispersed, decentralized, district, or embedded energy production.
How popular is the concept of microgrid?
In recent years, microgrids are becoming popular throughout the globe. From the first world developed countries to less-developed countries in Africa and South-East Asia. Here are some examples of how the concept and implementation of microgrids are taking place.
USA
As part of their pledge to honor the 2016 Paris Agreement on climate change, many cities in the US are passing legislation to make all new public buildings and developments emission-free. And microgrid is the front-runner to contribute here.
Energy market analyst Pike Research estimates that microgrid power generation has now increased 5x since 2012 levels. And with an increasing array of innovations coming to market, we could see entire cities and urban areas powered very differently in the years ahead.
Canada
In Canada, microgrid technologies have the potential to supply homes and businesses in parallel with the Hydro-Quebec grid. During the summer, when energy consumption is less, microgrids can power the whole neighbourhood.
Australia
Microgrids are supplying energy to the remote places of Western Australian outback where shipping the fuel of the diesel generators have reduced, along with the energy cost. Additionally resulted in a drop in carbon emission in that region.
Bangladesh
Solar panels are becoming popular and available in the remote Southern part of Bangladesh. But the demand is growing, and the local vendors are having a hard time supplying individual solar panels. Government and some NGOs are working to figure out a common ground to establish microgrids in that region, keeping the cost and profitability in mind.
What is solar-powered microgrid?
A solar microgrid is a small, freestanding distributed energy source designed to function independently from the wider electricity grid in emergency cases. It is composed of a network of electrical loads, generators, energy storage batteries, and solar photovoltaic systems.
In addition, solar-powered microgrids provide both green energy and electric reliability and resilience. Solar microgrids can consume energy, as well as produce and regulate it.
In the US, most of the solar panels operate through a grid connection. If the grid goes off, so do everything connected to it. With solar-powered microgrids, it can flip a switch (or switches) and "island" itself from the grid in case of a blackout, allowing it to power those connected temporarily.
Check out the infographic below shared with us by SolarNRG for some fast facts and stats about solar-powered microgrids.
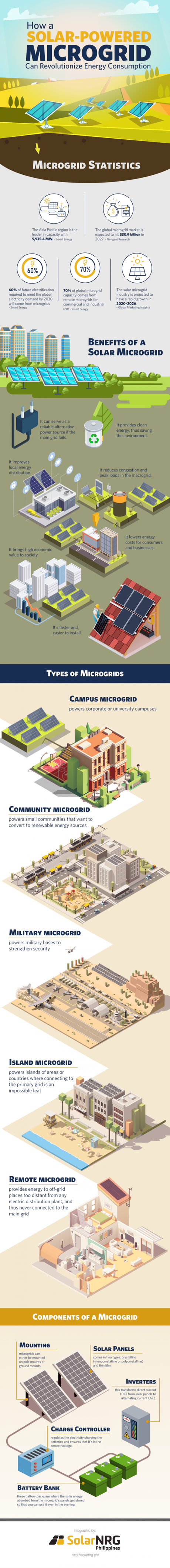
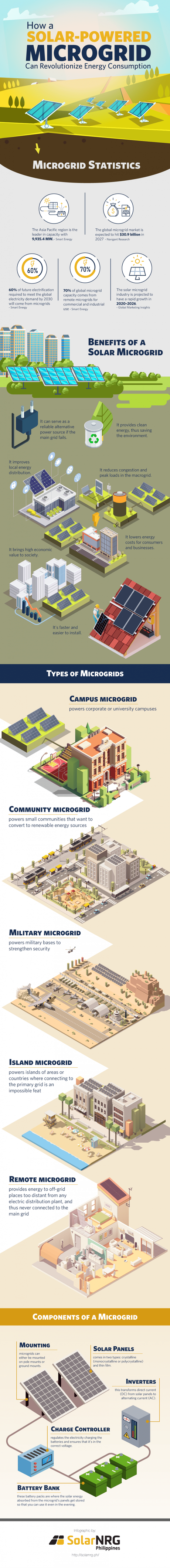
Benefits of solar-powered microgrid
- Greener energy source: Solar microgrids rely on renewable sources of energy, which means it doesn't burn fossil fuels and release harmful greenhouse gases. This makes it an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative over time.
- An excellent alternative power source: In case of a brownout or a power outage, a microgrid can function as a backup power source, with help from generators and batteries from renewable energy. Small and large-scale businesses can benefit from this, especially hospitals.
- Cost-effective energy source: Solar microgrids regulate the generation and consumption of energy, making it practical and reliable. Since it helps power up businesses amid power outages, it also saves money from potential losses due to the electricity interruption.
- Enhances local energy distribution: Microgrids are highly useful in distributing energy to remote places that the main grid cannot reach. Setting it up in the best possible place can efficiently disperse power to infrastructures connected to it.
- Decreases the main grid "congestion": There are times when the central grid can't hold up with the demand of the infrastructures and people using it. In such events, it will reach its maximum load and run out of power. One of the solar microgrid's best features is it can offload the main grid and minimize the energy demanded from it, preventing the central grid from congestion.
In a nutshell...
Shifting to solar is good, but solar-powered microgrids are a whole lot better. This alternative energy source has the potential to transform the way electricity is produced and consumed by people. It's up to the government and the international energy regulators to make that possible.
Resources
https://www.energy.gov/articles/how-microgrids-workFeatured image by Michael Schwarzenberger from Pixabayhttps://news.energysage.com/what-are-microgrids/
https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/microgrid

