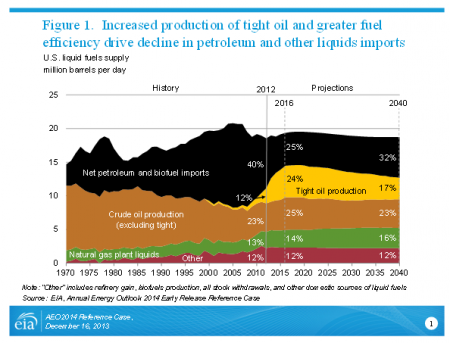
 Figure 1. Increased production of tight oil and greater fuel efficiency drive decline in
Figure 1. Increased production of tight oil and greater fuel efficiency drive decline in petroleum and other liquid imports. (Source: EIA, AEO2014 Reference case)
The Annual Energy Outlook 2014 (AEO2014) Reference case released yesterday by the EIA presents updated projections for U.S. energy markets through 2040. One of the key findings of the report is that advanced technologies for crude oil and natural gas production are continuing to increase domestic supply and reshape the U.S. energy economy as well as expand the potential for U.S. natural gas exports.
Among other key findings:
Domestic production of oil and natural gas continues to grow. Domestic crude oil production increases sharply in the AEO2014 Reference case, with annual growth averaging 0.8 million barrels per day (MMbbl/d) through 2016, when domestic production comes close to the historical high of 9.6 MMbbl/d achieved in 1970 (Figure 1). While domestic crude oil production is projected to level off and then slowly decline after 2020 in the Reference case, natural gas production grows steadily, with a 56% increase between 2012 and 2040, when production reaches 37.6 trillion cubic feet (Tcf).
Low natural gas prices boost natural gas-intensive industries. Industrial shipments grow at a 3.0% annual rate over the first 10 years of the projection and then slow to a 1.6% annual growth over the balance of the projection. Bulk chemicals and metals-based durables account for much of the increased growth in industrial shipments. Industrial shipments of bulk chemicals, which benefit from an increased supply of natural gas liquids, grow by 3.4% per year from 2012 to 2025, although the competitive advantage in bulk chemicals diminishes in the long term. Industrial natural gas consumption is projected to grow by 22% between 2012 and 2025.
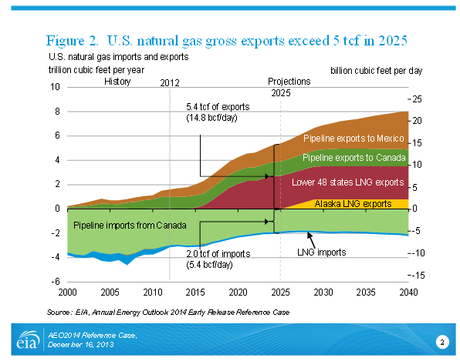
Figure 2. U.S. natural gas gross exports exceed 5 tcf in 2025. (Source: EIA, AEO2014 Reference case)
Higher natural gas production also supports increased exports of both pipeline and liquefied natural gas (LNG). In addition to increases in domestic consumption in the industrial and electric power sectors, U.S. exports of natural gas also increase in the AEO2014 Reference case (Figure 2). U.S. exports of LNG increase to 3.5 Tcf before 2030 and remain at that level through 2040. Pipeline exports of U.S. natural gas to Mexico grow by 6% per year, from 0.6 Tcf in 2012 to 3.1 Tcf in 2040, and pipeline exports to Canada grow by 1.2% per year, from 1.0 Tcf in 2012 to 1.4 Tcf in 2040. Over the same period, U.S. pipeline imports from Canada fall by 30%, from 3.0 Tcf in 2012 to 2.1 Tcf in 2040, as more U.S. demand is met by domestic production.
Car and light trucks energy use declines sharply, reflecting slow growth in travel and accelerated vehicle efficiency improvements. AEO2014 includes a new, detailed demographic profile of driving behavior by age and gender as well as new lower population growth rates based on updated Census projections. As a result, annual increases in vehicles miles traveled (VMT) in light-duty vehicles (LDV) average 0.9% from 2012 to 2040, compared to 1.2% per year over the same period in AEO2013. The rising fuel economy of LDVs more than offsets the modest growth in VMT, resulting in a 25% decline in LDV energy consumption decline between 2012 and 2040 in the AEO2014 Reference case.
Natural gas overtakes coal to provide the largest share of U.S. electric power generation. Projected low prices for natural gas make it a very attractive fuel for new generating capacity. In some areas, natural-gas-fired generation replaces power formerly supplied by coal and nuclear plants. In 2040, natural gas accounts for 35% of total electricity generation, while coal accounts for 32% (Figure 3). Generation from renewable fuels, unlike coal and nuclear power, is higher in the AEO2014 Reference case than in AEO2013. Electric power generation from renewables is bolstered by legislation enacted at the beginning of 2013 extending tax credits for generation from wind and other renewable technologies.
The Reference case projections from the Early Release Overview of the AEO2014 are available here. The AEO2014 full version will be released early Spring 2014.

