 Are successful people right, lucky or both?
Are successful people right, lucky or both?
In the mid-1980s, Nobel prize-winning finance professor, William Sharpe addressed the Hong Kong Society of Securities Analysts.
Sharpe was one of our heroes, having developed the Capital Asset Pricing Model, or CAPM. (We don’t need to go into that here but for investment geeks CAPM is up there with sex).
Then the professor told us it was impossible to consistently beat the market.
 Home truths and humility
Home truths and humility

Not everyone was happy with this. We admired the mathematics behind his models. It gave us the stamp-approval of science. But the idea that we couldn’t beat the market was less easy to digest. Our job was to come up with market-beating ideas. And after all, we were pretty smart.
Someone asked: how do you explain the track record of a particular fund manager (from memory, Peter Lynch, of Fidelity) who had been consistently beating the market?
Sharpe proposed a simple exercise. He reassured us we were all smart and that we would all toss a coin. Those with “tails”, roughly 50%, would leave the room. Then we’d do it again. And again, until one person was left. That person, said Sharpe, was Peter Lynch.

A decade later, another Nobel laureate, Myron Scholes – who developed even sexier models than Sharpe – launched a fully hedged bond fund that couldn’t fail. When it did, it took a multi-billion dollar bail-out to avoid a viral financial disaster.
Both Lynch and Scholes were smart people. They were good at what they did. Markets went right for one; wrong for the other.
That’s what the chart below says. It’s from Dennison Hambling, Chief Investment Officer at First Samuel.
It’s very simple. It assumes that changes in the value of shares reflect changes in earnings per share (eps). That makes sense – if earnings go up, so will the share price. Add the dividend and you get the total return. This applies to all markets.
Using Australia as an example, eps has grown at an average of 8% per annum over the long term; the dividend yield has been about 4%. If that’s right, then total return should rise around 12% a year on average.
As the chart shows, that’s pretty much what happens.
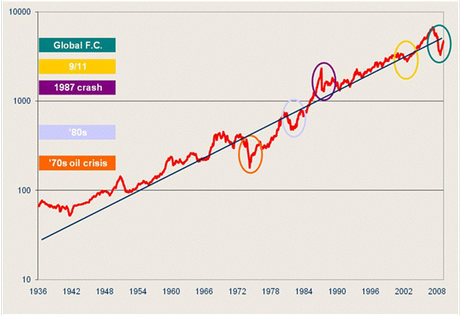
The straight line equals 12%. The red line tracks total return. It can soar above the line or drop sharply below it. Invariably, though, it reverts to the 12% mean.
Next time you see a smart person going better than the rest, acknowledge their smarts and their hard work, but remember they may also have been right-footed. Too often we see only the downside as an aberration. In reality, so is the upside.
Real value comes from sustaining earnings through both. If you can do that, it means when it comes to a business investment decision, you have the luxury of choosing your preferred aberration – whether it’s a time to sell a business, or alternatively, to invest in one.


