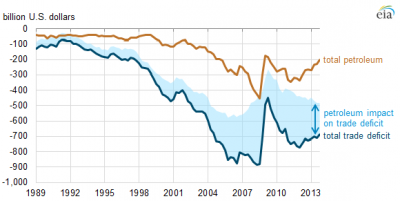
 Merchandise trade deficits, by quarter, 1989-2013. (Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic
Merchandise trade deficits, by quarter, 1989-2013. (Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) balance of payments adjustments to Census Foreign Trade data)
Since 2009, exports of petroleum and petroleum products have played a growing role in reducing the overall merchandise trade deficit.
Since the mid-1970s, the United States has run a deficit in merchandise trade, meaning that payments for imports exceeded receipts for exports. This large and growing deficit on the merchandise trade balance reached a maximum of $883 billion in the second quarter of 2008.
SEE ALSO: OPEC’s Annual Statistical Bulletin 2014 Released
As a result of the recession, dramatic declines of imports in excess of exports during the fourth quarter of 2008 and the first quarter of 2009 reduced the merchandise trade deficit by 49%, to $449 billion in the second quarter of 2009. This trend of declining imports resulted in the lowest quarterly deficit level since early 2002. The merchandise trade deficit then increased to $686 billion in the fourth quarter of 2013, with much of the difference from the 2008 level ($131 billion) attributable to a $158 billion increase in net exports of crude oil and petroleum products.
Crude oil and petroleum products play a significant role in the balance of U.S. trade accounts, and the value of petroleum trade is sensitive to both changes in price and volume. The United States has historically imported more petroleum and petroleum products than it has exported. The deficit reached a maximum of $452 billion in the third quarter of 2008, as a result of a sharp run-up in prices. By the first quarter of 2009 the petroleum trade deficit improved to $174 billion as energy prices and domestic demand fell and U.S. production increased. From the first quarter of 2009 to the second quarter of 2011, the deficit increased to $346 billion, because of continued economic recovery in the United States and higher crude oil prices. Since then, prices have remained high as exports of petroleum products have increased while crude oil imports have declined. As of the fourth quarter of 2013, the deficit was $203 billion.
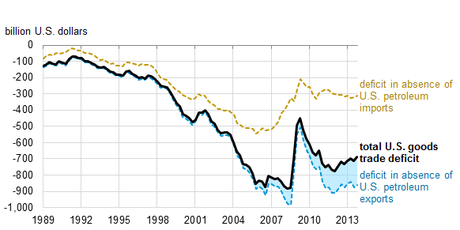
Effects of petroleum exports and imports on the total U.S. merchandise trade deficit, by quarter, 1989-2013. (Credit: Source: U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) balance of payments adjustments to Census Foreign Trade data)
Trade in petroleum and petroleum products contributes to the overall U.S. goods deficit, but this deficit would exist even if the United States did not import oil. Since 2009, exports of petroleum and petroleum products have played a growing role in reducing the overall merchandise trade deficit. While there have been recent increases in crude oil exports, nearly all of the petroleum exports through 2013 were refined petroleum products.

