Today we are using mobile phones for social media, shopping, banking, movies, online meetings, emails, and whatnot. Can we have a single day in our life without a mobile phone today? You’d be thinking of a no right? Something like ‘it’s near to impossible’.
Mobiles have different models, screen resolutions, operating systems, network types, hardware configurations, etc. How to make sure that an application works fine on all these different combinations? Also, how to test the hardware of the mobile phone itself, is it supporting all the software as it should?
To answer all these questions we need exhaustive mobile testing in place. Let us have a look at the most popular types of mobile testing for applications and hardware.
1. Functional Testing
Functional testing is a broad testing term can be applied to other types of products too and not only mobile. But here, because in this article, we will keep the scope limited to mobile.
As a type of mobile testing, functional testing ensures that the application works as per the requirements. We check that all the functionalities are working as intended. Functional testing is required to provide a quality product, meet product requirements, ensure customer satisfaction, and to reduce risk.
Example: Let’s take an example of an e-commerce mobile app.
Function: User is able to add product in the cart. A user logins into an app searches a product and adds a product to the cart. Here we have validated that the ‘Add to cart’ functionality is working fine.
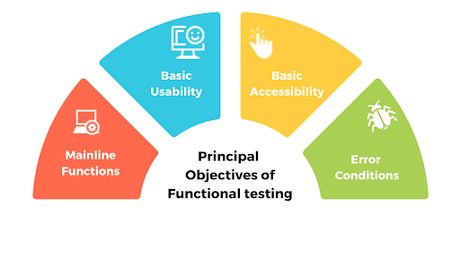
Reference: https://www.qatouch.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/Principal-Objectives-of-Functional-Testing.png
Functional testing for mobile applications can be performed by-
i. Unit Testing– Developers execute unit tests for the smallest unit of code, whenever they commit new code in the code repository.
Example: We are considering the same e-commerce app example, a small unit like ‘login’ may be tested during the unit testing.
ii. Integration Testing– Integration and working of different systems together are tested using integration testing.
Example: Here, we test the integration of two or more modules like- from cart to make a payment module.
iii. End-to-End testing– Testing of the whole system together is performed using end-to-end testing. It is executed on the real devices either using automated tools or manually.
Example: We check the flow starting from login->search->add to cart->payment.
We perform testing from the starting of the flow till the end of the flow.
Functional Testing can be easily automated once the features being tested are stable and are not expected to go through a lot of new changes. This automation should always be done looking at the long term returns.
2. Usability Testing
The mobile application is tested for a good user experience, good standard layout, intuitiveness of the UI, ease of use by the user. The users should be able to perform tasks on the application quickly without putting in the effort to understand the layout and buttons.
Usability testing is done with real devices and real users to gain actual insights about the user experience. The users are provided with test cases/tasks to complete on the application and then a questionnaire is provided to them. The feedback received during the usability testing is used to enhance the application for more user-friendliness and bug removal.
Hence, the steps involved are-
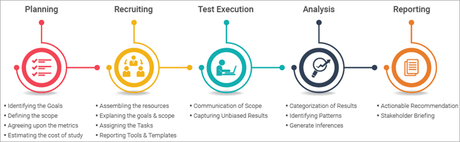
Reference- https://cdn.softwaretestinghelp.com/wp-content/qa/uploads/2020/11/Different-participants-or-elements-of-usability-testing.png
- Plan usability testing, write test cases and create test cycles
- Select appropriate users as testing candidates
- Get testing done by actual users
- Receiving feedback through a questionnaire and result in analysis
- Reporting and performing enhancements on the application
Example: Let’s assume that we have created a new app for e-learning. We may ask our users to use the app for searching a course of their choice and take a few classes on it after making the payment. We may have questions in the questionnaire like-
- Was it intuitive and easy for them to navigate through all pages?
- Did they find the assessment after the class easy and self-explanatory?
- Were the visuals present in the classes pleasing to the eyes?
- What do they want to change in the app?
- What can be done better?
- Was there a time they felt overwhelmed by the app and wanted to exit it?
Popular tools for usability testing are:
- Lookback
- Appsee
- Applause
- Userlytics
- Loop 11
You may learn more about Usability Testing, as a type of mobile testing, here. Read more about such tools here.
3. Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing is done to ensure that your mobile app is working and is compatible on all the different types of mobile devices that you aim to support. This testing is crucial to ensure standard usage and performance of your app on various devices, operating systems, hardware, browsers, and their different versions.
Compatibility testing is performed on a range of probable environments which includes-
- Operating Systems- Windows, iOS, Android, etc.
- Browsers- Firefox, Chrome, Safari, etc.
- Devices varying in screen size, resolution, memory, etc.
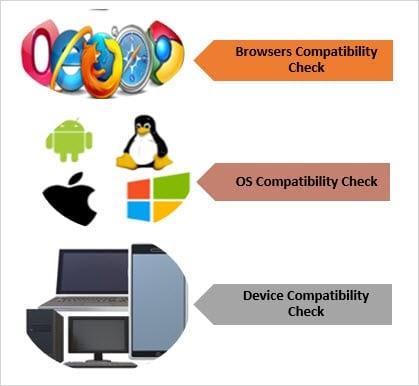
Reference: https://cdn.softwaretestinghelp.com/wp-content/qa/uploads/2018/04/Compatability-Testing.jpg
Here we are dealing with thousands of probable environments, therefore it is difficult to perform it manually.
Let’s take an example of Amazon Prime video, it is compatible on iOS and Android smartphones and tablets. Also, it is compatible with a range of smart TV’s, Blu-Ray players, PlayStations etc. Which results in thousands of combinations of devices, OS, resolutions, screen sizes etc.
In such scenarios where the manual testing can take up a lot of your time and costs, it is advisable to go for a tool that helps you do most of it manually. Testsigma is one such tool that eases the compatibility testing to a great extent. It provides thousands of environments which are ready to use without any setup and coding knowledge. You can setup your tests quickly on its intuitive test creation interface and soon get started with executing them.
Try Testsigma for a hassle-free iOS and Android automation and execution
Check how to automate your mobile application in 3 easy steps using Testsigma.
4. Performance Testing
Performance testing is executed on a mobile application to ensure that the application remains stable, functional, and responsive under an increased workload. The workload can be in terms of mobile device usage or website usage in case of the mobile web.
These tests are really important to have a mobile application which does not stop functioning under varied load. Users may not think twice about switching from a bad performing application and you don’t have to think much about it if you did your performance testing well.
Parameters that are measured during performance testing ( for mobile ) include – speed, memory consumption, battery life, data transfer, etc.
Different types of performance tests are-

Reference: artoftesting.com
i. Load tests– We test the application performance by providing real-life expected load, i.e. expected number of users.
Example: Let’s say, the expected load on a music streaming app is 20000 users per day. So we will load test it for different geo-locations, maximum users per day, session times etc. making sure that the app performs well under that load.
ii. Stress tests– We test the application performance by providing a higher than real life expected load. This helps in realising the breaking point of the application under a higher load. This helps ensure that the application will perform well even in case of unexpectedly high load.
Example:
You must have heard of result declaring websites crashing on the day of result declaration. Or e-commerce apps failing on the day of big sales. These are all the examples where sufficient stress tests were not done or the estimates of load were not in tandem with the real usage.
One of the tool that is widely used for such types of test is ‘Apache JMeter’. There are other such tools out there too.
iii. Endurance tests– We test the application performance by providing workload for a longer time to test its endurance.
Example: For a banking application, the number of online transactions is expected to increase before bank holidays. These transactions keep happening throughout the day. To ensure that the app performs well during such holidays, Endurance tests are done.
Some majorly used tools for this purpose are: LoadRunner, LoadComplete
iv. Volume tests– We test the application performance by providing a high volume of transactions/ data to the application for processing. This can be considered similar to load testing, endurance testing.
Example: On the last day of tax-filing, the website sees a high volume of submissions, the website should be volume-tested for such occasions. This includes- database, memory, CPU usage etc.
Majorly used Tools: JMeter, LoadRunner
v. Spike tests– We test the application performance by providing a number of sudden increases (spikes) and sudden decreases in workload.
Example: When an OTT platform like Netflix releases a famous web series, there is a flock of users on that platform. This causes an extreme spike in the workload for some time after which the app usage returns to normal levels. Such scenarios need to be tested via spike tests. Because it is difficult to have so many real users to test, we use automated tools to create virtual users.
Majorly used Tools: JMeter, LoadRunner
5. Security Testing
When we talk about Mobile Security testing, we need to cover below points-
- Authentication and Authorisation: Inefficient authentication and authorisation checks in the code may invite malicious attacks.
- Data Security: An application may expose sensitive data to other applications on the mobile phone and may cause intentional harm.
- Removing Hacking possibilities: Hackers are looking for vulnerabilities to find a way to hack the mobile phone and gain access.
- Safe communication: Transmission of sensitive data over networks without encryption may cause havoc to user sensitive data.
The Mobile Security Testing can be performed in three ways-
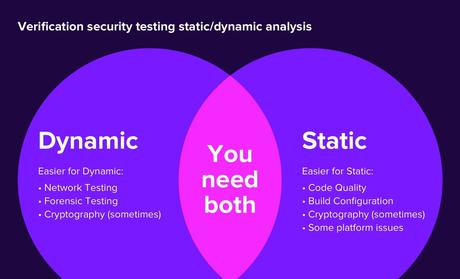
Reference: https://cdn.star.global/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/17050916/05_Content_1450x880.jpg
1. Static analysis: Code analysis is done to identify vulnerabilities and verify the implementation of security measures. The static analysis is done without actually executing the application. It can be done manually, using automated tools, or through a hybrid approach. During the manual review, we can take help of the IDE’s, or manually check the API and database calls. Many IDE’s provide plug-ins and external tools to perform automated static analysis.
2. Dynamic analysis: The applications are executed in real-time and tested for weak spots like authentication/authorisation issues, server issues, data transfer breaches.
3. Penetration testing: It is a type of security testing, which is conducted on a fully developed application. There are automated tools available for performing penetration testing on mobile applications.
Example: Authentication process between client and server is processed through the request-response model. If a basic HTTP protocol is being used for the authentication this may pose a risk. And hackers may steal the authentication information from here to break the system. Therefore, we should use secure SSL protocol for authentication. That was just a basic security test. But should give you an idea of its importance.
6. Installation Testing
When this type of testing is specific to a mobile,we test the ease and success of installing an application on various environments. We make sure that all the components of the application are successfully installed and working in coordination. This also, means that we need to check the uninstallation process as well. When the application is uninstalled from the device all related files should get deleted as well.
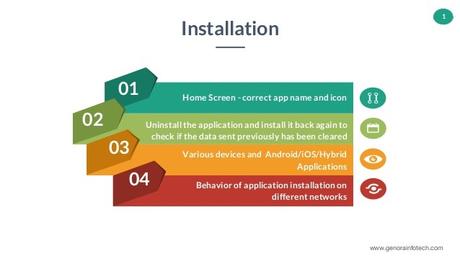
Reference: https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apptestingguidelinesatgenora-180201112026/95/mobile-app-testing-guidelines-at-genora-1-638.jpg?cb=1517484101
We check the below points while performing Installation Testing-
- Compatibility with the OS, hardware, devices, and their versions.
- Memory location where the application is getting stored i.e. internal memory or SD memory.
- Upgrade to a higher version should properly work. If the upgrade is interrupted mid-way then the older version should work successfully.
- Check for memory space and behavior of application during installation. If there is not enough memory then the application should show the appropriate message.
- Check for the battery and behavior of application during installation.
Example: An app is tested for installation, during the installation process the network is changed from wi-fi to mobile device’s 4G connection. We would want to confirm that the change in network connection doesn’t stop the app installation in the middle.
Another example is that an app is not properly tested for the forced stop of installation in the middle of the installation process. When used in real-life scenarios, apps when forced breaking the installation process app may cause some unexpected behavior on the mobile device.
7. Localization Testing
It is a customisation process which ensures that the application is compatible with the language/currency of the country or region where it is being used. As a type of mobile testing, It ensures that the GUI of the application is appropriately customised to make it relevant to the country of use.
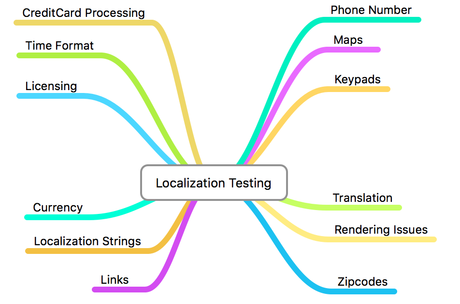
We check the following during Localization Testing:
- Linguistic accuracy
- Cultural appropriateness
- Messages, help document, commands are in accordance with the country/region
- Symbols, logos, and inputs to the application are properly customised
Example of a localization: For an e-commerce website there is no option to change the currency to the local currency of the country. It is a localization testing related bug.
Automation of the Localization testing:
Automation of the localization testing is challenging due to the variation in text lengths in different languages, the difference in currencies, zip-codes, symbols. Definitely writing the automation code covering all of these differences is quite challenging. To identify the ‘Web-elements’ can also become difficult with different languages.
Example a UI element(button) is recognised by caption ‘Cancel’, in any other language it will be different. Hence, we are required to use a locator which remains constant in all the languages.
Automation is difficult to implement, however, could be really rewarding in handling large projects. If automation testing is implemented from the early-development then it could be helpful for everyone in the team.
8. Exploratory Testing
“Exploratory Testing is not so much a thing that you do; it’s far more a way that you think.“, is a quote by Michael Bolton. Which clearly states that it is done by humans and not machines since machines/ automation cannot think. Exploratory testing means manually exploring the application to find its limitations and loopholes. Here, testers are not bound to follow the scripted tests, they run test cases on the fly by applying their thinking and creativity.
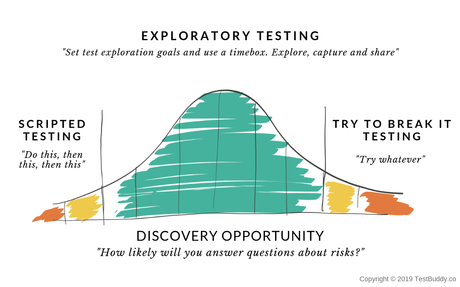
Reference: https://miro.medium.com/max/1200/1*16lX43SmbeiZrl_P0RVFGg.png
When considering this as a type of mobile testing, the testers explore the applications for-
- Compatibility on multiple devices
- Easy keypad usage
- Speed of the application
- Performance on interruptions by SMS, calls, and notifications
- Visual testing of the application in portrait and landscape mode of the device
- Proper display of navigation on the screen
Example: In real life when we are traveling through a car and we do not know the route, what do we do? That’s right, we explore! We explore by asking the people around or calling a friend or use the road signs. We explore on the fly and this is exactly the same as exploratory testing.
Consider a travel booking mobile app. On that app, a user usually applies a coupon code after they have decided the travel. But an exploratory test could be that the coupon was applied and then the user decided to do more of exploring and then change the travel details.
For exploratory testing, there are no scripted test cases, there is just a clear motive which can be written in a notebook. This testing is important though because your users are not going to use your app according to how you scripted it. They will use their brains and have the tendency to go about exploring your app without following a standard protocol. Sometimes, it is during this testing that major app crashes and security issues are uncovered.
9. Interruption Testing
This is the type of testing which is very important for mobile devices because there are a number of interruptions that can occur during an app use on a mobile device.
The main motive of this testing is that – while using an application if an interruption occurs then an application should be able to resume its state. To test that an application is able to resume work in case of an interruption is Interruption Testing.
Let us consider an example of a bug that came about because proper interruption testing was not performed on a mobile game app. The person was playing on the app, he was on a crucial stage and was about to finish the last stage of the game when the battery died.
The person quickly plugged it into charging and restarted the app, only to find that all their progress was lost. This app was not testing for interruption testing where the interruption was battery discharge.
During running an app, if a voice call comes over the phone then also that is an interruption. The app should not freeze/ or restart from the beginning after ending the voice call. The expected behavior is that the app should resume the game from where the user left it.
Interruptions for a mobile application can be-
- SMS
- Internet disconnection
- Device getting auto-locked while performing some other task like video/meeting
- Incoming call
- Notification from other applications
- Alarm
- Low battery notification
- Connecting charger

Reference: http://blogs.quovantis.com/what-is-interrupt-testing/
In case of interruption, the application starts running in the background and when resumed, it again starts working where we had left. Hence, Interruption Testing ensures the below points-
- Application is not crashed or hanged
- Application is resumed successfully
- If we do not tap on the interruption, the application successfully ignores the interruption.
We have tools for performing interruption Testing, e.g., UI AutoMonkey for iOS
10. Memory Leak Testing
Most of the Android applications are coded in Java. Fortunately, Java has its own garbage collection which frees all the memory which is unnecessary and unused. But sometimes there can be some scenarios where the previously used memory is not deallocated. Hence the pile of unused and occupied memory keeps on increasing. This causes applications to crash because of less memory at disposal. This phenomenon is called a memory leak.
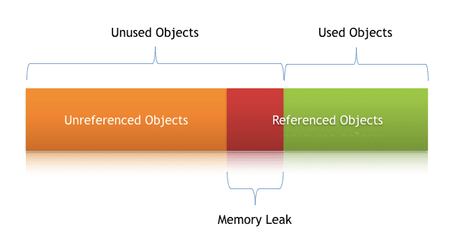
Reference: https://www.baeldung.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Memory-_Leak-_In-_Java.png
Memory Leak Testing cannot be performed using black-box techniques. Hence, it is performed via white-box techniques at the code level. Also, it is better to unit test the application to catch the memory leaks early in the development cycle.
It is advisable to test on multiple devices to understand the memory leak pattern better and get it fixed.
When this type of testing is not performed on a mobile application, it may cause the application to slow down and then finally crash in the middle of the user operations. To rectify such situations, the user needs to restart the application again and definitely is not a good user experience.
Tools to detect memory leak:
- Profiling tools like IDE e.g. Visual Studio, they help us determine which area of application is using how much memory.
- Memory Validator- Memory leak analysis for C#, .Net, C++
- Valgrind memcheck- Memory leaks for C and C++
11. Recovery Testing
During Recovery Testing, we test how well the application copes up with a failure and starts working again. It is a non-functional testing type.
The failure can be :
- Software failure
- Connection issues
- Device hardware issue
Reference: https://cdn.educba.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Recovery-Testing.png
During Recovery Testing, as a type of mobile testing, we will check that application is able to restore the data after recovery. Another example could be that the mobile application is able to execute transactions during low battery or battery removal.
Example: When we have multiple tabs of a browser open in a system and suddenly the browser crashes. When we restart the browser does it recover all the open sessions? This is recovery and to ensure this we perform recovery testing.
12. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi Testing
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are not application-related features. They are mobile-related features and is a type of testing that is required during mobile testing.
Bluetooth Testing:
A mobile phone may be connected via Bluetooth to speakers, laptops, another mobile phone, etc. It is important to test the connectivity under different scenarios. Few of them could be-
- Test the time for reconnection after a dropped connection
- Test connections after restarting the mobile phone
- Test connectivity while the mobile phone is already connected to other devices
- Test on different devices and OS
- Battery performance while a connection is on
- Optimised file transfer
Example: The Bluetooth of the mobile phone has been checked for phone-to-phone connectivity on multiple devices. You find it working and are happy with the testing. Then one day a user tries to connect the phone’s Bluetooth to the car’s Bluetooth to play songs. What if it does not work? It will be a really bad user experience.
Similarly, during Covid-19 we have seen many countries adopting contact tracing apps which work solely on Bluetooth. If the Bluetooth testing of the mobile devices is not proper, the Govt. will receive false information about the contact traces.
Wi-Fi Testing:
Mobile and its applications should work perfectly when connected to Wi-Fi. Few scenarios for Wi-Fi testing could be-
- When Wi-Fi connectivity is lost and then gained again, the application should resume.
- Test behavior of the application when the network type is changed – 3G, 4G, and Wi-Fi.
- Check the Wi-Fi speed
- Test the security of the Wi-Fi network, it should be safe from hackers
Example: A mobile app is working fine on Wi-Fi and other network types. Suddenly the internet connection is lost and you try to connect with another device’s internet network using tethering to continue the app usage. But why is it not working? Maybe the testing was not performed on the app to work on tethering mode.
Here is a quick mobile testing checklist to go about testing your mobile applications.
“Cloud computing is growing, especially as we are all used to having our mobile devices link us to data wherever we are.” said Steve Wozniak. This quote is apt to conclude this article as it perfectly depicts the importance of mobile and mobile applications.

