19 total views, 19 views today
The amount of data generated world-over is mind-boggling and unbelievable. Take a look at these hypnotizing numbers on data generated every minute. This gives rise to the need to have a highly effective database management system to sift through data for information.
- Snapchat users share 527,760 photos
- Google processed 40,000 searches
- 120 professionals joined LinkedIn
- 4,146,600 users watched YouTube videos
- 456,000 tweets sent on Twitter
- Instagram users posted 46,740 photos
- On Facebook 510,000 comments posted and 293,000 statuses updated
Data needs to be stored, organized and managed efficiently so that users are able to use the data efficiently and effectively.
SQL Database is a Relational Database and a structured one, but NoSQL is non-relational database that is document and distributed type.
SQL databases are scalable vertically and NoSQL databases horizontally.
NoSQL or Column-based databases are broadly used in managing data warehouses, CRM, business intelligence, Library catalogs. Column based databases/ NoSQL databases are HBase, CouchDB, Couchbase, Cassandra, MongoDB, Hypertable. These perform a significant role in handling, managing and using of the data.
Crucial features of MongoDB as stated below:
- Safety and Availability via ReplicaSets
- Performance and Scalability through automatic sharding
- Flexible schema
To take a decision which database management system would be most effective to use, we need to take into consideration features such as flexibility, expand-ability, presentation and accessibility needs to be taken into consideration. The success of any database depends on how effectively they meet the requirements of users.
There are plenty of NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Hbase, Redis, CouchDB, Cassandra, Couchbase, Oracle NoSQL, Amazon DynomaDB and Neo4j. Here we shall compare only MongoDB and Couchbase.
We shall look into features of others in a latter blog.
MongoDB stores data as BSON (Binary JSON), ruby hashes, etc., And stores data in a commendable manner being capable of saving documents and arrays. This document query language is supported by MongoDB which plays an important role in assisting active queries. It's also easy to scale.

Couchbase Server (also known as Membase), is an open-source NoSQL, distributed multi-model, document-oriented database optimized for interactive applications. This application serves concurrent users for varied tasks such as to create, store, retrieve, aggregate, manipulate and present data.
MongoDB is a database server with remarkable specification and an optional storage engine called WiredTiger. Hence the writing capability improves by ten times as compared to a normal one.
The inactive mode for the read and write activity lasts for 5 milliseconds at length. The performance of both (Mongo/Couchbase) DB can determined by their execution as users keep growing till the read and write inactivity overcomes the standard of 5 milliseconds. These two servers can be used on single or multiple servers as both of them store in documents. But they usually operate differently.
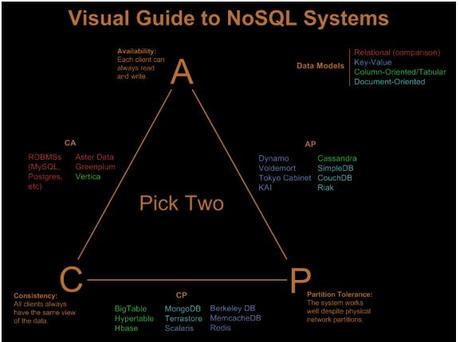
Database Management System Models

The Couchbase data model is a combination of both document and key-valued. And MongoDB is only document type. The Couchbase server is a mix of both document and key-valued. Therefore every document is assigned with a key value as all the documents have got keys. These can also be used to index services and query.
Query
MongoDB query is generally of Ad-hoc nature and with MapReduce aggregation. While the query of Couchbase server is more of N1QL, key-values and with Ad-hoc views.
Concurrency
As far as concurrency goes both Couchbase and MongoDB servers are optimistic as well as pessimistic locking, but the MongDB has an optional store machine called the WiredTiger.
MongoDB's work quality deteriorates as the users grow in number as it cannot handle too many customers and it starts performing adversely. More tools need to be added to serve more users through MongoDB which is expensive. While Couchbase supports a huge number of customers with a single node without its performance getting affected.
Performance
Couchbase is well managed and integrated completely for storing both data and indexes, without further needs of caching products for better performance.
MongoDB cache capability performs poorly and requires third-party tools for high performance. The performance is further affected by inefficient routing layers that add complexity and latency to any requests.
For some queries slow cross-node scatter and gather method is required due to rigid data and index partitioning limitations. Hence it limits query performance on large enterprise clusters.
Global indexes allow indexes to be partitioned independently of data, minimizing latency for important queries.Storage
MongoDB and Couchbase focus differently. Both scale across multiple nodes easily, MongoDB favors consistency while Couchbase availability.
Replication is a key concept in the database whereby data is copied from a database to another, so that a distributed database system can be created. This system ensures that users can access any data required without delay. CouchDB, allows master-master and master-slave replication which ensures that data can be accessed at various locations without delay. The append-only modifications of CouchDB ensure least chances of conflicts. And the option of selective replication controls the documents that will be copied. So you save a lot of space and time. MongoDB offers only master-slave replication. Setting up master-master replication is extremely complicated with greater chances of conflicts.
Fragmentation
In the MongoDB fragmentation process a fragmenting method needs to be chosen as well as a key has to be selected as the data model is document type. Couchbase fragments any given data on its own. This is then counted horizontally usually by spreading hash space to all nodes in the cluster of the given data. The key present in each document decides the placing of the hash space to a particular node.
The fragment key will give the correct location of the particular document in the cluster.
Therefore the difference between these two are, MongoDB depends on the user in selecting the fragment key and a fragmenting method, whereas the Couchbase server does the fragmenting on its own volition without any human intervention.
Mobile Conformability
Couchbase does in fact supports smartphones and it thus helps developing apps that you can go on to use with/without an internet connection. While MongoDB in truth does not support mobile applications because of which you have to write code for such Apps. This also entails that you need to have an internet connection always to use your apps.
Time Consumption and Management
CouchDB is a simple structure that is easy to deploy after its installation. It has also been found that the setup, adding and erasing of nodes are rudimentary and simple. MongoDB enquires physical and other added arrangements. Due to which the application is difficult, has lots of complexities and multi-parts.
Capacity To Perform
MongoDB fails all write operations when applied to too many data-centers due to its architecture. While CouchDB revels due to its simple architecture and duplication ability and performs all the write operations locally when it is applied to a large number of data-centers. Hence, the total effect is inactivity is minimized and performance is absolutely increased.
External Cache Required
MongoDB server does not have the capability to serve concurrent customers and the data size is high due to which there is a need of another cache to assist serving the customers which costs money and there could be complications. But with Couchbase the cache is incorporated initially and an organized entity which therefore does not require any external costs.
Conclusion Database Management System
NoSQL databases (Not Only SQL Databases) are non-relational database systems used for storing, saving and retrieving data. In times such as these it is not possible to store all data in table format which do not have fixed number of columns (predefined schema). Examples of data generated world over which is increasing tremendously: IoT generated data, social graphs, user generated data, and GEO-location data. Such data require processing to father information. Using NoSQL database such data can be stored in document form or graph-based data easily and quickly.
The genuine motivation to use NoSQL is the simplicity of its design, horizontal scaling of these to clusters of machines which is challenging to realize otherwise.


