Here’s a bit of energy news that didn’t make it into our daily coverage during the past week. In this review, we collected some of less big, but nonetheless interesting news, of the week that went by, from the world of energy science and technology.
SEE ALSO: 8/8/2014 This Week in Energy: Beyond Headlines
Solar Energy
Big Box Stores Unmet Renewable Energy Demand
12 companies have signed the Renewable Energy Buyers’ Principles to better communicate their purchasing needs and expectations to the marketplace. The companies — Bloomberg, Facebook, General Motors, Hewlett-Packard, Intel, Johnson & Johnson, Mars, Novelis, Procter and Gamble, REI, Sprint, and Walmart — hope the principles will open up new opportunities for collaboration with utilities and energy suppliers to increase their ability to buy renewable energy sharing a combined renewable energy target of 8.4 million MWh per year through 2020.
China Requests Extension for US Solar Trade Case Settlement
The Government of the People’s Republic of China has this week requested its lawyers to issue a plea for more time in submitting a proposed suspension agreement in the ongoing solar trade dispute with the U.S.
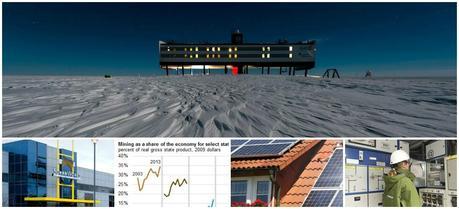
Solar Panels Lower Electric Bills, Increase Home Value
What were once considered an expensive novelty for environmentalists have become a growing trend among energy-conscious homeowners: rooftop solar panels.
Electrical Grid
Iberdrola Completes Installation of First Three Million Smart Meters in Spain
In the month of July, Iberdrola finished installing Spain’s first three million smart meters within the framework of the remotely managed and automated grid system project, otherwise known as the “STAR” project, or Sistema de Telegestión y Automatización de la Red, underway in all Spanish autonomous communities with distribution grids. The Company has likewise adapted 14,500 transformation stations to enable them for remote management, supervision and automation.
Research
Study of Aerosols Stands to Improve Climate Models
Of all the factors that influence Earth’s changing climate, the effect that tiny particles in Earth’s atmosphere called aerosols have on clouds is the least well understood. Aerosols scatter and absorb incoming sunlight and affect the formation and properties of clouds. Among all cloud types, low-level clouds over the ocean, which cover about one-third of the ocean’s surface, have the biggest impact on the albedo, or reflectivity, of Earth’s surface, reflecting solar energy back to space and cooling our planet.
U.S. Department of Energy Increases Access to Results of DOE-Funded Scientific Research
The U.S. Department of Energy is introducing new measures to increase access to scholarly publications and digital data resulting from Department-funded research. The Energy Department has launched the Public Access Gateway for Energy and Science — PAGES — a web-based portal that will provide free public access to accepted peer-reviewed manuscripts or published scientific journal articles within 12 months of publication.
International Antarctic Community Formulates Tomorrow’s Challenges to Research
Appearing online in the scientific journal Nature is a forward-looking article by 75 leading Antarctic researchers and science managers from 22 countries. The so-called “SCAR Horizon Scan” catalogues the 80 most pressing questions to be pursued during the next 20 years of research in the Antarctic and the Southern Ocean. In this interdisciplinary exchange of ideas, three scientists from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research contributed to working out the topics that now establish the thrust of Antarctic research.
Oil and Natural Gas
EIA Publishes Upstream Financial Review of the Global Oil and Natural Gas Industry 2013
This analysis focuses on financial and operating trends of the oil and natural gas production business segment, often referred to as upstream operations, of 42 global oil and natural gas producing companies (the upstream group).
Energy Production and Other Mining Account for Large Percentage of Some State Economies
At the national level, establishments that extract crude oil and natural gas as well as naturally occurring mineral solids, such as coal and ores, collectively referred to as the mining sector in economic data, accounted for about 2% of the U.S. economy last year. In some states, though, the mining sector accounts for a much larger share of the economy. Of the six states where mining comprised more than 10% of the state’s economy in 2013, mining growth resulted in five of those states having higher economic growth than the national average.

