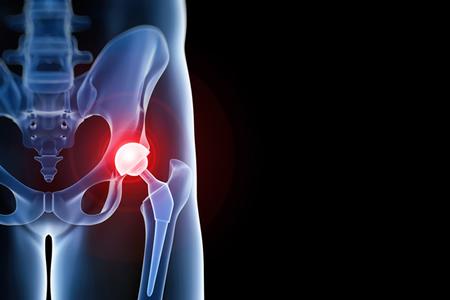
Artificial joints are a prosthesis or prosthetic joint, made of metal, ceramic, or plastic, which is implanted to replace a diseased or damaged natural joint. Joints can be damaged by various causes, arthritis, injuries, and other diseases. Replacement arthroplasty, also known as joint replacement surgery, is an invasive procedure of cosmetic orthopedic surgery where an arthritic or degenerative joint surface is replaced by artificial joints.
This operation involves the surgical reconstruction of a joint and its surrounding tissues. When serious joint pain or stiffness is not relieved by more-restful non-surgical therapies, joint replacement is usually considered as an effective treatment. Although replacement arthroplasty is more invasive than other joint reinstalls, it can often be performed in less time and at a lower cost than other reconstructive surgeries.
Other factors that can cause arthroplasty to be recommended include prior damage to the joint, the presence of osteoarthritis or other autoimmune diseases, and progressive bone age. These conditions are sometimes associated with arthritis, which makes arthroplasty an ideal treatment for them. Other factors that can make this treatment desirable include a bony growth on the joint, or a joint deformation that does not respond to traditional anti-inflammatory treatments.
Patients with severe joint inflammation can also benefit from artificial joints because their pain has progressed to the point at which conventional treatments have been ineffective. Moreover, some patients find that their arthritic condition makes healing difficult because of decreased range of motion. Moreover, osteoarthritis is the most prevalent musculoskeletal disease, which affects geriatric population. Thus, with the growing geriatric population, demand for artificial joints is also increasing with a rapid pace.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the nation's 65-and-older population is projected to reach 83.7 million in the year 2050, almost double in size from the 2012 level of 43.1 million. There were 54 million U.S. residents 65 years and older in the 2019. However, high cost of artificial joints is expected to hamper the demand for artificial joints.
artificial joints, prosthetic joints, prosthesis joints, damaged joint, healthcare, joint inflammation, tissues, surgical reconstruction, autoimmune diseases
