Recently we were thinking about approaches to detect Fake News. Fake news is false or misleading information presented as news. It often has the aim of damaging the reputation of a person or entity or making money through spreading the news. However, the term does not have a fixed definition and has been applied more broadly to include any type of false information, including unintentional and unconscious mechanisms, and also by high-profile individuals to apply to any news unfavourable to their personal perspectives.
What If we could change the FaceBook algorithms that magnify conflicts and love naked opinions in order to keep the participants busy with reading ads, into an educating machine for sound thinking and communicating.
What if we could flag Fake News on the Internet?
Some approaches
Overview of approaches to detect fake News we came up with.

- Interpretations of interests and motivations
- Fallacies
- Thinking errors
- Lack of Orderly Argumentation
- Speech Patterns
Interpretations of Interests and Motivations
Anytime a text mentions a possible explanation why the writer expresses what he thinks, it will be flagged as ”Possible Biased”. This means that the thinking as such is not discussed, but that an interpretation is given to it, which cannot be found in the text itself.
The critics have attributed a motivation for what the writer has given his opinion, mostly a psychological reason or an economic motive. For example:

- It is quite logical the way she thinks, she depends on the subsidy!
- Of course he thinks so, he has shares in that company
- She will never make a controversial statement, so don’t accept her arguments
- He can react no other, because, if he still wants to make a career
- Of course she reasons that way, she is a climate alarmist/climate denier
A “frame” is set up that ensures that it is no longer necessary to look at the substantive argumentation of the statement or conclusion. If such attributions are systematically detected, worldwide, a kind of sanitizing of discussions arises.
It shouldn’t be that hard to discover framing with software. There is after all a difference between the words used in the argumentation and the words in the response or critique to it.
Fallacies
It must not be that difficult to design software that with the help of analysis of language can detect known fallacies. A fallacy is reasoning that is logically incorrect, undermines the logical validity of an argument, or is recognized as unsound. Some examples are ;
24 most common logical fallacies

- Strawman. Your logical fallacy is strawman
- False cause. Your logical fallacy is false cause
- Appeal to emotion. Your logical fallacy is appeal to emotion
- The fallacy fallacy. Your logical fallacy is the fallacy fallacy
- Slippery slope
- Ad hominem
- Tu quoque
- Personal incredulity
See also List of Fallacies, Wikipedia
Thinking Errors
Thinking Errors or Cognitive Distortions could be

- All-or-Nothing Thinking / Polarized Thinking
- Overgeneralization
- Mental Filter
- Disqualifying the Positive
- Jumping to Conclusions – Mind Reading
- Jumping to Conclusions – Fortune Telling
- Magnification (Catastrophizing) or Minimization
- Emotional Reasoning
Also here, we assume that it might be easily detected by AI algorithms, see also Cognitive Distortions: When Your Brain Lies to You (+ PDF Worksheets)
See also 50 Cognitive Biases in the Modern World.
Lack of Argumentation

If we might better analyze the logical structure of reasoning with software, then we are able to recognize fake news.
There are several methodologies available to assess reasoning as reasonable, rather reasonable, not believable or bull shit. Below is an example, made with Rationale, argument mapping software.
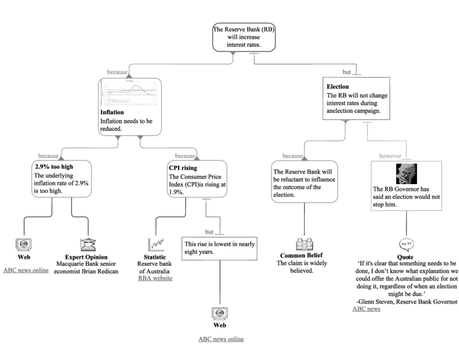
If even one element of the argument is missing, the text is flagged as “not critical” or “does not meet the requirements of an orderly argument”.
Speech Patterns

Studies show that psychopaths who have been convicted for murders, use certain speech patterns when they describe their crimes. Researchers believe that analyzing the playlists of certain individuals could be used to recognize potential psychopaths without them knowing it.

John Gotman measured how often certain speech patterns occurred during the span of a 15-minute conversation found; he could predict which marriages would end in divorce 93% of the time.
Perhaps we could build an AI algorithm that analyzes speech patterns that can disclose fake news.
