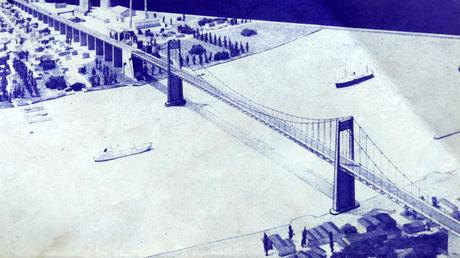
A few weeks ago, I picked up a pamphlet that was produced around 1960 and which provided a full overview of the ambitious project to build a suspension bridge over the Garonne between the Bacalan quarter of Bordeaux and Lormont. The bridge, referred to at the time as the “Nouveau Pont de Bordeaux”, went on to be inaugurated in 1967 and is now a familiar local landmark: the Pont d’Aquitaine.
Of course, the bridge was already the subject of a full Invisible Bordeaux report a few years ago, along with a video clip taking in the view from the cycle paths! But what more would I learn from this unusual fold-out pamphlet, credited to Ponts et Chaussées de la Gironde and comprising an impressive amount of originally handwritten data and information, along with a series of pre-computer age technical illustrations and cartography? And how did the technical drawings and maps compare with the finished product, 50 years on from completion?
 For a start, the financial structure of the project is detailed. The bridge itself and the left-bank viaduct were set to cost 97 million “nouveaux francs” (France had just switched systems) which, when accounting for inflation (using calculation methods developed by national statistics institute Insee), represents around 154 million euros in today’s money. The French State was delivering on two-thirds of the budget, while the Gironde département and the city of Bordeaux split the remainder in two. Throw in the right-bank connecting road and the bridge amounted to a 100-million-franc project.
For a start, the financial structure of the project is detailed. The bridge itself and the left-bank viaduct were set to cost 97 million “nouveaux francs” (France had just switched systems) which, when accounting for inflation (using calculation methods developed by national statistics institute Insee), represents around 154 million euros in today’s money. The French State was delivering on two-thirds of the budget, while the Gironde département and the city of Bordeaux split the remainder in two. Throw in the right-bank connecting road and the bridge amounted to a 100-million-franc project.The document also lists the quantities of the main raw materials that would be needed to build the bridge. To highlight but a few, these included 132,000 cubic metres of ordinary and reinforced concrete, 8,500 tons of steel for the reinforced concrete, 1,900 tons of cables for the support and suspension system and 4,350 tons of rolled steel for the bridge's main framework. In its initial configuration, the surface area of the bridge and viaduct amounted to 25,000 square metres.
 This is one of the things which may have changed over time: as specified in the pamphlet, the bridge originally comprised 2x2 lanes for road traffic (equating to a width of 14 metres), with 40-centimetre-wide reservations separating them from 1.50-metre-wide cycle paths on either side, in turn coupled with additional 1.10-metre-wide footpaths. When the suspension structure was overhauled between 2000 and 2005, the deck was extended to 2x3 lanes; as a result automobile traffic took up all the available space between the pylons. The cycle path was now aligned with the pylons; when reaching the pylons, the path was diverted, snaking around the pillars on newly-added platforms. The footpaths had already disappeared in 1980 (freeing up space for a "fifth" central lane of traffic) and today the bridge very much remains a non-pedestrian zone.
This is one of the things which may have changed over time: as specified in the pamphlet, the bridge originally comprised 2x2 lanes for road traffic (equating to a width of 14 metres), with 40-centimetre-wide reservations separating them from 1.50-metre-wide cycle paths on either side, in turn coupled with additional 1.10-metre-wide footpaths. When the suspension structure was overhauled between 2000 and 2005, the deck was extended to 2x3 lanes; as a result automobile traffic took up all the available space between the pylons. The cycle path was now aligned with the pylons; when reaching the pylons, the path was diverted, snaking around the pillars on newly-added platforms. The footpaths had already disappeared in 1980 (freeing up space for a "fifth" central lane of traffic) and today the bridge very much remains a non-pedestrian zone.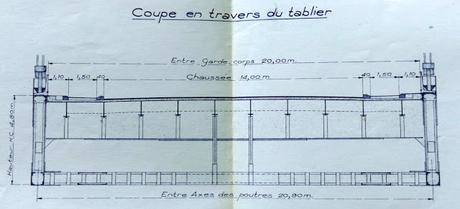
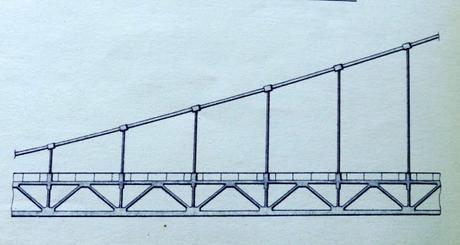
Cross-section of the original deck, showing the cycle paths and footpaths on either side.

The cycle path (which lies just behind the red barriers) now loops around the exterior of the pylons.
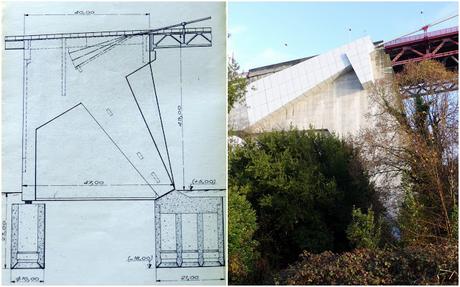
Leafing through the technical drawings, it does look as if the design of the top of the pylons must have been revised ahead of construction, with slightly slimmer horizontal sections connecting the vertical pillars on the finished product.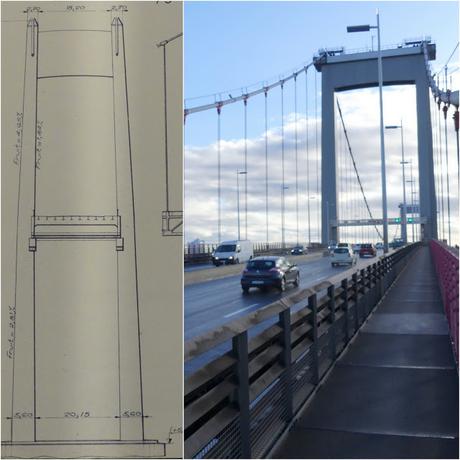
Reassuringly, the engineers’ calculations regarding the viaduct’s 4.66% gradient and the curvature of the suspension system translated seamlessly into reality.
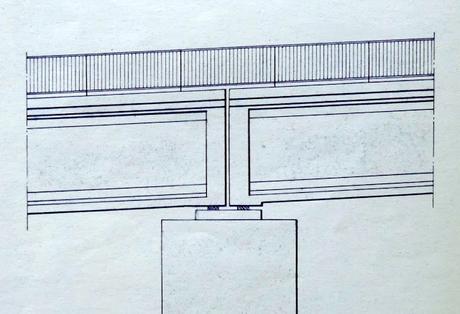


The deck now spills over the edge of the structure (where the cycle path passes) when it must have been perfectly aligned in the bridge's original configuration.
The pamphlet also provides a cross-section view of the bridge's original suspension cables, each of which was made up of 37 individual cables that were 78.5 millimetres in diameter. Elsewhere in the document, it is explained that those individual cables comprised 208 4.7-millimetre steel wires. In all, each 48cm x 55cm suspension cable weighed in at 1.15 ton per meter. During the 21st-century renovation, all that changed was the diameter of the individual cables (72.6mm) and associated steel wires (127 4.1 mm wires), along with the overall size of the suspension cables (45cm x 51cm).
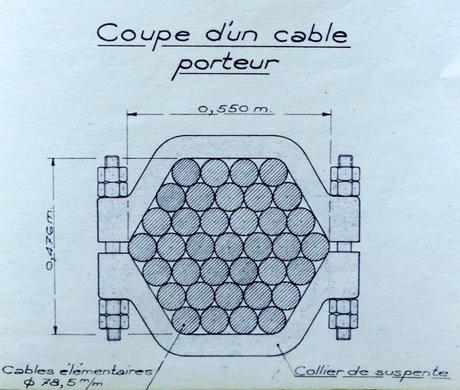

A close-up view of one of the sealed suspension cables, at one of the points where it is clamped to the bridge, and the point where it enters the foundation block pictured further up the page.
Finally, while the bridge itself is still, at the time of writing in 2017, a highly recognisable result of those early-1960s designs, one thing which has changed considerably is the surrounding road infrastructure. Take, for instance, the lowly roundabout which would have provided an initial means of connecting traffic to and from Bordeaux and the bridge with the “futurs boulevards extérieurs” (now lovingly referred to as the Bordeaux Rocade) which has, over time, become a complex spaghetti junction notably fed by traffic from the busy Bordeaux Lac business, exhibition, hotel and retail park.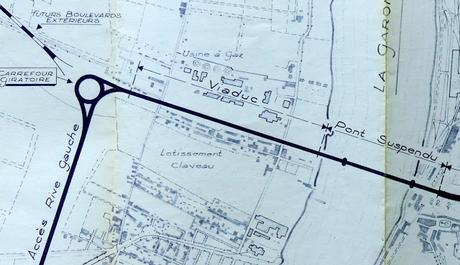
The way it was planned in the 1960s and the way it is now (via Googlemaps): the humble roundabout has become a spaghetti junction.
All of which brings us back to the present-day Pont d’Aquitaine, the Bordeaux suspension bridge which isn’t doing so badly for a 50-year-old! Despite the arrival of leaner, more fashionable counterparts spanning the Garonne, and even though it will never quite have the picture-postcard cachet of the Pont de Pierre, the Pont d’Aquitaine still stands tall and proud, enjoying its prominent status as the main gateway between the city and the Gironde Estuary which lies beyond (a little further downstream), and providing the final physical means of crossing the river ahead of the Atlantic ocean.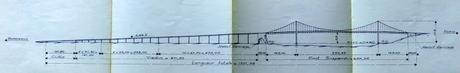
> Locate it on the Invisible Bordeaux map: Pont d'Aquitaine, Bordeaux/Lormont> Read the original Invisible Bordeaux introduction to the Pont d'Aquitaine> Ce dossier est également disponible en français !
> Big thanks to Frédéric Llorens for the additional information about when the pedestrian footpaths were removed. > And check out the exclusive Invisible Bordeaux guide to the view from the bridge!
Click here if video does not display properly on your device.
