It’s human nature to catalog what exists in the world. From early explorers to modern birdwatchers, people have always wanted to know what’s out there. The internet is no different

Search engines began appearing in the mid-1990s, scouring websites in an attempt to catalog the early web. Since those early days, websites have wanted to see their sites appear high in the result rankings.
The Early Days
Back then, just as now, webmasters were anxious to get their sites listed on these newly emerging search engines.
In 1992, Gopher entered the scene, becoming the first search engine to use a hypertext paradigm.
Web Crawler, which arrived two years later, was the first search engine to provide full text search and remains the oldest surviving search engine on the internet today.
Yahoo! also came on the scene in 1994 and quickly came to dominate the space.
In those days, the folks in charge of websites would submit their page’s URL to sites like Web Crawler and Gopher.
At that point, a “spider” would “crawl” through the page, extracting links to other pages as it went, and returning those links and other information to be indexed.
But this was no easy undertaking. These efforts were undertaken in the days before concepts like “cloud computing” were even a glimmer in the collective eye of the internet.
The search engine spider would need to download these pages and store them on the search engine’s own server. Once there, a second program - known as an indexer - would extract information about the page like the words it contained, where it was located, and any links the page contained.
The term “search engine optimization” is thought to have come into existence in 1997, according to industry analyst Danny Sullivan.
In these early days of SEO, algorithms relied on webmaster-provided information like keyword meta tags or index files. Meta tags would provide a guide to each page’s content.
This proved rather unruly though, as webmaster’s could easily manipulate the keywords in the meta tag to misrepresent their site’s content.
This made it very difficult for these nascent search engines to create an accurate overview of the internet.
On the flipside, webmasters suffered from a drought of data. Unless you had BIG BUCKS to spend, there weren’t really analytics available for websites.
What few options did exist to help provide insight certainly didn’t come cheap.
Enter Google
Even as search engines and web developers continued to bump up against issues, it was becoming increasingly clear that there was a lot of money to be made on this crazy newfangled thing called the internet.
However, these issues would need to be resolved before people could start seeing the big bucks.
The main issue was that the top results often weren’t the ones with the highest quality content. That’s because search engine results matched words from user queries. Thanks to this, many site owners started keyword stuffing - repeating various keywords again and again throughout the text of the site - to bolster their rankings.
This way they could drive traffic to their site and garner high numbers to show potential investors. This type of activity was able to propagate because these young search engines had no criteria for their rankings.
So, thanks to some collusion, keyword stuffing, and spam-filled backlinks, the overall information being returned was quickly decreasing in quality.
But then Sergey Brin and Lawrence Page arrived on the scene.

When these two Stanford students set out to create Google, this was one of the main problems they hoped to solve.
In 1998, the two released a thesis paper where they introduced the idea of PageRank, the technology that Google still uses today to help rank search results based on quality. Not on keywords alone.
Expansion Of SEO Ideas
Throughout the 2000s, Google would continue to grow, attempting to refine these ideas as it went.
In 2003, for example, the company rolled out its “Florida” update, which would mark a drastic change in Google’s algorithm.
For the first time, sites were penalized for actions like keyword stuffing. For many, this signalled Google’s intention to put the user first by providing quality content.
In 2005, Google partnered with Yahoo and MSN to announce the Nofollow attribute, which decreased the number of spammy links and comments on websites, especially blogs.
A few months later, Google announced personalized search, which looked at a person’s search and browsing history to ensure their results were more relevant. That year also saw the launch of Google Analytics, which is still widely used today to help people measure traffic and campaign ROI (returns on investment)
But How Has This Impacted SEO Experts?
That’s a great question.
Content Is King
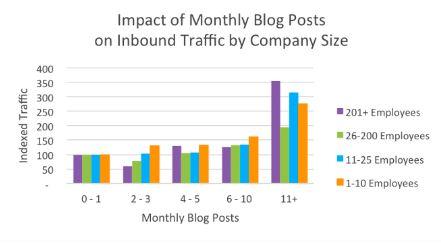
Content marketing has emerged as an integral part of any successful SEO strategy since Google rolled out its Panda update in 2011.
That update sounded the final death knell for spammy content and keyword stuffing.
Google has been refining what it considers “good” content ever since but after Panda, it was nearly impossible to use gimmicky content-based tactics to bolster your ranking. The sites that have emerged with the best results since then have shown themselves to produce valuable content.
This single update alone is nearly entirely responsible for the adoption of content marketing amongst SEOs.
Goodbye Link Schemes
Link schemes are any links that are created with the purpose of manipulating PageRank or search rankings, according to Google’s definition.
Here are a few examples of what Google considers perpetrators of these schemes:

Google started attacking these schemes in 2000, but it wasn’t until the 2012 Penguin update that it began penalizing, banning, or de-listing websites that were found using link schemes.
This put the emphasis on valuable link building strategies, gaining backlinks from authorities, and other link attraction methods like guest posting.
Reimagining “Local”
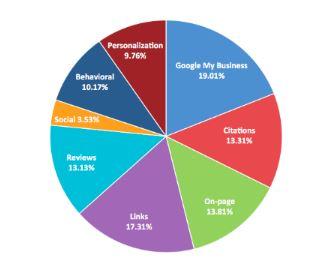
With the 2014 Pigeon update, Google began incorporating traditional web ranking signals into its algorithm.
The proliferation of mobile searching has also improved how Google thinks about local search results.
Prioritizing Mobile
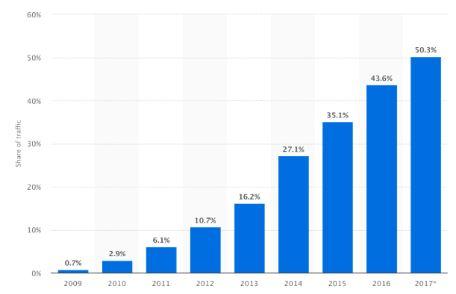
Speaking of mobile, last year Google made headlines when it announced its mobile-first indexing. That meant that pages with a proper mobile-dedicated version of their site would receive a higher ranking.
Indeed, mobile searches have surpassed desktop queries since 2015. As a result, creating a mobile page is required work for any SEO campaign.
Goodbye Keywords
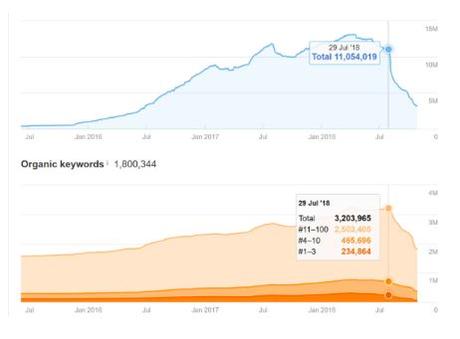
As mentioned above, keyword stuffing has been the bane of search engines for decades. Thankfully, Google’s Panda and Penguin updates largely killed off this practice. But a third updated in 2013 - Hummingbird - introduced something called semantic search which essentially killed off keyword optimization altogether.
Semantic searching is Google’s way of figuring out user intent, rather than mapping out individual keywords or phrases.
Keyword research is still alive and well though, given that it can be used to help guide your strategic focus, which can in turn be used to look for ranking opportunities.
Conclusion
SEO has come a long way. When it began, webmasters were jamming keywords into meta tags and submitting URLs to web-crawling spiders.
These days, entire teams of people are being paid big bucks to create content, develop mobile sites, and carry out keyword research to find new opportunities. But it’s a story that’s far from done. People will continue to find ways to game the system and Google will continue to find ways to fend them off. This industry is constantly evolving.
Author
Roberto Garvin is the co-founder of Mofluid. He is amazed to see how technology continues to evolve. From email to browsers, search engines, mobile, AI and now blockchain, he feels fortunate to witness it all and is really excited to see what’s next. Twitter –@mofluid / Facebook –@mofluid

