Electricity prices are constantly changing and there is no way to reliably predict the cost of your electricity at any given moment. The price could jump up and down as you use it, or it might stay the same for days on end. It all depends.
To have peace of mind you can sign up for a fixed-rate contract and guarantee price stability, but otherwise, prices will fluctuate. Understanding the factors that affect kWh price is important for us as consumers, and they allow us to make smarter decisions that can reduce the overall cost of our electric bill.
Table of Contents
Why Do Electricity Prices Fluctuate?
Price changes in the electricity market are actually a function of supply and demand. In very simple terms there are times when there is a lot of power available and times when there isn’t, leading to price movement. With this supply-demand model, price is very unlikely to drop during peak demand hours when everyone wants to use their power, but it can decrease by 20% or more during a period when supply is greater than demand.
In Texas, the cost of electricity is determined by supply and demand and is regulated by ERCOT, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas. When there’s a high demand for power in Texas, the price of power increases to incentivize production, where the maximum price allowed by law is $9,000 per megawatt‐hour — which is equivalent to $9 per kilowatt‐hour. That is very expensive!
The good news is, when there’s a surplus in the production of electricity, the prices decrease to encourage consumption and take more load off the grid.
What Drives Energy Prices?
During the normal market conditions, electricity prices are determined primarily by the costs of electricity supply (e.g., fuel costs and energy purchases) and by the demand for electricity from customers. Prices fluctuate gradually, but the rate of increase typically remains within an anticipated range. Multiple external factors can intensify volatility and cause prices to increase in a short period of time:
- Weather: Weather can affect the price by directly impacting the demand for electricity. The demand for electricity is typically higher on hotter days because homes use more air conditioning. Based on their own estimations, electricity suppliers may have to raise prices during these times as a result of a shortage of resources.
- Government Regulations: When regulatory agencies propose or introduce changes, the wholesale market reacts in a self-reinforcing way. For example, when the European Union approved carbon emission regulations to be enacted in the European Union, these rules resulted in increased transportation costs leading to increasing fossil fuel prices. When gas and fuel prices increase, electricity suppliers will have to raise electricity prices to make up for the difference.
- Cost of Source Fuels: The electricity and natural gas markets depend on one another. They are influenced by the supply, demand, and pricing of other fuel sources, such as crude oil and coal. The dependency of one fuel source on another in the energy market is known as the “supply chain”. This effect can cause a spike in the price of one fuel source if the supply of another is restricted, for example, due to an industrial accident or a natural disaster.
- Natural Disasters: Nature has its own influence on the price of electricity by imposing an abundance or scarcity of resources.
- Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical events in regions that import or export oil or gas may have profound effects on the price of energy, especially during times of war, or civil unrest.
Are Electricity Prices Changing Every Year?
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) has data on all of the country’s electricity sectors and regions dating back to 1973 and provides its data in a way that it is easy to view and compare over time. If you compare the same month’s electricity prices in different years, you’ll notice that the average cost of a kWh in the US has been increasing over time. However, Texas has seen prices rise and fall over the last 2 decades.
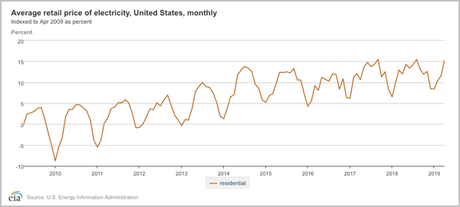
An increase in prices is partly caused by inflation, which affects all industries, as well as the power industry, but electricity prices are sensitive to many other factors.
- The cost of solar panels and wind turbines is dropping, which has helped make the price of electricity at certain locations more affordable. For instance, Texas is the leader in wind generation capacity among the fifty states of the US.
- When a grid heavily relies on fossil fuels, electricity prices will greatly fluctuate when price of fossil fuels fluctuates.
- Population growth and economic development force power companies to upgrade infrastructure and build new power plants and power lines. These expensive projects are reflected in the overall price.
Electricity prices are usually highest in the summer
Unlike other materials, electricity cannot easily be stored. The power that is consumed by the entire region needs to match the power generated by the grid, in real-time.
The electricity market tends to follow cycles:
- Seasonal cycle: Demand for energy increases in the summer and winter, and falls in the spring and autumn.
- Energy market cycle: Energy prices fluctuate between low, high, and falling phases over four- to eight-year cycles.
What time of day is electricity most expensive?
The most expensive time of the day to buy electricity is usually in the hottest hours of the day, between 2 pm and 3 pm, because this is when the air conditioners are at their highest levels of use. To reduce your electric bill, it is usually cheapest to use major appliances in the evening or early morning, or at the very least use a smart thermostat that will halt your AC when not in need.
What time of day are electric rates the lowest
The electricity price changes throughout the day, regardless of the season. The cheapest time of the day to buy electricity is usually in the early morning between 4 am and 6 am when everyone is asleep.
What uses the most electricity in a home
- AC/Heater – The air conditioner and heater are often left on for long periods of time. Their combined energy consumption is about 20% of household usage. Running AC during the winter can lead to an increase in your electric bill by 50%. It’s best to turn off these machines when you’re not home or at least set them to use as little electricity as possible, according to the guidelines set by manufacturers.
- Dishwasher, Dryer & Washing Machine – These three big appliances account for roughly 10% of a home’s electricity consumption. To reduce their impact on your electric bill, use them only when they are full.
- Refrigerator – Running your refrigerator at full capacity every day can result in a huge electricity bill. Make sure to keep the cold inside and only open the refrigerator door when need.
