, the oldest bearded dragon ever recorded, died at the age of 18 years and 237 days! Even though reaching this age is uncommon, it demonstrates that with good husbandry and care, longevity can be increased.
There are several imposing factors that influence why some bearded dragons live longer than others; let's look at what these factors are and how they affect their life span.
Aging
Aging is a natural process that all living things go through, including Bearded Dragons.
After sexual maturity, most living things degenerate slowly; as time passes, cell regeneration slows, and older cells are no longer replaced and function as effectively as they did when they were younger, causing us to age and our bodies to decline, making us more susceptible to disease and death.
The rate of degeneration varies greatly between species, with some degenerating faster than others.
Thermoregulation

Bearded dragons are ectotherms (cold-blooded); in the wild, they control their body temperature by basking in the sun in a process known as thermoregulation, which leads to a decreased metabolic rate and extends their lifespan.
Size
Larger species typically have longer lifespans than smaller ones due to their increased body mass. Because they are more effective at fending off predators and are less likely to be attacked by them, larger species can spend more time growing and reproducing in the wild. On the other side, small reptiles have a poorer chance of surviving in the wild since they can't get big enough to defend themselves.
Environment
Neglected bearded dragons are prone to illness and disease. Poor husbandry is to blame for the majority of bearded dragon health issues; it accounts for roughly 70% of reptile illnesses and conditions, as well as 20% of reptile deaths each year. It is critical that the four fundamental basics of husbandry are managed correctly for bearded dragon longevity. These are:
Failure to get these fundamentals correct can result in the following:
More information on Bearded Dragon Diseases is available at Bearded Dragon Diseases
Diet
Bearded Dragons are typically omnivores, eating invertebrates, fruit, and plants.
For a full list of food: Bearded Dragon Food List
Maintaining a healthy diet for your bearded dragon is absolutely essential to its longevity. Failure to provide a consistent diet can result in a variety of diseases and even death.
Here are some things to think about when planning your bearded dragon dietOver Feeding
Bearded dragons in the wild expend excess energy by being active for the majority of the day, and limited food sources ensure that they consume only what they need. Bearded dragons in captivity should be fed carefully and exercised on a regular basis, as this can lead to obesity and disease.
Bearded Dragons are Ectotherms (cold-blooded animals) that spend 80% of their energy on thermal regulation. They would naturally go without food for a day or two in the wild; this is their natural state. As a result, providing them with multiple meals per day is likely to result in obesity.
High Sugar Content
Fruit with a high sugar content should be consumed in moderation. In addition to being unhealthy, Fruit is naturally soft and can get stuck in the mouth of a bearded dragon, causing mouth and gum infections.
Due to their lower reproductive capacity, female bearded dragons have shorter life expectancies. As the belly expands, the limbs and pelvis lose mass. Her life is shortened and her entire body is affected by these disorders.
How to Increase Your Bearded Dragon's Life Span

Diet, proper husbandry, and the ability to spot signs of illness and disease are the keys to increasing your bearded dragon's life.
Unfortunately, there are several mistakes that most owners make that shorten the life of their Bearded Dragon.
- Insufficient Temperature
- Inadequate UVB Lighting
- Unbalanced Diet
- Failure To Recognise Symptoms Of Illness & Disease
- Inadequate Enclosure Size
Fortunately, these flaws are easily preventable. We'll guide you through each mistake and teach you how to avoid it.

A nutritious diet will keep your dragon happy and healthy. Furthermore, it increases the bearded dragon's life span because providing it with a healthy diet rich in balanced nutrients helps it stay healthy and fend off disease.
Depending on their developmental stage, you should feed them a nutrient-rich diet.- Hatchlings and juvenile bearded dragons should be fed more insects because they require more protein in their diet.
- Adult bearded dragons that are no longer developing require a diet that is higher in plants and vegetables.
It's critical to keep track of what foods you feed them and how long it's been since their last meal.
A calcium supplement should be added to hatchling food at least five times per week. Adults should take a supplement once a week, and juveniles should take one every day.
Note: Too much calcium can harm organs and cause bowel problems if calcium intake is not reduced. Adults' droppings turn yellow when they consume a lot of calciumFor More Information: Feeding Bearded Dragons
There are five basic fundamentals of husbandry. Following these guidelines will ensure that your bearded dragon lives a long and happy life.
Housing, temperature, lighting, humidity, and water are all factors to consider.
The enclosure should be as close to a replication of the bearded dragon's natural habitat as possible. Glass or Plexiglass enclosures are preferred over wooden enclosures because wood is a naturally porous material that is more difficult to clean. The habitat should be large enough (minimum size 40 gallons) to allow the bearded dragon to develop and move about. Enclosures must be escape-proof, with secure entrances and vents.
Housing Bearded Dragons in pairs or multiples are not ideal, but if you insist on doing so, you must keep careful watch to ensure intraspecific competition does not emerge. Failure to recognize warning signals can result in unnecessary stress, damaged limbs, and even death.
A suitable substrate should boost enrichment, reduce stress, be safe, and be simple to clean.
- Newspaper is an excellent substrate in many contexts since it is affordable, non-toxic, and simple to maintain, despite its unappealing appearance.
- The reptile carpet is more enticing and less challenging to clean.
WARNING: Use particle substrates since they can become caught in the reptile's digestive system and cause impaction if eaten.
Hiding places should be placed in the enclosure to provide the bearded dragon with its own personal space where it can feel safe and comfortable. Branches and foliage can be utilized to help the animal climb and find basking spots as well as additional shelter.
Temperature
This is a critical aspect of bearded dragon care; maintaining proper temperatures in the enclosure keeps the bearded dragon's metabolism running smoothly. Knowing what temperatures are required for your lizard's health and the parameters in which they should be is critical, and the use of a thermometer is vital.
The enclosure must have both a thermal inclination and a calm side with a cover. Temperature source that should not be installed all the way down the tank. This could lead to overheating.
A bearded dragon's vivarium should be between 22 and 26 degrees Celsius on the shaded end and 38 to 42 degrees Celsius on the bright end for climbing and basking.
Turn on the heat lamp first thing in the morning to give your dragon an hour to refuel for the day.
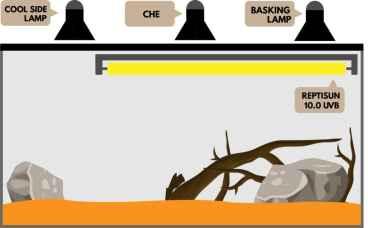
Light in the enclosure is also an important aspect of creating the proper environment for the bearded dragon because it allows us to simulate a day/night cycle. Second, specific wavelengths lower the risk of calcium deficiency.
The use of UVB (Ultra Violet) light produced Vitamin D in the beard dragon's skin. Vitamin D's role in the body allows intestinal calcium absorption.
The closer the light source is to the lizard, the more intense it is; consequently, the light source should be placed as far away as possible to avoid burning the lizard.
Humidity is another important factor. All reptiles, including bearded dragons, lose water. The recommended humidity level for a bearded dragon is between 30 to 40%, which may be verified in the enclosure with a hydrometer. The hydrometer should be placed where the beardy spends the majority of his time.
The following procedures can be used to maintain humidity levels.
- Misting the cage well every day.
- An automatic mist system is far superior because it can adjust to humidity and temperature.
- Living plants and waterfalls in the cage will also contribute to the humidity.
- Occasionally soaking the reptile, although this must be done with caution because of the risk of drowning.
Water is a dietary necessity and an environmental/habitat requirement for all reptiles. It is critical to keep your bearded dragon hydrated.
Keeping your bearded dragon healthy and disease-free is critical to its longevity. The leading cause of illness and disease in bearded dragons is poor husbandry. The second step is to keep track of your bearded dragon's health in order to extend its life. Early disease detection and prevention are critical.
Here are some of the diseases and illnesses that bearded dragons can contract.
Check out this video from Nature's Edge Wildlife and Reptile Rescue on YouTube to see how severe MBD can become if left untreated.
