Email, social media, and messaging apps are great for sending files around the world, but as the size of the files we share grows larger, we quickly discover their limitations. We’ll look at the best ways to transfer, send, and share large files in this post.
Transferring large files can be a pain without the right tools, whether you’re trying to send a promotional video to a client or a home tape to a family member.
Attempting to send a large number of video files via email is not ideal. You’ll need an alternative because email providers like Google (Gmail) only allow you to attach files up to 25MB.
11 Ways to Transfer, Share and Send Large Files
Here are the 11 most effective methods for transferring, sending, and sharing large files:
- Upload your files to the cloud. Cloud storage systems such as Files.com and Dropbox allow files to be distributed by sending links to the file’s location.
- Files should be compressed. Reduce the file size before sending using programs like 7-Zip, Express Zip, and WinZip.
- Use a virtual private network (VPN). ISPs impose restrictions on the size of the file and its true destination.
- USB Memory Stick Carry the file on removable storage to move it physically.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Use a simple, unencrypted file transfer system that is quick and capable of moving large files.
- SFTP allows you to send files over a secure tunnel and resume file transfers that have been interrupted by dropped connections.
- TLS protects secure browser connections in HTTPS, and FTPS is a secure file transfer system protected by TLS.
- Jumpshare is a service that allows you to share A link-sharing system with the option of creating a free account.
- Delivering a Hard Drive Transport a large number of files over long distances in a secure manner.
- Send to any location A system for storing and sharing files up to 10 GB in size.
WeTransfer is a service that allows you to send files. A free file access and distribution system that can handle files up to 2 GB in size and can be upgraded to handle files up to 20 GB in size for a fee.
How do I send large files via email?
1. Save your files to the cloud.
Uploading large files, such as photos and videos, to cloud storage is a great way to transfer them. Google Drive, Files.com, Dropbox, and OneDrive are just a few examples of popular cloud storage services. Each of these products has plenty of storage space to accommodate most file types.
These solutions are affordable, so you won’t have to pay a monthly fee to store and access your files in the cloud. Google Drive, for example, is free for the first 15 GB of storage space.
What characteristics should you look for in a large file transfer system?
We looked at the transfer software market and compared the options using the following criteria:
- The ability to handle large file transfers
- A number of safe transfer options are available.
- Options for air-gap transfers and an easy-to-use interface
- Logging of activities
- A free tool or a risk-free trial period
- A good set of useful tools at a fair price that provides good value for money.
Files.com is a website where you can download files.
Users pay a monthly subscription to Files.com, which comes in three different levels. The monthly fee for the Starter plan is $10 (£8.10). A 30-day free trial is available for users to test the system.
Media companies frequently use the Files.com system because it is especially good at transferring large files of up to 5 TB. To speed up file transfers to the server, the cloud service uses a transfer accelerator.
Instead of transferring a large file, once it is stored at Files.com, the user simply sends a link to the intended recipient for access to the server.
Pros:
1. Scalable solution that is suitable for both small and large businesses.
2. Long-term use is supported by robot user management, permissions, and access control.
3. Users can create links to files with special rules, such as expiration dates or click tracking.
4. Large files can be compressed for faster transfer.
5. Supports Dropbox, Google Drive, and OneDrive as well as other cloud-based storage options.
Cons:
While the platform is simple to use, learning and implementing some of the more advanced features can take some time.
Dropbox is another popular option among the three because it offers both a desktop and mobile application that allows you to upload files of any size. If you upload these files to the Dropbox website, you must stay under the 50GB limit.
The desktop application’s user interface is also very user-friendly; all you have to do is right-click the Share button on the file you want to send and then enter the email addresses of the recipients.
Pros:
- Allows file transfers between mobile and desktop devices.
- Automatic synchronization is supported.
- Is a subscription-based scalable platform
- Excellent for teamwork.
Cons:
- The app could do a better job of separating personal and work files.
- It might be easier to switch between accounts if this is the case.
- Permission management can be difficult to grasp and put into practice on a large scale.
Dropbox is free if you don’t need more than 2GB of storage. However, for $19.99 (£16.19), you can upgrade to the Professional version, which includes up to 2 TB of storage.
2. Prepare the Files for Compression

All you have to do is make a folder and put all of the files you want to move into it. After you’ve created the folder, right-click it and choose to Send to > Compressed from the menu (Zipped folder). The files are complete and ready to send.
It’s worth noting that file compression for JPEG and MP3 files is ineffective because they’ve already been compressed! Free compression software such as 7-Zip, Express Zip, and WinZip can be used to process the files.
Pros:
- You have more control over which channel the files are sent through.
- Saves time and money when transferring files and storing them on a cloud-based system like Google Drive.
Cons:
- It’s a manual process that necessitates file compression knowledge.
- Isn’t automatically applied to files, which wastes time when transferring files frequently.
- Isn’t useful for files that have already been compressed.
- The recipient must be able to decompress the files and retrieve them.
3. Use a virtual private network (VPN).
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a useful technique for transferring files because it allows you to bypass your internet service provider’s broadband traffic management restrictions (ISP). Many ISPs limit upload bandwidth in order to limit the size of files you can send.
A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your traffic and keeps your online activities private. When you use a VPN, your ISP is unable to see the contents of your web traffic. When it comes to file transfers, this means that your ISP won’t be able to determine the size of the files and thus won’t be able to place any restrictions on you.
Sending files through a VPN has its drawbacks. The internet connection will almost certainly slow down, and the files will not always arrive intact. So, if the quality is a major concern, it’s best to try a different tool.
Pros:
- Enables secure and private data transfer between two sites.
- Throttling based on protocol or application is bypassed.
- It’s possible that it’ll be faster than using a public service.
Cons:
- Technical knowledge of how to set up a site-to-site VPN or how to install one on your own is required.
- Not suitable for one-time transfers; rather, it is better suited to long-term file-trading, such as EDI partnerships.
4. USB memory stick

Transferring files with a flash drive is simple because all you have to do is plug the drive into your computer’s USB ports. You can drag and drop files into the drive once the computer recognizes them.
You can then eject the draft and send it to another device or person. While this method requires a little more legwork, it is very simple to implement. This one is a good choice if you want simplicity and dependability.
Pros:
- Possibly the most straightforward method of file transfer.
- It’s very simple to do.
- The files can be easily retrieved by the recipient.
Cons:
- Unless the drive is properly encrypted, it is not secure.
- If the drive is lost or corrupted, the data is lost.
- The process of ‘sneakernetting’ entails physically sending the USB drive.
- Not recommended for file transfers that must be completed within a certain amount of time.
- Not recommended for site backups or large file transfers.
- Continuous backups are not a viable option.
5. FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is a method of transferring files that have been around for a long time. FTP (File Transfer Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a TCP/IP protocol for transferring files between FTP servers and clients. FTP was created with the purpose of transferring large files in mind. All you need is an FTP client to get started with the protocol.
The advantage of FTP is that it makes up for its lack of security with its file management capabilities. Single transfers are unrestricted in size, and you can queue transfers, schedule future transfers, and send multiple files at once. FTP’s advantages make it one of the most efficient ways to send and receive files.
FileZilla and Xlight are two free FTP clients available online. FTP’s only drawback is that it is not secure. Passwords and usernames are sent in plain text, allowing an attacker to read the contents of files. Use FTP for non-confidential data to protect against attackers.
Pros:
- Simple to use, even for non-tech savvy users
- There are no limitations on the type of file, the size of the file, or the number of transfers.
- It’s a great way to trade files with someone you know and trust.
Cons:
- It isn’t as secure by nature.
- If it is misconfigured or has weak credentials, it can be hacked.
- If either site’s server or the internet is down, the system will not work.
- The technical setup is required, which necessitates IT knowledge.
6. Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
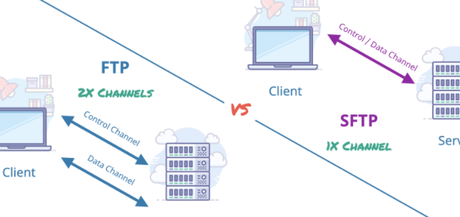
The server must authenticate the client user and ensure that the channel is secure before transferring a file. SFTP’s built-in security features make it ideal for sending sensitive data in a corporate setting.
SFTP transfers are included by default on most FTP servers. SolarWinds SFTP/ SCP Server, FileZilla, and Syncplify.me Server are all good free SFTP servers. When compared to FTPS, SFTP has the advantage of not requiring a large number of open ports to function (open ports are potential entry points into your network).
However, because you must install and configure an SFTP server, SFTP is less convenient than some of the other options on this list. So, if you want simplicity, a cloud storage solution is the way to go. Furthermore, if regulatory compliance is a concern, the absence of user activity logs can be problematic.
Pros:
- It’s a more secure option than FTP, and it helps protect data while it’s in transit.
- Doesn’t make extensive use of open ports
- CLI can be used to move files.
Cons:
- If misconfigured or has weak credentials, it can be hacked.
- If either site’s server or the internet is down, the system will not work.
- The technical setup is required, which necessitates IT knowledge.
7. FTPS (File Transfer Protocol Secure), also known as FTPS, is a secure version of FTP.
Secure Sockets Layer, or SSL (also known as TLS), is used to encrypt connections in FTPS. Passwords, client certificates, and server certificates can all be used to authenticate file transfers with this protocol. FTPS uses a user ID and password or a certificate to authenticate connections and verifies the certificate of the server you’re connecting to.
The main benefit of FTPS is that it is a secure way to send confidential data due to its encryption. It also has the advantage of complying with the majority of regulatory frameworks. PCI DSS, SOX, HIPAA, and HITECH all require FTPS transfers. It’s important to keep in mind that FTPS isn’t without flaws.
A port is opened every time a file transfer is made, which could be an entry point for an attacker. As a result, many firewalls make using FTPS connections difficult. Although not all FTP servers support FTPS, many products do. FTPS is supported by Syncplify.me, SolarWinds FTP Voyager, and FileZilla.
Pros:
- Another secure FTP variant that improves privacy and security.
- Can transfer files while remaining compliant with HIPAA, PCI, SOX, and other regulations.
Cons:
- If misconfigured or has weak credentials, it can be hacked.
- If either site’s server or the internet is down, the system will not work.
- The technical setup is required, which necessitates IT knowledge.
Each file transfer opens a new port, making firewall rules more difficult to implement. - Multiple connections across different sites are more difficult to manage and audit.
8. Participate in a Jumpshare
When compared to most email services’ 25 MB limit, there is a significant difference. These tools are also very simple to use. You can, for example, drag and drop the files you want to share to the menu bar icon in Jumpshare. A link will be copied to your clipboard after that.
If you want the convenience of transferring files online without having to use any more technical “workarounds,” Jumpshare is a good option. To get started, all you have to do is register on the vendor’s website.
Pros:
- Easy-to-use interface with drag-and-drop functionality.
- Files can be sent as simple downloadable links.
- There is no technical setup required.
Cons:
- Free file transfers are limited to 25 MB.
- Login with your email address is required.
- Long-term, this is not the best option.
9. Send a Hard Drive
Filling up a hard drive and sending it off with a courier is an effective approach to transfer files if you have a lot of large files to transmit. Using a courier to send a large volume of files is often much faster than trying to upload those files over a broadband connection.
Damage and theft are two issues that can arise while shipping hard drives. If you decide to ship your hard drive through a courier, be sure it is properly packaged so that it does not get damaged during transport.
Pros:
- It’s about as simple as ordering pizza.
- The files can be simply retrieved by the recipient.
Cons:
- If the drive is damaged during shipping, the data may be lost. If the drive is lost, the data may be stolen unless it is encrypted.
- Shipping a big volume of data over numerous drives could be prohibitively expensive.
- For regular data transfers, this is not a good long-term option.
10. Send to any location
Transmit Anywhere is a file-sharing program that lets you send files from your device to any destination you want with a 6-digit key. You can create a file access link so that other people can access your shared files from anywhere. Files also have an expiration date, which means they will be unavailable after a certain period of time. The maximum filesize for Send Anywhere is 10 GB. Windows, Mac OS, Linux, Android, iOS, Amazon Kindle, and Outlook Add-In are among the operating systems supported by the app.
If you need more firepower, Send Anywhere PLUS, which includes a server, is available for purchase. Send Anywhere PLUS is faster, with a transfer rate of 100 MB/s and the ability to upload up to 50 GB at once. At $5.99 (£4.85) per month, the paid version is also very affordable.
Pros:
- Supports up to ten gigabytes of data per send
- To access the files securely, a six-digit code is used.
- Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux are all supported.
- Mobile apps for iOS and Android provide file access.
Cons:
- For EDI transactions or files that must remain compliant, this is not the best option.
- For site replication or server backups, this is not a viable option.
11. WeTransfer

For $12 (£9.72) a month, you can upgrade to WeTransfer Plus, which allows for simultaneous file transfers of up to 20 GB and total storage of up to 100 GB. You can also password-protect your files and customize the emails you send. The large file transfer limit should be sufficient for most enterprise users.
WeTransfer is a great option for transferring files because you don’t have to sign up or download anything. So, if you want to share files without any hassle, this is the place to go.
Pros:
- The free version includes 2GB of file transfers.
- It’s ideal for one-off files that are too large to send via email.
- There is no need to download anything.
- It is not necessary for the recipient to register or install anything.
Cons:
- For EDI transactions or files that must remain compliant, this is not the best option.
- For site replication or server backups, this is not a viable option.
- Large Files Can Be Transferred, Sent, or Shared in Any Way You Want!
Whatever number of large files you need to send, there is a medium that can help. You can make your file transfer service as complicated or as simple as you want. Don’t get snagged by your email provider’s file size restrictions! Choose a storage solution that can handle the amount of data you’ll be transferring (and a VPN if your ISP is capping your uploads).
If you prefer the old school, purchasing a flash drive will provide you with a quick and easy way to transfer your data. A cloud storage provider like Google Drive or Dropbox, on the other hand, is probably a better fit if you want something you can access from anywhere.
Downloading an FTP server for low priority files might be worth it if you’re more technically inclined and want to manage a large volume of file transfers (make sure to use FTPS or SFTP for secure file transfers if you go this route!).
Also check: Best WeTransfer Alternatives You Can Use
What is the best way to send large files from my phone?
Sending files from a phone or tablet is identical to sending files from a computer in terms of technical specifications. The most significant issue with file transfers from a phone is the user’s data plan. If it’s metered, an extra data allocation could cost a lot of money. If this is the case, send the file while connected to WiFi and temporarily disable data.
With a slow connection, how can I send a large file?
One of the most serious dangers of slow connections is that the longer a session lasts, the greater the chance of a dropped connection. In the event of a lost connection, use a data transfer app that will pause and resume the transfer. Some transfer utilities will split a file into segments and send them all at once. However, if your bandwidth is limited, this will not solve the problem.
Can my cloud storage be hacked?
In the past, there have been a number of well-publicized cloud storage hacks. However, with the introduction of two-factor authentication, many cloud storage providers have tightened up their account access procedures (2FA). This involves a challenge question being sent to your phone, making it impossible for a hacker from afar to gain access to your account, even if they know your password.
What is the best way to get around Google Drive’s virus scan warning about large files?
If you request to download or send a file, Google Drive scans it before downloading it. It can only scan files up to 25 MB in size; anything larger prompts a warning that the file is too large to scan. Regardless, the file will be downloaded. Split the file up to completely avoid this message. If you want to send someone the file, send them a link to view it online instead.

